What is Hand Tendon Repair?
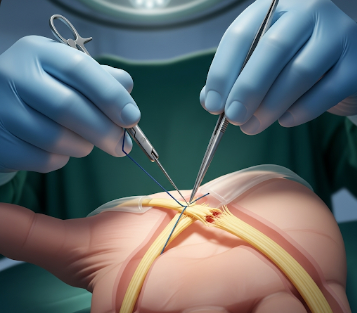
Hand tendon repair is a surgical procedure aimed at restoring the function of damaged or severed tendons in the hand, which connect muscles to bones and enable movement of fingers and the wrist.
💡 Key Points About Hand Tendon Repair:
✔️ Restores hand and finger mobility – Enables grasp, pinch, and fine motor movements
✔️ Repair of flexor or extensor tendons – Flexor tendons bend the fingers, extensor tendons straighten them
✔️ Prevents permanent disability – Early repair is critical to restore function
✔️ Minimally invasive or open surgery – Depending on severity and location of injury
Types of Hand Tendon Injuries:
➡️ Flexor tendon injuries – Usually caused by cuts or lacerations on the palm or fingers
➡️ Extensor tendon injuries – Often due to trauma on the back of the hand or fingers
➡️ Chronic tendon rupture – Degenerative changes may require reconstruction
In Korea, hand tendon repair is performed in orthopedic and microsurgery centers, often using microsurgical techniques to optimize outcomes.
Why It’s Done
Hand tendon repair is performed to restore hand function, prevent deformity, and reduce pain:
✔️ Traumatic injury – Cuts, crush injuries, or industrial accidents
✔️ Sports injuries – Tendon rupture from high-impact activities
✔️ Degenerative or chronic rupture – Tendon damage due to arthritis or aging
✔️ Loss of fine motor control – Inability to grip, pinch, or perform daily tasks
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Restores strength and dexterity → Critical for occupational and daily activities
➡️ Prevents permanent deformity → Malaligned tendons can lead to contractures
➡️ Reduces pain and swelling → Early repair limits inflammation and scarring
➡️ Optimizes functional outcomes → Especially with timely microsurgical repair
In Korea, hand tendon repair is commonly recommended within 12–24 hours of acute injury, though delayed repair may still be possible depending on tendon condition.
Alternatives
Alternative approaches may be considered depending on injury severity:
⭐ Non-surgical management – Splinting and physiotherapy for minor partial tendon tears
⭐ Tendon grafts or transfers – For chronic or irreparable injuries
⭐ Rehabilitation alone – May be used if surgery is contraindicated or patient preference
⭐ Assistive devices – Splints or orthotics to improve function temporarily
👉 Key Point: Surgical repair is generally the most effective method to restore full tendon function, while alternatives may only provide partial improvement.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures surgical success and recovery:
🔹 Medical evaluation – Blood tests, ECG, and review of medications
🔹 Assessment of hand function – Extent of tendon damage, finger mobility, and nerve involvement
🔹 Pre-operative imaging – Ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess tendon integrity
🔹 Medication management – Adjust anticoagulants, diabetes medications, or chronic drugs
🔹 Informed consent – Discuss risks, benefits, and expected functional outcomes
⭐ Arrange post-operative support – Assistance with daily activities and transportation
⭐ Pre-surgery counseling – Educate patient on immobilization, splinting, and rehabilitation
How It’s Done
Hand tendon repair is typically performed using microsurgical techniques under local or general anesthesia:
- Anesthesia
✔️ Local, regional (brachial plexus block), or general anesthesia depending on injury extent - Surgical Procedure
🔹 Damaged tendon ends are located and cleaned
🔹 Tendon ends are sutured using specialized microsurgical techniques (e.g., modified Kessler or core suture technique)
🔹 Tension is checked to ensure normal range of motion
🔹 Incision closed carefully to minimize scarring
🔹 Splint applied to immobilize hand and fingers - Surgical Duration
➡️ Typically 1–3 hours depending on number and complexity of tendons involved
➡️ Microsurgery allows precise alignment and improved functional outcomes
Highlights:
✔️ Early repair within hours of injury is critical for optimal recovery
✔️ Microsurgical techniques enhance tendon healing and reduce adhesions
✔️ Post-surgical splinting supports tendon repair and minimizes rupture
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery from hand tendon repair is gradual and requires structured rehabilitation:
✔️ Initial immobilization – Splint or cast for 3–6 weeks
✔️ Controlled passive motion – Physical therapist guides gentle movements to prevent stiffness
✔️ Active motion – Gradual finger movement starts under supervision
✔️ Strengthening exercises – After 6–8 weeks, depending on tendon healing
✔️ Follow-up visits – Monitor wound healing, tendon integrity, and function
⭐ Expected recovery timeline:
- 6–8 weeks: Tendon healing sufficient for light activities
- 3–6 months: Restoration of near-normal strength and dexterity
- 6–12 months: Full recovery possible with rigorous rehabilitation
In Korea, hand rehabilitation programs are integrated into surgical care, ensuring patients regain maximum function.
Complications / Risks
Potential complications are related to surgery, healing, and tendon function:
⚠️ Infection – Rare but requires prompt treatment
⚠️ Tendon rupture or gap formation – If excessive stress applied early
⚠️ Scar adhesion – Restricts motion and requires physical therapy
⚠️ Nerve or blood vessel injury – Can cause numbness or reduced circulation
⚠️ Stiffness and reduced range of motion – Common without rehabilitation
⚠️ Delayed healing – In patients with diabetes, smoking, or poor nutrition
➡️ In Korea, high-volume hand surgery centers with microsurgical expertise significantly reduce complication rates.
Treatment Options / Hand Tendon Repair in Korea
Korea offers advanced surgical and rehabilitative options for hand tendon repair:
🏥 Acute tendon repair – Immediate surgical repair after trauma
🏥 Delayed or chronic repair – Tendon grafts or tendon transfer for long-standing injuries
🏥 Microsurgical techniques – Precision suturing to enhance functional outcomes
🏥 Post-operative rehabilitation – Physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and splinting programs
🏥 Specialized hand centers – Integrated care from surgeons, therapists, and rehabilitation specialists
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Highly trained microsurgeons – Skilled in hand and finger tendon repair
✔️ Advanced operating facilities – High-precision surgical instruments and imaging
✔️ Comprehensive rehabilitation programs – Ensures optimal recovery
✔️ Rapid and safe procedures – Minimized complications with expert care
✔️ Cost-effective treatment – Efficient care with high success rates
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Acute tendon repair (per tendon) → $2,000 – $4,000
🔹 Complex multi-tendon repair → $4,000 – $8,000
🔹 Microsurgical tendon graft or transfer → $5,000 – $10,000
🔹 Rehabilitation sessions (per session) → $50 – $100
Conclusion
Hand tendon repair is a critical procedure for restoring hand function, preventing permanent disability, and improving quality of life.
It helps patients:
✔️ Restore finger and hand mobility
✔️ Recover strength and dexterity for daily and occupational activities
✔️ Prevent deformities and contractures
✔️ Reduce pain and inflammation
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Expert microsurgeons and hand specialists
✔️ Advanced surgical techniques and microsurgery
✔️ Integrated rehabilitation programs
✔️ High success rates with minimal complications
👉 Key Message: Hand tendon repair in Korea provides precise, safe, and effective treatment, restoring hand function and ensuring the best possible outcome through expert surgical care and structured rehabilitation.