What is a Heart Bypass?
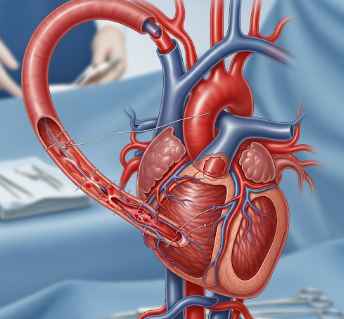
A heart bypass, medically known as a Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG), is a surgical procedure that improves blood flow to the heart. It involves rerouting blood around blocked or narrowed coronary arteries using a vessel graft, which can be taken from the leg, chest, or arm.
💡 Key Points About Heart Bypass Surgery:
✔️ Restores oxygen-rich blood flow to heart muscle
✔️ Reduces symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD) – Chest pain, shortness of breath
✔️ Can prevent heart attacks – Especially in severe blockages
✔️ May improve long-term survival – Particularly in multi-vessel coronary artery disease
Types of Bypass Grafts:
➡️ Saphenous vein graft (SVG) – From the leg
➡️ Internal mammary artery (IMA) – From the chest wall
➡️ Radial artery graft – From the forearm
In Korea, CABG is performed in cardiothoracic centers with advanced surgical teams and high-volume experience, ensuring high success rates and minimal complications.
Why It’s Done
Heart bypass surgery is performed to restore blood flow to the heart and relieve symptoms caused by coronary artery disease:
✔️ Severe coronary artery blockage – Detected on coronary angiography
✔️ Angina – Persistent chest pain despite medications
✔️ Heart attack prevention – Especially in patients with multi-vessel disease
✔️ Improved heart function – When coronary arteries are severely narrowed
✔️ Diabetes, left main artery disease, or reduced heart function – Conditions that benefit more from surgery than from stents
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Relieves angina → Improves quality of life and physical activity tolerance
➡️ Prevents heart attacks → Reduces risk of myocardial infarction
➡️ Improves survival → Especially in high-risk patients
➡️ Enhances exercise capacity → Patients can return to daily and occupational activities
Korean cardiac centers follow evidence-based protocols to determine which patients benefit most from bypass surgery versus less invasive interventions.
Alternatives
Depending on severity and anatomy of coronary disease, alternatives may include:
⭐ Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI / stent placement) – Less invasive, suitable for certain blockages
⭐ Medical therapy – Anti-anginals, statins, antiplatelets, and lifestyle modifications
⭐ Hybrid procedures – Combination of minimally invasive bypass and stenting
⭐ Lifestyle and risk factor management – Diet, exercise, smoking cessation, blood pressure and diabetes control
👉 Key Point: CABG is often preferred for multi-vessel disease, left main coronary artery disease, and diabetes, whereas stents or medications may be used for less severe blockages.
Preparation
Proper preoperative preparation is essential for safety and optimal outcomes:
🔹 Medical evaluation – Blood tests, ECG, echocardiogram, chest X-ray, coronary angiography
🔹 Medication review – Anticoagulants, antiplatelets, or other chronic medications may need adjustment
🔹 Anesthesia assessment – To evaluate heart, lung, and kidney function
🔹 Lifestyle preparation – Smoking cessation, balanced diet, and exercise if possible
🔹 Informed consent – Discuss risks, benefits, expected outcomes, and alternative treatments
⭐ Hospital admission – Usually 1–2 days before surgery
⭐ Pre-surgery counseling – Educate patient and family about procedure, ICU stay, and rehabilitation
How It’s Done
CABG can be performed using traditional open-heart surgery or minimally invasive techniques:
- Anesthesia
✔️ General anesthesia administered by a specialized cardiac anesthesiologist - Surgical Procedure
🔹 Median sternotomy (chest opening) or minimally invasive incision
🔹 Heart-lung machine may be used for “on-pump” surgery; off-pump surgery is also an option
🔹 Graft vessels harvested from leg, chest, or arm
🔹 Grafts sewn onto blocked coronary arteries to bypass obstruction
🔹 Heart restarted (if on-pump) and chest closed - Post-Surgery Protocol
➡️ ICU monitoring for 24–48 hours
➡️ Pain management, fluid balance, and cardiac monitoring
➡️ Early mobilization and breathing exercises to prevent complications
Highlights:
✔️ Surgery duration typically 3–6 hours
✔️ On-pump vs off-pump decision depends on patient’s condition
✔️ Korea uses high-tech surgical theaters and monitoring equipment for precision and safety
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery from heart bypass surgery is gradual and structured:
✔️ ICU stay – 1–2 days for monitoring
✔️ Hospital stay – Typically 5–10 days depending on recovery
✔️ Wound care – For sternotomy or minimally invasive incision
✔️ Medications – Antiplatelets, statins, beta-blockers, and other cardiac drugs
✔️ Physical rehabilitation – Cardiac rehab programs to improve exercise tolerance
✔️ Follow-up visits – Monitor heart function, graft patency, and overall recovery
⭐ Expected recovery timeline:
- 2–6 weeks: Resume light activities
- 6–12 weeks: Return to work and normal routines
- 3–6 months: Full physical activity and cardiac rehabilitation completion
Complications / Risks
CABG is generally safe, but potential complications exist:
⚠️ Bleeding – May require transfusion or reoperation
⚠️ Infection – Wound or systemic infections
⚠️ Heart rhythm disturbances – Atrial fibrillation is common post-op
⚠️ Stroke or neurological complications – Rare but possible
⚠️ Kidney dysfunction – Temporary or permanent in high-risk patients
⚠️ Graft blockage or failure – Long-term risk requiring follow-up
➡️ In Korea, experienced cardiac surgeons and advanced post-op care minimize risks and improve survival outcomes.
Treatment Options / Services in Korea
Korea provides world-class cardiac surgical services for coronary artery disease:
🏥 Traditional CABG – Open-heart surgery using saphenous vein, internal mammary artery, or radial artery grafts
🏥 Minimally invasive CABG – Smaller incision, off-pump techniques
🏥 Hybrid procedures – Combining stenting with minimally invasive bypass
🏥 Cardiac rehabilitation programs – Supervised exercise, dietary counseling, and risk factor management
🏥 Advanced imaging and monitoring – High-resolution angiography, intraoperative echocardiography, and ICU monitoring
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Highly skilled cardiothoracic surgeons – Extensive experience in CABG
✔️ State-of-the-art operating theaters – On-pump and off-pump surgery capability
✔️ Comprehensive perioperative care – ICU, pain management, and cardiac rehab
✔️ High survival and low complication rates – Evidence-based protocols
✔️ Cost-effective and efficient care – Competitive pricing with high-quality outcomes
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 CABG surgery → $15,000 – $25,000 depending on complexity and hospital
🔹 Minimally invasive or off-pump CABG → $18,000 – $30,000
🔹 Post-operative cardiac rehab → $50 – $150 per session
🔹 Hospital stay (per day) → $500 – $1,000 depending on ICU and ward care
Conclusion
Heart bypass surgery (CABG) is a life-saving procedure that restores blood flow, relieves symptoms, and improves survival for patients with severe coronary artery disease.
It helps patients:
✔️ Reduce angina and chest pain
✔️ Prevent heart attacks
✔️ Improve quality of life and physical activity
✔️ Restore cardiac function and long-term health
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Expert cardiac surgeons and multidisciplinary teams
✔️ Advanced surgical technology and ICU monitoring
✔️ Integrated cardiac rehabilitation programs
✔️ High success rates and minimized complications
👉 Key Message: CABG in Korea provides safe, effective, and precise treatment, ensuring improved heart function, symptom relief, and long-term health benefits.