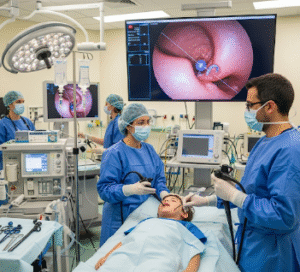
What is Gastroscopy?
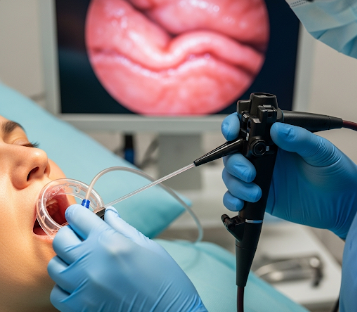
Gastroscopy, also known as upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy, is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). A flexible tube with a camera and light (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth to visualize the upper digestive tract.
💡 Key Points About Gastroscopy:
✔️ Diagnostic tool – Detects ulcers, inflammation, tumors, polyps, and bleeding
✔️ Therapeutic tool – Allows biopsy, polyp removal, dilation of strictures, and treatment of bleeding
✔️ Minimally invasive – Usually performed under sedation with local anesthesia to the throat
Benefits:
➡️ Provides direct visualization of the upper GI tract
➡️ Enables early detection of stomach cancer or precancerous lesions
➡️ Reduces the need for more invasive procedures
In Korea, gastroscopy is a standard procedure in gastroenterology departments, widely used for screening, especially for gastric cancer, which has a high incidence in East Asia.
Why It’s Done
Gastroscopy is recommended for diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of various conditions:
✔️ Persistent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
✔️ Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – Heartburn, regurgitation
✔️ Peptic ulcers – For diagnosis and monitoring
✔️ Bleeding – Detects source of upper GI bleeding
✔️ Suspicious lesions – Biopsy for cancer or precancerous conditions
✔️ Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) – Evaluates strictures or obstruction
✔️ Chronic nausea or vomiting – To identify underlying causes
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Early detection of cancer → Critical in Korea due to high gastric cancer rates
➡️ Accurate diagnosis → Biopsy and histology possible during procedure
➡️ Treatment during procedure → Polyp removal, bleeding control, or stent placement
➡️ Minimal discomfort and rapid recovery → Outpatient procedure with sedation
Gastroscopy is often included in routine gastric cancer screening programs in Korea, especially for adults over 40 or high-risk groups.
Alternatives
While gastroscopy is the gold standard for upper GI evaluation, alternatives include:
⭐ Barium swallow / upper GI series – X-ray imaging of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
⭐ Capsule endoscopy – Swallowed camera pill for small intestine imaging; limited in therapeutic ability
⭐ CT or MRI scan – Non-invasive imaging for structural evaluation
⭐ Empirical treatment – Medications for reflux or ulcers without direct visualization (diagnostic limitation)
👉 Key Point: Only gastroscopy allows direct visualization, biopsy, and therapeutic intervention, making it superior to imaging alone.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures accuracy, safety, and comfort during gastroscopy:
🔹 Fasting – Usually 6–8 hours before procedure to ensure an empty stomach
🔹 Medication review – Anticoagulants, diabetes medications, or chronic therapy adjustments
🔹 Medical history – Allergies, heart or lung conditions, previous endoscopies
🔹 Consent – Understanding procedure, risks, and potential interventions
⭐ Arrange transportation – Sedation may impair driving; a companion is recommended
⭐ Comfort measures – Wear loose clothing and avoid jewelry
Pre-procedure tips in Korea:
✔️ Many hospitals provide pre-endoscopy counseling
✔️ Sedation options discussed with patient (light, moderate, or deep)
✔️ Helicobacter pylori testing may be suggested concurrently
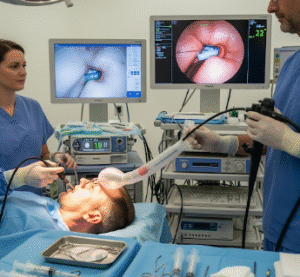
How It’s Done
Gastroscopy is performed by a trained gastroenterologist in a controlled clinical setting:
- Sedation and anesthesia
✔️ Local anesthetic spray to the throat
✔️ Optional intravenous sedation for relaxation and comfort - Procedure steps
🔹 Flexible endoscope inserted through the mouth and advanced into the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
🔹 Camera transmits high-resolution images to a monitor
🔹 Biopsy or minor therapeutic procedures performed if needed - Duration and monitoring
➡️ Usually 10–30 minutes
➡️ Vital signs monitored throughout
➡️ Recovery from sedation in 15–30 minutes
Highlights:
✔️ Minimally invasive, outpatient procedure
✔️ Enables both diagnosis and treatment in a single session
✔️ Real-time visualization allows immediate management of bleeding, strictures, or polyps
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery from gastroscopy is usually quick and uncomplicated:
✔️ Post-procedure observation – 15–30 minutes until sedation wears off
✔️ Mild throat discomfort – Temporary soreness or mild bloating from air insufflation
✔️ Diet – Resume normal diet after 1–2 hours if no complications
✔️ Follow-up – Biopsy results typically available in 3–7 days
✔️ Next steps – Treatment plan discussed based on findings, including surgery, medication, or surveillance
⭐ Return to normal activity – Most patients can resume daily activities the same day
Complications / Risks
Gastroscopy is generally safe, but potential risks include:
⚠️ Sore throat or hoarseness – Usually mild and temporary
⚠️ Bleeding – Rare, may occur after biopsy or polyp removal
⚠️ Perforation of GI tract – Rare but serious
⚠️ Reaction to sedation – Allergic reaction or cardiovascular/respiratory issues
⚠️ Infection – Very rare due to sterilized equipment
➡️ In Korea, experienced gastroenterologists and strict infection control protocols make gastroscopy extremely safe.
Treatment Options / Gastroscopy in Korea
Korean hospitals provide comprehensive gastroscopy services:
🏥 Diagnostic Gastroscopy – Screening for ulcers, gastritis, and cancer
🏥 Therapeutic Gastroscopy – Polyp removal, bleeding control, stricture dilation
🏥 Advanced Imaging Endoscopy – Narrow-band imaging (NBI), magnifying endoscopy, or chromoendoscopy for early cancer detection
🏥 Helicobacter pylori assessment – Biopsy or urease testing during procedure
🏥 Sedation Options – Light, moderate, or deep sedation according to patient preference and medical condition
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ High gastric cancer screening rate – Early detection improves survival
✔️ Advanced technology – High-resolution endoscopes, NBI, and endoscopic ultrasound
✔️ Expert gastroenterologists – Skilled in diagnosis and therapeutic interventions
✔️ Minimal discomfort – Sedation and modern techniques ensure patient comfort
✔️ Quick results and follow-up – Efficient biopsy processing and treatment planning
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Diagnostic Gastroscopy → $150 – $400
🔹 Therapeutic Gastroscopy (polyp removal, biopsy) → $300 – $700
🔹 Sedation fee → $50 – $150
🔹 Hospital consultation and follow-up → $50 – $100
Conclusion
Gastroscopy is a safe, effective, and essential procedure for diagnosing and treating upper gastrointestinal conditions.
It helps patients:
✔️ Detect ulcers, cancer, and inflammation early
✔️ Perform biopsies or therapeutic interventions in a single session
✔️ Reduce risk of complications such as bleeding or obstruction
✔️ Achieve peace of mind through accurate diagnosis
In Korea, gastroscopy offers:
✔️ Advanced diagnostic and therapeutic endoscopic services
✔️ Expert gastroenterologists and high-tech equipment
✔️ Safe, minimally invasive, and comfortable procedures
✔️ Efficient biopsy and follow-up systems
👉 Key Message: Gastroscopy in Korea ensures early detection, accurate diagnosis, and minimally invasive treatment, providing excellent outcomes and high patient safety.