What is Heart Valve Replacement?
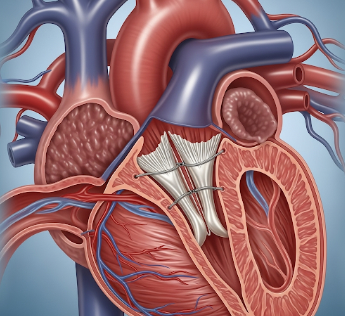
Heart valve replacement is a surgical procedure in which a diseased or damaged heart valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological prosthetic valve. The heart valves – aortic, mitral, tricuspid, and pulmonary – control blood flow through the heart chambers, and dysfunction can compromise cardiac function.
💡 Key Points About Heart Valve Replacement:
✔️ Restores normal blood flow → Reduces strain on the heart
✔️ Replaces stenotic (narrowed) or regurgitant (leaky) valves
✔️ Can involve open-heart or minimally invasive surgery
✔️ Mechanical valves – Durable, require lifelong anticoagulation
✔️ Biological (tissue) valves – Limited lifespan but often do not require long-term anticoagulants
Types of Valve Replacement Procedures:
➡️ Aortic valve replacement (AVR) – Most common, treats aortic stenosis
➡️ Mitral valve replacement (MVR) – Treats mitral stenosis or regurgitation
➡️ Tricuspid and pulmonary valve replacement – Less common, usually congenital or secondary disease
In Korea, heart valve replacement is performed in advanced cardiothoracic centers with expert surgeons and state-of-the-art operating facilities, often integrating minimally invasive and robotic approaches.
Why It’s Done
Heart valve replacement is indicated to restore cardiac function, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications from severe valve disease:
✔️ Severe valve stenosis – Narrowing reduces blood flow
✔️ Valve regurgitation – Leaky valves cause backward blood flow
✔️ Heart failure – Secondary to chronic valve dysfunction
✔️ Endocarditis – Infection of the heart valves causing irreversible damage
✔️ Congenital valve defects – Present at birth, may worsen over time
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Relieves shortness of breath and fatigue → Improves quality of life
➡️ Reduces risk of heart failure and arrhythmias
➡️ Prevents complications → Stroke, blood clots, or cardiac arrest
➡️ Enhances long-term survival → Particularly for severe valve disease
Korean hospitals follow guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) and European Society of Cardiology (ESC) to determine timing and type of replacement.
Alternatives
Alternatives to valve replacement depend on disease severity and patient suitability:
⭐ Valve repair – Preferred when feasible, preserves native valve
⭐ Transcatheter valve replacement (TAVR / TMVR) – Minimally invasive for high-risk patients
⭐ Medical management – Medications to control symptoms, delay progression, or manage heart failure
⭐ Lifestyle modification – Blood pressure control, diet, and exercise to reduce cardiac strain
👉 Key Point: Valve replacement is the definitive treatment for severe, symptomatic valve disease, whereas alternatives may be considered for milder disease or high surgical risk patients.
Preparation
Preparation ensures safety and optimal surgical outcomes:
🔹 Comprehensive cardiac evaluation – Echocardiography, coronary angiography, chest X-ray, ECG, and blood tests
🔹 Medication review – Adjust anticoagulants, antiplatelets, and other cardiac medications
🔹 Anesthesia assessment – Evaluates lung, kidney, and overall health
🔹 Informed consent – Discuss procedure, risks, valve type selection, and expected recovery
🔹 Hospital admission – Usually 1–2 days prior to surgery for pre-op testing
⭐ Lifestyle preparation – Smoking cessation, proper nutrition, and exercise if feasible
⭐ Family counseling – Understand post-operative care, rehabilitation, and anticoagulation monitoring
How It’s Done
Heart valve replacement can be performed via open-heart surgery or minimally invasive approaches:
- Anesthesia
✔️ General anesthesia administered by a cardiac anesthesiologist - Surgical Procedure
🔹 Traditional open-heart approach involves median sternotomy
🔹 Heart-lung machine may be used (“on-pump”) or off-pump approaches for select patients
🔹 Diseased valve excised, prosthetic valve implanted and secured
🔹 Heart restarted (if on-pump) and chest closed
🔹 Minimally invasive approaches may involve small chest incisions or robotic-assisted surgery - Post-Surgery Care
➡️ ICU monitoring for 24–48 hours
➡️ Pain control, fluid management, and cardiac monitoring
➡️ Early mobilization and breathing exercises to prevent lung complications
Highlights:
✔️ Surgery duration typically 3–6 hours depending on valve type and approach
✔️ Valve selection (mechanical vs biological) based on age, lifestyle, and anticoagulation needs
✔️ Korea uses advanced operating theaters and robotic systems to optimize precision
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery after valve replacement is gradual and structured:
✔️ ICU stay – 1–2 days for intensive monitoring
✔️ Hospital stay – 5–10 days for post-op stabilization
✔️ Wound care – Sternotomy or minimally invasive incision
✔️ Medications – Anticoagulants for mechanical valves, heart medications, and antibiotics as needed
✔️ Cardiac rehabilitation – Supervised exercise, dietary counseling, and risk factor management
✔️ Follow-up visits – Echocardiography and clinical assessment for valve function and cardiac performance
⭐ Expected recovery timeline:
- 2–6 weeks: Resume light activities
- 6–12 weeks: Gradual return to work and daily activities
- 3–6 months: Full rehabilitation and optimized cardiac function
Complications / Risks
Heart valve replacement carries potential risks, which are minimized by modern cardiac care:
⚠️ Bleeding – May require transfusion or reoperation
⚠️ Infection – Sternum or prosthetic valve endocarditis
⚠️ Blood clots – Especially with mechanical valves, requires lifelong anticoagulation
⚠️ Stroke or neurological events – Rare but serious
⚠️ Arrhythmias – Atrial fibrillation is common post-op
⚠️ Valve dysfunction – Paravalvular leak or structural valve deterioration over time
➡️ In Korea, experienced surgeons, high-tech monitoring, and ICU protocols minimize risks and optimize outcomes.
Treatment Options / Services in Korea
Korea provides world-class heart valve replacement services:
🏥 Conventional open-heart valve replacement – Mechanical or biological valves
🏥 Minimally invasive valve surgery – Small incisions, robotic-assisted, or thoracoscopic approaches
🏥 Transcatheter valve replacement (TAVR / TMVR) – For high-risk or elderly patients
🏥 Cardiac rehabilitation programs – Exercise, dietary counseling, and risk factor management
🏥 Advanced imaging and monitoring – 3D echocardiography, intraoperative TEE, ICU monitoring
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Highly experienced cardiothoracic surgeons
✔️ State-of-the-art operating theaters and robotic systems
✔️ Comprehensive perioperative care and rehabilitation
✔️ High survival rates and low complication rates
✔️ Cost-effective, efficient treatment with personalized care
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Open-heart valve replacement → $20,000 – $35,000 including hospital stay and surgery
🔹 Minimally invasive or robotic valve replacement → $25,000 – $40,000
🔹 Transcatheter valve replacement (TAVR) → $30,000 – $50,000
🔹 Cardiac rehab sessions → $50 – $150 per session
Conclusion
Heart valve replacement is a critical procedure for restoring cardiac function, relieving symptoms, and preventing life-threatening complications.
It helps patients:
✔️ Improve blood flow and heart efficiency
✔️ Reduce fatigue, shortness of breath, and other symptoms
✔️ Prevent heart failure, stroke, and other complications
✔️ Enhance long-term survival and quality of life
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Expert cardiothoracic surgeons and multidisciplinary care teams
✔️ Advanced surgical technology and minimally invasive options
✔️ Comprehensive rehabilitation and follow-up programs
✔️ High safety standards, precision care, and optimized outcomes
👉 Key Message: Heart valve replacement in Korea offers safe, effective, and modern treatment, ensuring patients achieve improved cardiac function, symptom relief, and long-term heart health.