Overview
Umbilical hernia repair (child) is a surgical procedure used to correct a condition where a portion of the intestine, fat, or fluid pushes through the abdominal wall near the belly button. While many umbilical hernias in children close naturally within the first 3–5 years of life, some may persist or cause complications, requiring surgical intervention.
In South Korea, pediatric surgeons are highly skilled in minimally invasive and open hernia repair, with advanced technology ensuring safe, precise, and quick recovery for children. Korean hospitals provide child-friendly surgical care, advanced anesthesia techniques, and comprehensive post-operative support.
What is Umbilical Hernia Repair (Child)?
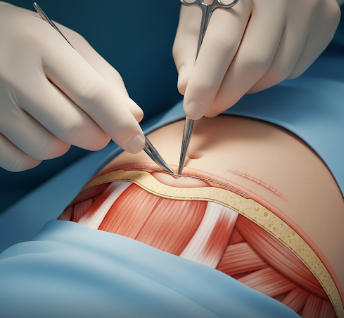
An umbilical hernia repair is a surgery performed when a child’s hernia does not close on its own or poses risks such as incarceration (trapped intestine) or strangulation (blocked blood supply).
The operation involves:
- ➤ Making a small incision at the belly button
- ➤ Returning herniated tissue to its proper place
- ➤ Strengthening the abdominal wall with sutures
- ➤ In rare cases, mesh reinforcement may be used (more common in adults than children)
What are the Benefits?
✔ Permanent repair of the hernia
✔ Prevents complications such as pain, intestinal blockage, or strangulation
✔ Improves abdominal strength and appearance
✔ Safe and effective with very low recurrence rates in children
✔ Minimally invasive options available in Korean hospitals for faster healing
Procedure Details:
1) How should I prepare for Umbilical Hernia Repair (Child)?
- ● Pre-surgery check-up: Pediatric evaluation and blood tests to ensure safe anesthesia
- ● Fasting: Child must not eat or drink for 6–8 hours before surgery
- ● Parental preparation: Parents receive detailed counseling on anesthesia and recovery
- ● Korean approach: Hospitals provide child-centered care, including play therapy or distraction techniques to reduce anxiety
2) What happens during the procedure Umbilical Hernia Repair (Child)?
- ➤ Anesthesia: General anesthesia is used to keep the child asleep and pain-free
- ➤ Incision: A small cut is made at or below the belly button
- ➤ Repair: Herniated tissue is gently pushed back into the abdomen
- ➤ Closure: Abdominal wall defect is closed with strong dissolvable stitches
- ➤ Duration: Typically 30–60 minutes
- ➤ Advanced Korean practice: Many hospitals use laparoscopic techniques for quicker recovery and less scarring
3) What happens after a Umbilical Hernia Repair (Child)?
- ● Recovery room: Child is monitored as anesthesia wears off
- ● Same-day discharge: Most children go home within a few hours
- ● Pain management: Mild discomfort is treated with prescribed pain medicine
- ● Activity: Child should avoid strenuous activity for 1–2 weeks
- ● Korean advantage: Hospitals provide follow-up support and parental guidance with clear instructions in multiple languages
Risks / Benefits
✔ Benefits:
- ✦ Quick, effective, and permanent cure
- ✦ Prevents dangerous complications
- ✦ Minimally invasive techniques available
- ✦ Low recurrence rates in children
⚠ Possible Risks (though rare):
- ➔ Infection at incision site
- ➔ Reaction to anesthesia
- ➔ Minor bleeding or swelling
- ➔ Very rare recurrence of hernia
Recovery and Outlook
- ➤ Recovery time: Most children return to school/normal activities in 1 week
- ➤ Full healing: Usually within 2–4 weeks
- ➤ Scar: Minimal and often hidden within the belly button
- ➤ Long-term outlook: Excellent — once repaired, umbilical hernias rarely come back in children
- ➤ Korean advantage: Parents can expect safe, precise care with pediatric-specialized surgeons and advanced facilities
When To Call the Doctor
Parents should contact their doctor if the child develops:
- ⚠ Redness, swelling, or pus at the incision site
- ⚠ Fever above 38°C (100.4°F)
- ⚠ Severe abdominal pain or vomiting
- ⚠ Bulge reappearing at the belly button
- ⚠ Difficulty breathing or unusual weakness after surgery
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers some of the most advanced pediatric surgical care in Asia. Umbilical hernia repairs are performed in specialized children’s hospitals and top general hospitals with pediatric surgery departments.
Why choose Korea?
- 🌟 Minimally invasive surgery options for reduced pain and faster healing
- 🌟 Pediatric anesthesia specialists ensuring maximum safety
- 🌟 Comprehensive parental support with counseling and multilingual care
- 🌟 Affordable compared to Western countries while maintaining global standards
- 🌟 Excellent post-operative follow-up
Top Korean Hospitals for Pediatric Umbilical Hernia Repair:
- ✅ Seoul National University Children’s Hospital
- ✅ Asan Medical Center (Pediatric Surgery Department)
- ✅ Severance Children’s Hospital (Yonsei University)
- ✅ Samsung Medical Center (Child & Adolescent Surgery Unit)
✅ Quick Highlights Recap
- ➤ Umbilical hernia repair is safe, effective, and often outpatient
- ➤ Minimally invasive techniques make recovery faster in Korea
- ➤ Prevents life-threatening complications like strangulation
- ➤ Low risks, excellent outcomes with expert Korean surgeons
- ➤ Top Korean hospitals offer world-class pediatric surgical care