Overview
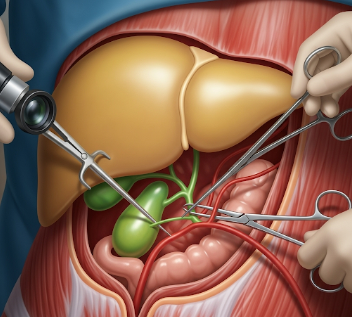
Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder, typically due to gallstones, inflammation, or other gallbladder diseases. The gallbladder is a small organ that stores bile, which aids in digestion of fats. Removal of the gallbladder does not usually affect digestion significantly because bile flows directly from the liver into the small intestine.
Importance of cholecystectomy:
- Treats gallstones and gallbladder disease causing pain or complications.
- Prevents recurrent gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis).
- Reduces risk of gallbladder cancer in select cases.
- Improves quality of life in patients with chronic gallbladder symptoms.
In South Korea, cholecystectomy is performed using advanced laparoscopic techniques in major hospitals, ensuring minimal invasiveness, faster recovery, and high success rates.
Why It’s Done
Cholecystectomy is indicated for various gallbladder-related conditions.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Gallstones (cholelithiasis): Stones causing pain, infection, or obstruction.
- ➤ Inflamed gallbladder (cholecystitis): Acute or chronic inflammation.
- ➤ Gallbladder polyps: Risk of malignancy or growth causing symptoms.
- ➤ Biliary dyskinesia: Dysfunctional gallbladder causing pain without stones.
- ➤ Gallbladder cancer (rare): Removal as part of treatment.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Relieves abdominal pain and digestive discomfort.
- ✔️ Prevents complications such as pancreatitis or infection.
- ✔️ Improves overall digestive function and quality of life.
- ✔️ Offers definitive treatment for recurrent gallbladder disease.
Alternatives
While cholecystectomy is the standard treatment, alternatives may be considered for select patients:
- ➤ Watchful waiting: For asymptomatic gallstones without complications.
- ➤ Medication: Ursodeoxycholic acid may dissolve small cholesterol stones in rare cases.
- ➤ Endoscopic procedures: ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) for bile duct stones.
- ➤ Lifestyle modifications: Diet changes may reduce gallstone formation but cannot remove existing stones.
Key point: Surgery remains the most effective and definitive treatment, especially for symptomatic or complicated gallbladder disease.
Preparation
Preparation for cholecystectomy involves medical evaluation and preoperative planning.
Steps include:
- ✅ Medical history and physical examination: Assess overall health and risk factors.
- ✅ Blood tests: Check liver function, coagulation, and general health.
- ✅ Imaging studies: Ultrasound, CT, or MRI to assess gallbladder and bile ducts.
- ✅ Medication review: Adjust blood thinners or other medications before surgery.
- ✅ Fasting: Typically no food or drink 6–8 hours before surgery.
- ✅ Informed consent: Discuss procedure type, risks, recovery, and alternatives.
Important: Proper preparation reduces surgical risks and ensures safe recovery.
How It’s Done
Cholecystectomy can be performed using laparoscopic (minimally invasive) or open surgery, depending on patient condition.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (most common):
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered.
- Small incisions: Typically 4 small incisions in the abdomen.
- Insertion of instruments: Camera (laparoscope) and surgical tools inserted.
- Gallbladder removal: Dissected and removed through one of the incisions.
- Closure: Incisions closed with sutures or surgical glue.
- Postoperative observation: Short recovery in hospital.
Open cholecystectomy (less common):
- Larger incision in the upper abdomen for direct removal.
- Used for complex cases or complications.
Duration:
- Laparoscopic: 45–90 minutes
- Open: 1–2 hours
Hospital stay:
- Laparoscopic: Usually 1–2 days
- Open: 3–5 days
Key point: Laparoscopic surgery offers smaller scars, less pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stay.
Recovery & Postoperative Care
Recovery after cholecystectomy depends on surgery type and patient condition.
Immediate post-surgery:
- Monitor vital signs and pain control.
- Begin gentle movement to prevent blood clots.
- Gradually resume oral intake as tolerated.
Short-term recovery:
- Avoid heavy lifting for 2–4 weeks (laparoscopic) or 6–8 weeks (open).
- Manage pain with prescribed medications.
- Resume normal daily activities gradually.
- Follow up with surgeon for wound check and removal of sutures if needed.
Long-term recovery:
- Normal diet usually tolerated within weeks; may need temporary low-fat diet.
- Some patients may experience mild digestive changes such as bloating or diarrhea.
- Long-term outcomes are excellent, with minimal complications in most patients.
Important: Adherence to postoperative guidance ensures smooth recovery and reduces complications.
Possible Complications
Cholecystectomy is generally safe, but complications can occur:
- ⚠️ Bleeding or infection at the incision site.
- ⚠️ Bile leak requiring additional intervention.
- ⚠️ Injury to bile ducts, liver, or intestines (rare).
- ⚠️ Deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism post-surgery.
- ⚠️ Digestive changes: Diarrhea or bloating, usually temporary.
- ⚠️ Anesthesia-related risks: Reactions or complications.
In South Korea, modern laparoscopic techniques, experienced surgeons, and advanced monitoring minimize the risk of complications.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
Cholecystectomy is widely performed in major hospitals and specialized surgical centers across South Korea.
Key features:
- 🏥 Laparoscopic cholecystectomy as the preferred method for minimal invasiveness.
- 🏥 Advanced imaging and diagnostics for preoperative planning.
- 🏥 Multidisciplinary care including surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses.
- 🏥 Postoperative rehabilitation with dietary guidance and follow-up.
- 🏥 Access to specialized surgical centers nationwide for complex cases.
Hospitals and clinics performing cholecystectomy in Korea:
- Seoul National University Hospital – Advanced laparoscopic gallbladder surgery
- Asan Medical Center – Multidisciplinary hepatobiliary and gallbladder care
- Samsung Medical Center – Minimally invasive and complex gallbladder surgery
- Local tertiary hospitals – Nationwide accessibility
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ High success rates with minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques.
- ✔️ Short hospital stays and rapid recovery for most patients.
- ✔️ Comprehensive postoperative care ensures optimal long-term outcomes.
- ✔️ Modern surgical protocols minimize pain, scarring, and complications.
Highlights
- ➤ Cholecystectomy removes the gallbladder to treat gallstones, inflammation, or polyps.
- ➤ Indicated for symptomatic gallstones, cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, or gallbladder cancer.
- ➤ Alternatives include watchful waiting, medication, endoscopic procedures, or lifestyle changes.
- ➤ Preparation involves medical evaluation, imaging, fasting, and informed consent.
- ➤ Laparoscopic surgery is minimally invasive, shortens recovery, and reduces pain.
- ➤ Recovery includes gradual return to activities, temporary dietary changes, and follow-up care.
- ➤ South Korea provides advanced laparoscopic cholecystectomy with high safety, rapid recovery, and nationwide accessibility.