Overview
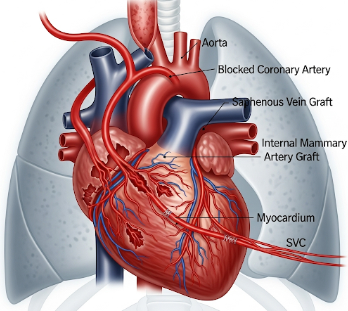
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure designed to restore blood flow to the heart muscle in patients with severe coronary artery disease (CAD). This involves bypassing blocked or narrowed coronary arteries using grafts from other blood vessels, usually from the chest, arm, or leg.
Importance of CABG:
- Restores oxygen supply to the heart.
- Reduces chest pain (angina) and improves quality of life.
- Prevents heart attacks in high-risk patients.
- Improves long-term survival in patients with severe CAD or left main coronary artery disease.
In South Korea, CABG is performed in advanced cardiac centers with modern operating theaters, cardiac anesthesia, and post-operative intensive care units, ensuring high safety and success rates.
Why It’s Done
CABG is indicated to improve blood flow and reduce cardiac risk.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Severe coronary artery blockage not amenable to stenting or medication.
- ➤ Multiple blocked coronary arteries causing angina.
- ➤ Left main coronary artery disease, which is high-risk.
- ➤ Failed angioplasty or stenting procedures.
- ➤ Diabetic patients with multivessel CAD, who benefit more from CABG than stenting.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Alleviates angina symptoms.
- ✔️ Improves exercise tolerance and heart function.
- ✔️ Reduces risk of heart attacks in high-risk patients.
- ✔️ Enhances long-term survival and quality of life.
Alternatives
While CABG is highly effective, other treatment options exist depending on severity:
- ➤ Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)/Angioplasty: Non-surgical method using stents to open blocked arteries.
- ➤ Medication therapy: Anti-anginal drugs, antiplatelets, statins, and blood pressure control.
- ➤ Lifestyle modification: Diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and weight management.
- ➤ Hybrid procedures: Combination of minimally invasive bypass and stenting.
Key point: CABG is preferred for complex, multivessel disease, or left main artery disease, whereas angioplasty may suffice for single-vessel or less complex blockages.
Preparation
CABG requires careful preoperative evaluation and preparation.
Steps include:
- ✅ Comprehensive cardiac assessment: ECG, echocardiography, coronary angiography.
- ✅ Blood tests: CBC, kidney function, liver function, coagulation profile.
- ✅ Medication review: Adjust blood thinners, diabetic medications, and others.
- ✅ Lifestyle adjustments: Smoking cessation, healthy diet, and physical preparation.
- ✅ Consent and counseling: Discuss procedure, risks, benefits, and post-operative expectations.
- ✅ Fasting: Usually overnight fasting before surgery.
Important: Preoperative preparation reduces complications and ensures optimal surgical outcomes.
How It’s Done
CABG is a major cardiac surgery performed under general anesthesia.
Step-by-step process:
- Anesthesia: Patient is fully sedated and intubated.
- Access: Median sternotomy (breastbone incision) or minimally invasive techniques.
- Graft harvesting:
- Internal mammary artery (IMA) from the chest.
- Saphenous vein from the leg.
- Radial artery from the arm.
- Cardiopulmonary bypass (on-pump CABG):
- Heart-lung machine temporarily circulates blood while the heart is stopped.
- Grafting: Blocked coronary arteries bypassed using harvested grafts.
- Weaning off bypass: Heart resumes beating; grafts checked for blood flow.
- Closure: Sternum wired, chest and surgical sites closed; drains placed for fluid.
Off-pump CABG (beating heart surgery): Performed without heart-lung machine; reduces certain complications.
Duration: 3–6 hours depending on complexity.
Hospital stay: 5–10 days, including ICU care.
Recovery
Recovery after CABG involves gradual rehabilitation and monitoring.
Immediate post-op:
- ICU monitoring for 24–48 hours.
- Ventilator support may be required temporarily.
- Pain management and infection prevention.
Early recovery (first 1–2 weeks):
- Gradual mobilization and physiotherapy.
- Wound care and monitoring for signs of infection.
- Medications continued for heart protection.
Long-term recovery:
- Full recovery may take 6–12 weeks.
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs: Exercise, education, diet, and lifestyle modification.
- Regular follow-up with cardiologists for heart function and graft patency.
Important: Compliance with medications, diet, and activity restrictions is crucial for long-term success.
Possible Complications
CABG is generally safe but carries risks associated with major surgery.
- ⚠️ Bleeding – may require transfusion or reoperation.
- ⚠️ Infection – wound or chest infection.
- ⚠️ Arrhythmias – abnormal heart rhythms, especially atrial fibrillation.
- ⚠️ Stroke or cognitive changes – rare, may occur post-surgery.
- ⚠️ Heart attack – intraoperative or post-operative risk.
- ⚠️ Kidney complications – especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
- ⚠️ Graft occlusion or failure – long-term monitoring required.
In South Korea, advanced surgical techniques, experienced cardiac teams, and modern ICU care minimize complications and improve survival rates.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
CABG is widely performed in leading cardiac centers in South Korea with state-of-the-art facilities and high success rates.
Key features:
- 🏥 Advanced cardiac hospitals with hybrid ORs and modern cardiopulmonary bypass systems.
- 🏥 Experienced cardiac surgeons performing both on-pump and off-pump CABG.
- 🏥 Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted CABG available in specialized centers.
- 🏥 Post-operative cardiac rehabilitation programs integrated with long-term care.
- 🏥 Emergency and elective CABG services for high-risk or multivessel disease.
Hospitals offering CABG in Korea:
- Asan Medical Center – High-volume cardiac surgery center
- Samsung Medical Center – Advanced CABG and hybrid cardiac procedures
- Seoul National University Hospital – Comprehensive cardiac care program
- National Heart Center – State-of-the-art CABG and cardiac rehabilitation
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Advanced surgical and ICU care ensures high safety and survival rates.
- ✔️ CABG reduces angina, heart attacks, and improves quality of life.
- ✔️ Integration with cardiac rehabilitation ensures long-term success.
- ✔️ Cutting-edge techniques available for complex or high-risk patients.
Highlights
- ➤ CABG restores blood flow to blocked coronary arteries, reducing heart attack risk.
- ➤ Indicated for multivessel disease, left main artery disease, or failed stenting.
- ➤ Alternatives include angioplasty, medications, lifestyle changes, but CABG preferred for complex cases.
- ➤ Preparation includes cardiac evaluation, blood tests, medication review, and fasting.
- ➤ Procedure duration: 3–6 hours, performed under general anesthesia; may involve on-pump or off-pump techniques.
- ➤ Recovery involves ICU care, gradual mobilization, and cardiac rehabilitation.
- ➤ South Korea provides advanced CABG services, integrating surgical expertise, technology, and long-term follow-up.