What It Is
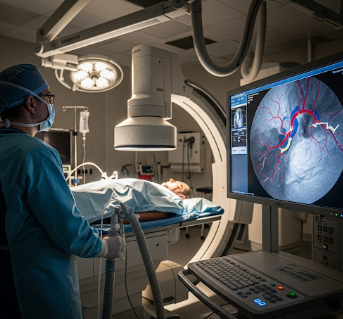
Angiography (also called an angiogram) is a specialized medical imaging test that uses X-rays and a contrast dye to visualize blood vessels in detail. It allows doctors to detect blockages, narrowing, aneurysms, malformations, and other vascular problems in arteries and veins throughout the body.
The procedure plays a critical role in diagnosing and planning treatment for cardiovascular diseases, brain circulation disorders, kidney issues, gastrointestinal bleeding, and many other conditions. Because it provides a direct view of the blood vessels, angiography is often considered the “gold standard” for vascular imaging.
There are different types of angiography, including:
- ➤ Coronary angiography – examines heart arteries.
- ➤ Cerebral angiography – looks at blood vessels in the brain.
- ➤ Peripheral angiography – assesses blood flow to arms and legs.
- ➤ Pulmonary angiography – examines vessels in the lungs.
- ➤ Renal angiography – evaluates kidney blood supply.
Why It’s Done
Doctors may recommend angiography for various reasons, especially when vascular disease is suspected.
Main purposes include:
- ➤ Detecting blockages or narrowing in blood vessels (caused by atherosclerosis, plaque, or blood clots).
- ➤ Identifying aneurysms (weakened blood vessel walls that may rupture).
- ➤ Locating bleeding sites in the gastrointestinal tract, brain, or lungs.
- ➤ Evaluating tumors that may have abnormal blood supply.
- ➤ Planning interventions such as angioplasty, stent placement, or surgery.
- ➤ Guiding treatment for stroke, heart attack, or vascular malformations.
Benefits of angiography:
- ✔️ Provides detailed, real-time imaging.
- ✔️ Helps doctors choose the most effective treatment plan.
- ✔️ Can be combined with treatment procedures (e.g., angioplasty, embolization).
- ✔️ Minimally invasive compared to open surgery.
Alternatives
Although angiography is highly accurate, other imaging methods may sometimes be used as alternatives or complementary tests:
- ➤ CT angiography (CTA): Uses CT scans with contrast to create 3D vessel images. Less invasive but exposes patients to radiation.
- ➤ MR angiography (MRA): Uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to view vessels, often without radiation.
- ➤ Ultrasound (Doppler): Non-invasive, commonly used for carotid arteries, veins, and peripheral circulation.
- ➤ Echocardiography: Helps assess heart function but not detailed vessel imaging.
- ➤ Blood tests & ECG: Provide indirect information on cardiovascular health.
While these methods are useful, angiography remains the most definitive diagnostic tool for vascular conditions.
Preparation
Preparing for angiography ensures safety and accuracy.
Typical preparation steps include:
- ✅ Medical history & consent – doctor reviews health background, allergies, and medications.
- ✅ Blood tests – check kidney function (since contrast dye is processed by kidneys).
- ✅ Fasting – usually no food or drink 4–6 hours before procedure.
- ✅ Medication review – blood thinners may be paused; diabetic medications may need adjustment.
- ✅ Allergy precautions – patients allergic to iodine may receive pre-medication.
- ✅ IV line placement – for dye and medications during procedure.
- ✅ Arrange transportation – patients usually cannot drive home afterward.
How It’s Done
Angiography is typically performed in a catheterization lab (cath lab) under sterile conditions.
Step-by-step process:
- Sedation and local anesthesia: The patient is awake but relaxed; a local anesthetic numbs the insertion site (groin, wrist, or arm).
- Catheter insertion: A thin tube (catheter) is inserted into a blood vessel, usually the femoral artery in the groin or radial artery in the wrist.
- Guided navigation: Using real-time X-ray (fluoroscopy), the catheter is gently threaded through the vessels toward the target area (heart, brain, lungs, etc.).
- Contrast dye injection: Special iodine-based contrast is injected through the catheter, making blood vessels visible on X-ray images.
- Imaging: Multiple X-ray pictures or videos are taken from different angles to examine blood flow.
- Additional interventions (if needed): In some cases, treatment (angioplasty, stent, embolization) can be performed immediately.
- Completion: The catheter is removed, and pressure or closure devices are applied to prevent bleeding.
Duration: 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on complexity.
Hospital stay: Often outpatient, but sometimes requires overnight monitoring.
Recovery
Recovery from angiography is generally quick but depends on whether treatment was done during the procedure.
Immediately after angiography:
- ✔️ Patient rests flat for several hours if groin access was used.
- ✔️ Vital signs and puncture site are closely monitored.
- ✔️ IV fluids may be given to flush contrast dye from kidneys.
At home:
- ➤ Mild bruising or soreness at puncture site is common.
- ➤ Patients should avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for a few days.
- ➤ Drink plenty of fluids to help kidneys clear the dye.
- ➤ Monitor for complications like bleeding, swelling, or fever.
Return to normal activities:
- 🕒 Light activities: 1–2 days.
- 🕒 Work: 2–5 days depending on job.
- 🕒 Exercise/sports: 1–2 weeks unless intervention was done.
Possible Complications
Although angiography is considered safe, risks exist:
- ⚠️ Bleeding or hematoma at catheter site.
- ⚠️ Allergic reaction to contrast dye.
- ⚠️ Kidney damage due to contrast in patients with weak kidney function.
- ⚠️ Infection at insertion site.
- ⚠️ Blood clots or vessel injury from catheter.
- ⚠️ Radiation exposure (minimal but cumulative with repeated tests).
- ⚠️ Rare but serious: stroke, heart attack, or severe allergic reaction.
Doctors weigh risks against benefits, and most patients undergo angiography safely with minimal issues.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is internationally recognized for advanced cardiovascular and radiology care, making it a popular destination for medical travelers.
Why Korea for angiography?
- 🏥 Cutting-edge facilities – Specialized cardiovascular centers with world-class cath labs.
- 🏥 Highly trained specialists – Interventional cardiologists and radiologists with extensive experience.
- 🏥 Integration with treatment – Korean hospitals often perform diagnosis and treatment (angioplasty, stenting) in one session.
- 🏥 Advanced imaging – Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) for ultra-clear images.
- 🏥 Medical tourism support – English-speaking staff, streamlined appointments, and packaged services for international patients.
- 🏥 Affordable care – Costs are typically 40–60% lower compared to the US or Europe, while maintaining high standards.
Examples of top angiography services in Korea:
- ✔️ Coronary angiography & stenting for heart blockages.
- ✔️ Neuro-angiography for stroke prevention and treatment.
- ✔️ Peripheral angiography to diagnose leg artery disease.
- ✔️ Interventional angiography (embolization, aneurysm repair).
Highlights
- ➤ Angiography is an imaging test that visualizes blood vessels using X-rays and contrast dye.
- ➤ Helps diagnose blockages, aneurysms, bleeding, and vascular malformations.
- ➤ Can be combined with treatments like angioplasty or stent placement.
- ➤ Preparation includes fasting, blood tests, and allergy check.
- ➤ Recovery is quick, but patients must avoid heavy activity for a few days.
- ➤ Risks include bleeding, contrast allergy, kidney effects, and rare major complications.
- ➤ Korea offers world-class angiography with advanced technology, expert doctors, and affordable prices.