Overview
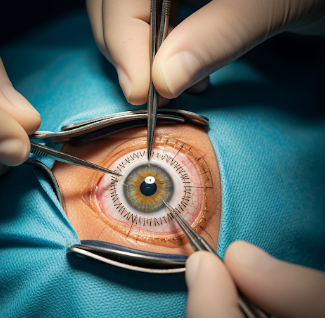
A cornea transplant, also known as keratoplasty, is a surgical procedure in which damaged or diseased corneal tissue is replaced with healthy donor cornea. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped front part of the eye responsible for focusing light onto the retina.
Importance of cornea transplant:
- Restores vision in patients with corneal scarring, thinning, or clouding.
- Reduces pain and discomfort in eyes affected by corneal disease.
- Prevents further deterioration in severe corneal conditions.
- Enhances quality of life by restoring functional vision.
In South Korea, cornea transplants are performed in major ophthalmology centers with advanced microsurgical techniques and access to high-quality donor corneas through certified eye banks.
Why It’s Done
Cornea transplants are performed to replace damaged corneal tissue and improve vision or alleviate pain.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Keratoconus: Progressive thinning and bulging of the cornea.
- ➤ Corneal scarring from infections (e.g., herpes simplex, bacterial keratitis) or trauma.
- ➤ Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy: Degeneration of the corneal inner layer causing swelling and vision loss.
- ➤ Corneal edema or swelling due to endothelial dysfunction.
- ➤ Failed previous corneal transplant requiring repeat surgery.
- ➤ Chemical or thermal injuries damaging corneal clarity.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Improved visual acuity.
- ✔️ Reduced eye pain and irritation.
- ✔️ Restored corneal clarity for daily activities and independence.
- ✔️ Prevention of further corneal deterioration in progressive diseases.
Alternatives
Depending on the condition, alternatives may include:
- ➤ Medical therapy: Eye drops, medications for infections, or anti-inflammatory agents.
- ➤ Corneal cross-linking: Strengthens corneal tissue in early keratoconus.
- ➤ Intacs (corneal rings): Inserted to reshape cornea in keratoconus.
- ➤ Laser vision correction: For mild corneal irregularities.
- ➤ Contact lenses: Specialty lenses to correct vision in keratoconus or irregular corneas.
Key point: Cornea transplant is usually reserved for patients with severe corneal damage or disease not responding to medical or non-surgical treatments.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures safe surgery, optimal graft survival, and minimal complications.
Steps include:
- ✅ Comprehensive eye examination: Visual acuity, slit-lamp exam, corneal thickness measurement, and endothelial cell count.
- ✅ Systemic health evaluation: Screening for diabetes, hypertension, or autoimmune conditions affecting healing.
- ✅ Preoperative tests: Blood work, eye imaging, and infectious disease screening for donor tissue.
- ✅ Patient counseling: Discuss procedure, graft types (full-thickness vs. partial-thickness), recovery, and risks.
- ✅ Medication adjustment: Stop anticoagulants or other medications if advised by the surgeon.
Important: Preoperative preparation improves graft success and minimizes post-surgical complications.
How It’s Done
Cornea transplant is a microsurgical procedure performed under local or general anesthesia.
Types of cornea transplants:
- Penetrating keratoplasty (PK): Full-thickness corneal replacement.
- Lamellar keratoplasty: Partial-thickness corneal replacement, sparing healthy layers.
- Anterior lamellar keratoplasty (ALK): Replaces front layers of cornea.
- Endothelial keratoplasty (DSEK/DMEK): Replaces inner corneal layer only.
Surgical steps (generalized):
- Anesthesia: Local or general depending on patient and procedure.
- Corneal removal: Diseased cornea is excised using precision instruments.
- Donor graft placement: Healthy donor cornea is positioned and sutured (full-thickness) or inserted (lamellar).
- Closure: Fine sutures or tissue adhesive used; eye shield applied post-surgery.
Duration: Typically 45 minutes to 2 hours depending on graft type.
Hospital stay: Usually outpatient or 1-day admission; overnight stay in complex cases.
Key point: Advanced microsurgical techniques allow precision graft placement and improved visual outcomes.
Recovery & Post-Use Care
Recovery after cornea transplant is gradual and requires careful follow-up.
Immediate post-op care:
- Eye shield for protection.
- Topical antibiotics and steroids to prevent infection and graft rejection.
- Rest and avoidance of eye rubbing or trauma.
Short-term care:
- Frequent ophthalmology visits to monitor graft clarity and healing.
- Suture management: Some sutures may remain for months to years, depending on healing.
- Monitor for signs of graft rejection: Redness, pain, blurred vision, or light sensitivity.
Long-term outcomes:
- Visual acuity may improve gradually over 6–12 months.
- Regular follow-up ensures optimal graft survival.
- Most patients achieve functional vision and improved quality of life.
Important: Patient adherence to post-op instructions is critical for graft success and complication prevention.
Possible Complications / Risks
While generally safe, cornea transplant carries potential risks:
- ⚠️ Graft rejection: Redness, pain, blurred vision, or light sensitivity.
- ⚠️ Infection: Bacterial or viral keratitis affecting the graft.
- ⚠️ Astigmatism: Irregular curvature causing blurred vision.
- ⚠️ Suture-related problems: Loose sutures, irritation, or infection.
- ⚠️ Glaucoma or cataract formation: Secondary complications in some patients.
- ⚠️ Graft failure: May require repeat corneal transplant.
In South Korea, cornea transplants are performed under strict sterility and donor screening protocols, reducing infection risk and improving graft survival rates.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
Cornea transplants in South Korea are well-established procedures performed in advanced ophthalmology centers.
Key features:
- 🏥 Performed in hospitals such as Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital.
- 🏥 Access to high-quality donor corneas through certified eye banks.
- 🏥 Advanced surgical techniques allow lamellar and endothelial keratoplasty for tailored treatment.
- 🏥 Post-operative follow-up programs ensure early detection of rejection and complication management.
- 🏥 Integrated into comprehensive ophthalmology care, including management of keratoconus, Fuchs’ dystrophy, and corneal scars.
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Modern microsurgical techniques improve visual outcomes and graft longevity.
- ✔️ Ophthalmologists provide personalized care plans including pre- and post-operative management.
- ✔️ High success rates with improved functional vision and quality of life.
- ✔️ Comprehensive patient education ensures adherence to post-op care.
Highlights
- ➤ Cornea transplant replaces damaged or diseased corneal tissue to restore vision.
- ➤ Indicated for keratoconus, corneal scarring, Fuchs’ dystrophy, corneal edema, or trauma.
- ➤ Alternatives include medical therapy, corneal cross-linking, Intacs, laser correction, or specialty contact lenses.
- ➤ Preparation involves eye examination, systemic evaluation, pre-op tests, and counseling.
- ➤ Surgery involves precision removal of diseased cornea and donor graft placement, usually outpatient.
- ➤ Recovery requires post-op care, eye protection, medications, and regular follow-up.
- ➤ South Korea offers advanced corneal transplant techniques with high-quality donor tissue, skilled surgeons, and integrated ophthalmology care.