Overview
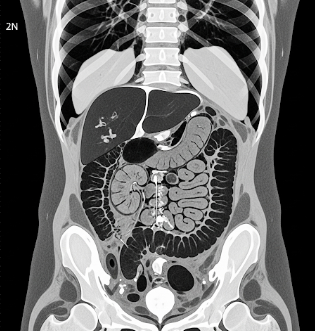
A CT scan (computed tomography scan) is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. CT scans provide clear visualization of bones, organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues, enabling precise diagnosis of various medical conditions.
Importance of CT scans:
- Detects injuries, tumors, infections, and internal bleeding.
- Guides surgical planning, biopsy procedures, and treatment monitoring.
- Offers rapid, non-invasive assessment in emergency situations.
- Enhances diagnostic accuracy compared to conventional X-rays.
In South Korea, CT scans are widely available in hospitals, diagnostic centers, and specialized imaging clinics, using advanced multi-slice and high-resolution CT scanners.
Why It’s Done
CT scans are performed to diagnose, monitor, and guide treatment for a variety of conditions.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Trauma assessment: Detect fractures, internal bleeding, or organ injuries.
- ➤ Cancer detection and staging: Identify tumors, metastases, and monitor therapy response.
- ➤ Cardiovascular evaluation: Detect aneurysms, blockages, or blood clots.
- ➤ Infection and inflammation: Identify abscesses, pneumonia, or inflammatory bowel disease.
- ➤ Neurological assessment: Evaluate stroke, brain tumors, or traumatic brain injuries.
- ➤ Guidance for interventions: Biopsy, drainage, or surgical planning.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Rapid diagnosis in emergent and non-emergent cases.
- ✔️ Non-invasive visualization of internal organs and structures.
- ✔️ Accurate treatment planning and follow-up monitoring.
- ✔️ Reduces the need for exploratory surgery.
- ✔️ Allows detailed imaging of complex anatomy in 3D reconstruction.
Alternatives
CT scans are highly effective but alternatives may be used depending on patient condition and imaging goals:
- ➤ MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Better for soft tissue contrast, brain, spine, and joints.
- ➤ Ultrasound: Real-time imaging, preferred for pregnancy, abdominal organs, and vascular assessment.
- ➤ X-ray: Limited to bone and chest imaging, less detailed than CT.
- ➤ PET-CT: Combines metabolic imaging with structural imaging for cancer evaluation.
- ➤ Clinical examination: Complementary for initial assessment or screening.
Key point: CT scans are preferred for rapid, high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging, while alternatives are chosen based on specific clinical needs or to reduce radiation exposure.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures accurate imaging and patient safety.
Steps include:
- ✅ Medical history: Inform the radiologist about allergies, medications, kidney disease, or pregnancy.
- ✅ Fasting: Required if intravenous contrast is used, usually 4–6 hours before the scan.
- ✅ Contrast considerations: Discuss iodine-based contrast allergies; premedication may be required.
- ✅ Clothing and metal removal: Wear hospital gown, remove jewelry, watches, and metal objects.
- ✅ Hydration: May be recommended before and after contrast administration to protect kidneys.
- ✅ Anxiety management: Sedation or calming techniques for claustrophobic patients.
Important: Adhering to preparation guidelines ensures high-quality images and reduces risks from contrast agents.
How It’s Done
CT scans are fast, painless, and non-invasive, though the procedure varies slightly depending on the body area being imaged.
Procedure steps:
- Positioning: Patient lies on a motorized table that slides into the CT scanner.
- Contrast administration (if required): Intravenous or oral contrast to enhance visualization of blood vessels and organs.
- Scanning: X-ray tube rotates around the patient, capturing multiple images.
- Image reconstruction: Computer processes the data into cross-sectional images; 3D images may be generated.
- Completion: Scan typically takes 10–30 minutes, longer if multiple body areas or contrast is used.
Key point: Modern CT scanners provide low-radiation, high-resolution imaging with rapid acquisition, minimizing patient discomfort.
Recovery & Post-Care
CT scans generally require no recovery, though some post-scan measures may apply if contrast is used.
Immediate post-scan care:
- ✅ Drink plenty of water to flush contrast material from the body.
- ✅ Monitor for allergic reactions if contrast was administered.
- ✅ Resume normal activities unless otherwise advised.
Follow-up:
- Radiologist evaluates images and provides a detailed report to the referring physician.
- Physician discusses results, further testing, or treatment plans.
Long-term outcomes:
- Enables early detection of disease for timely intervention.
- Guides surgical or therapeutic procedures accurately.
- Reduces the need for invasive diagnostic procedures.
Important: CT scans are safe for most patients, but repeated exposure should be minimized due to cumulative radiation risk.
Possible Complications / Risks
CT scans are generally safe, but potential risks include:
- ⚠️ Radiation exposure: Small but cumulative, with higher risk for repeated scans.
- ⚠️ Allergic reactions to contrast: Ranging from mild itching to rare anaphylaxis.
- ⚠️ Kidney damage: Rare, related to iodine-based contrast, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
- ⚠️ Discomfort or anxiety: Claustrophobia or inability to remain still during scanning.
- ⚠️ Pregnancy considerations: Radiation may affect fetal development; alternative imaging preferred.
In South Korea, hospitals use state-of-the-art low-dose CT scanners, contrast safety protocols, and trained radiology staff to minimize risks.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
CT scanning in South Korea is widely accessible, highly advanced, and integrated with modern healthcare.
Key features:
- 🏥 Available in general hospitals, specialized imaging centers, and university hospitals.
- 🏥 Multi-slice and high-resolution CT scanners enable precise imaging for complex cases.
- 🏥 Supports emergency trauma assessment, cancer staging, cardiovascular evaluation, and neurological imaging.
- 🏥 Integration with digital health records and PACS systems ensures rapid diagnosis and collaboration.
- 🏥 Radiologists provide expert interpretation and consultation for treatment planning.
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Rapid access to advanced CT imaging for emergency and routine cases.
- ✔️ Low-dose protocols reduce radiation exposure.
- ✔️ High-resolution imaging supports surgical planning, biopsy guidance, and follow-up monitoring.
- ✔️ Integrated care ensures timely intervention and comprehensive management.
- ✔️ Technologically advanced scanners provide 3D reconstruction and AI-assisted diagnostics.
Highlights
- ➤ CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of bones, organs, and soft tissues.
- ➤ Indicated for trauma, cancer detection, cardiovascular evaluation, infection, neurological assessment, and procedural guidance.
- ➤ Alternatives include MRI, ultrasound, X-ray, PET-CT, and clinical examination.
- ➤ Preparation involves medical history review, fasting, contrast considerations, metal removal, and hydration.
- ➤ Procedure involves positioning, scanning, contrast administration (if needed), and image reconstruction.
- ➤ Post-scan care includes hydration, monitoring for allergic reactions, and follow-up with the physician.
- ➤ South Korea offers advanced, low-dose CT scanning in hospitals and imaging centers, supporting precise diagnosis, treatment planning, and integrated healthcare.