Overview
Junctional Rhythm is a type of cardiac arrhythmia in which the heart’s electrical impulses originate from the atrioventricular (AV) junction instead of the sinoatrial (SA) node. This rhythm acts as a backup when the SA node fails to function normally. In Korea, Junctional Rhythm is often diagnosed during cardiac evaluations for slow heart rate, dizziness, or fainting. Advanced cardiology and electrophysiology centers provide accurate diagnosis and management, ensuring effective treatment and follow-up care.
What is Junctional Rhythm?
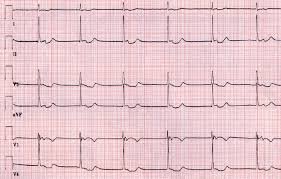
Junctional Rhythm occurs when the AV node or surrounding tissues generate electrical impulses to maintain the heartbeat, typically at a rate of 40–60 beats per minute. It is a protective mechanism, preventing dangerously slow heart rates when the SA node is impaired. ECG findings often show absent, inverted, or retrograde P waves, with a normally narrow QRS complex.
Symptoms
- Slow heart rate (bradycardia)
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fainting or syncope
- Palpitations or awareness of irregular heartbeat
- Mild chest discomfort
Causes
- Dysfunction of the SA node (Sick Sinus Syndrome)
- Atrioventricular (AV) conduction block
- Electrolyte imbalances such as high potassium
- Certain medications, including beta-blockers or digoxin
- Ischemic heart disease
- Heart muscle diseases or infiltrative conditions
Risk Factors
- Older age
- Pre-existing heart disease
- Use of medications affecting heart rhythm
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Previous heart surgery or structural heart abnormalities
Complications
- Progression to more severe forms of heart block
- Persistent symptomatic bradycardia requiring a pacemaker
- Risk of additional arrhythmias
- Reduced exercise tolerance or activity limitations
- Rarely, syncope-related injuries
Prevention
- Regular heart check-ups and ECG monitoring
- Managing underlying conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease
- Avoiding medications that slow the heart rate without medical supervision
- Maintaining a balanced diet and electrolyte levels
- Engaging in safe physical activity appropriate to cardiac status
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options for Junctional Rhythm:
- Diagnosis: Electrocardiogram (ECG) is the first-line test. Major centers like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide comprehensive cardiac evaluations and monitoring.
- Medical Management: Adjustment or discontinuation of medications that may contribute to bradycardia. Intravenous atropine can be used temporarily to increase heart rate in acute cases.
- Pacemaker Therapy: Permanent pacemaker implantation is indicated for patients with symptomatic or persistent junctional rhythm associated with bradycardia. Tertiary hospitals in Korea have specialized electrophysiology labs for this procedure.
- Electrophysiology Studies and Ablation: In select patients with associated arrhythmias, invasive studies and catheter ablation are performed to restore normal rhythm.
- Rehabilitation and Follow-Up: Cardiac rehabilitation programs, monitoring, and lifestyle counseling help patients manage symptoms and maintain heart health. Korean hospitals provide structured follow-up care to ensure optimal outcomes.