Overview
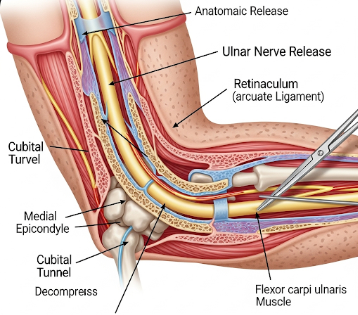
Ulnar nerve release is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on the ulnar nerve, which runs along the inner side of the elbow and controls sensation and movement in the forearm, hand, and fingers. Compression of this nerve, a condition known as cubital tunnel syndrome, can cause numbness, tingling, weakness, and hand dysfunction.
South Korea is a leading destination for nerve decompression surgeries thanks to its highly skilled orthopedic and neurosurgeons, advanced minimally invasive surgical techniques, and strong rehabilitation programs. Korean hospitals offer excellent treatment for patients with persistent ulnar nerve problems who do not improve with non-surgical therapies.
What is Ulnar Nerve Release?
Ulnar nerve release is a surgical intervention that relieves compression of the ulnar nerve, usually at the elbow. The goal is to restore normal nerve function, improve sensation, and relieve pain or weakness in the arm and hand.
Surgical approaches include:
- ➤ Simple decompression – releasing the tight tissues pressing on the nerve
- ➤ Medial epicondylectomy – removing part of the bony prominence to relieve pressure
- ➤ Anterior transposition – moving the nerve to a new position in front of the elbow to prevent it from stretching or compressing
What are the Benefits?
✔ Relieves pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm
✔ Restores grip strength and finger coordination
✔ Prevents permanent nerve damage if performed early
✔ Improves quality of life and allows return to work or sports
✔ Minimally invasive options available in Korean hospitals with faster recovery times
✔ High success rate when performed in specialized nerve surgery centers in Korea
Procedure Details:
1) How should I prepare for Ulnar Nerve Release?
- ● Medical evaluation: Electromyography (EMG), nerve conduction studies, and imaging to confirm compression
- ● Medication review: Patients may need to stop blood thinners or adjust certain prescriptions
- ● Fasting: No food or drink for 6–8 hours before surgery if general anesthesia is planned
- ● Lifestyle advice: Avoid smoking and alcohol to promote healing
- ● Korean hospitals provide: Pre-operative counseling and multilingual staff to guide international patients
2) What happens during the procedure Ulnar Nerve Release?
- ➤ Anesthesia: Local, regional, or general anesthesia depending on the case
- ➤ Incision: A small cut is made near the elbow to access the nerve
- ➤ Decompression techniques:
- Simple decompression by cutting tight ligaments or fascia
- Medial epicondylectomy to remove bony obstruction
- Nerve transposition (moving nerve to the front of elbow)
- ➤ Duration: Usually 30–90 minutes depending on complexity
- ➤ Korean surgical advantage: Minimally invasive or endoscopic techniques are used in many centers, resulting in smaller scars and faster healing
3) What happens after an Ulnar Nerve Release?
- ● Recovery room monitoring until anesthesia wears off
- ● Hospital stay: Often same-day discharge or 1 night in hospital
- ● Pain management: Oral pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medicines
- ● Wound care: Stitches are removed in 1–2 weeks
- ● Rehabilitation: Physical therapy may be needed to regain strength and motion
- ● Korean patient care model: Patients receive structured rehab programs, including occupational therapy for hand function
Risks / Benefits
✔ Benefits:
- ✦ Restores normal sensation and motor function
- ✦ Prevents long-term disability from nerve damage
- ✦ Improves hand dexterity and grip strength
- ✦ High satisfaction rate with modern Korean surgical techniques
⚠ Risks:
- ➔ Infection or bleeding at incision site
- ➔ Temporary stiffness or soreness
- ➔ Scar tissue formation
- ➔ In rare cases, persistent nerve symptoms if compression is severe or prolonged
- ➔ Nerve injury risk, though minimized with Korean microsurgical precision
Recovery and Outlook
- ➤ Recovery period: Light activities within 1–2 weeks, full recovery in 6–12 weeks
- ➤ Return to work: Office jobs within 1–2 weeks, heavy labor within 6–8 weeks
- ➤ Physical therapy: Strengthening and mobility exercises improve long-term results
- ➤ Outlook: Most patients experience significant symptom relief, especially if surgery is performed before permanent nerve damage occurs
- ➤ Korean hospitals: Provide customized rehab programs, ensuring excellent functional recovery rates
When To Call the Doctor
Patients should contact their surgeon if they notice:
- ⚠ Excessive swelling, bleeding, or pus at incision site
- ⚠ Severe pain not relieved by medication
- ⚠ Numbness or weakness worsening after surgery
- ⚠ Fever or chills indicating possible infection
- ⚠ Inability to move fingers properly after the procedure
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a top destination for ulnar nerve release surgery because of its:
- 🌟 Expert orthopedic and neurosurgeons specializing in peripheral nerve surgery
- 🌟 Minimally invasive surgical approaches with faster recovery and smaller scars
- 🌟 Advanced diagnostic systems (MRI, nerve conduction tests, high-resolution ultrasound)
- 🌟 Comprehensive rehab programs including hand therapy and physiotherapy
- 🌟 Affordable packages for international patients with world-class care
Leading Korean hospitals for nerve release surgery:
- ✅ Seoul National University Hospital
- ✅ Asan Medical Center
- ✅ Samsung Medical Center
- ✅ Severance Hospital (Yonsei University)
These centers are equipped with modern technology, bilingual staff, and international patient services, ensuring smooth treatment experiences for foreign patients.
✅ Quick Highlights Recap
- ➤ Ulnar nerve release relieves pressure on the nerve at the elbow
- ➤ Surgical approaches include decompression, epicondylectomy, or transposition
- ➤ Minimally invasive options available in Korea with high success rates
- ➤ Recovery: 6–12 weeks with physical therapy for best results
- ➤ Risks are low, but infection, stiffness, or persistent symptoms can occur
- ➤ Korean hospitals provide world-class surgical and rehab care