Overview
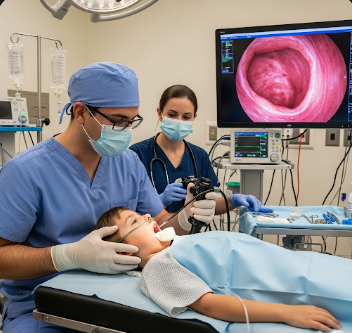
Upper GI endoscopy (child), also called esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the small intestine (duodenum). It is commonly recommended for children with persistent vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, gastrointestinal bleeding, or suspected ulcers.
South Korea is recognized for advanced pediatric endoscopy, offering minimally invasive procedures, sedation safety protocols, and expert pediatric gastroenterologists. Children benefit from gentle care, accurate diagnosis, and fast recovery in leading Korean hospitals.
What is Upper GI Endoscopy (Child)?
Upper GI endoscopy is a procedure where a thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth to visualize the upper digestive tract.
Uses include:
- ➤ Diagnosing ulcers, inflammation, or esophagitis
- ➤ Detecting infections like Helicobacter pylori
- ➤ Evaluating congenital anomalies
- ➤ Biopsy of suspicious areas for histological analysis
In children, sedation is used to ensure comfort and safety during the procedure.
What are the Benefits?
✔ Accurate visualization of the upper GI tract
✔ Early detection of gastrointestinal disorders
✔ Ability to perform biopsies for definitive diagnosis
✔ Minimally invasive with low complication risk
✔ Quick procedure and fast recovery
✔ Specialized pediatric endoscopy centers in Korea
Procedure Details:
1) How should I prepare for Upper GI Endoscopy (Child)?
- ● Fasting: Child must not eat or drink for 6–8 hours before the procedure
- ● Medication review: Certain medications may need adjustment, e.g., blood thinners
- ● Pre-procedure counseling: Parents are briefed on sedation, procedure steps, and post-procedure care
- ● Comfort measures: Korean hospitals often provide child-friendly environments, toys, and distraction techniques to reduce anxiety
2) What happens during the procedure Upper GI Endoscopy (Child)?
- ➤ Sedation or anesthesia: Ensures the child is relaxed or asleep
- ➤ Endoscope insertion: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is gently inserted through the mouth
- ➤ Visual examination: The gastroenterologist inspects the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
- ➤ Biopsy or treatment (if needed): Tissue samples can be collected, or minor procedures like polyp removal performed
- ➤ Duration: Usually 15–30 minutes
- ➤ Korean advantage: Pediatric gastroenterologists use high-definition scopes and advanced monitoring for precision and safety
3) What happens after an Upper GI Endoscopy (Child)?
- ● Recovery: Child monitored until sedation wears off, usually 1–2 hours
- ● Feeding: Small sips of water after 30–60 minutes, then light meals
- ● Observation: Parents are advised to watch for vomiting, bleeding, or abdominal pain
- ● Results: Biopsy results available in a few days; findings explained by pediatric gastroenterologists
- ● Korean approach: Hospitals provide multilingual support and detailed post-procedure care instructions
Risks / Benefits
✔ Benefits:
- ✦ Minimally invasive and highly accurate
- ✦ Can identify and treat issues in a single session
- ✦ Safe with pediatric sedation protocols
- ✦ Fast recovery, often same-day discharge
⚠ Possible Risks (rare in children):
- ➔ Sore throat or mild discomfort
- ➔ Reaction to sedation or anesthesia
- ➔ Bleeding at biopsy sites
- ➔ Very rare perforation of the GI tract
- ➔ Infection risk, minimized with sterile techniques
Recovery and Outlook
- ➤ Immediate recovery: Child may rest at home after a few hours
- ➤ Diet: Resume normal diet gradually as tolerated
- ➤ Full recovery: Usually 24–48 hours
- ➤ Follow-up: Depending on biopsy results or findings, further treatment may be recommended
- ➤ Korean advantage: Hospitals provide structured follow-up and guidance for parents, ensuring the child’s safety and comfort
When To Call the Doctor
Parents should contact their doctor if the child develops:
- ⚠ Persistent vomiting or inability to eat/drink
- ⚠ Fever or chills
- ⚠ Abdominal swelling or severe pain
- ⚠ Blood in vomit or stool
- ⚠ Unusual lethargy or weakness
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a top destination for pediatric upper GI endoscopy due to:
- 🌟 Specialized pediatric gastroenterologists with international training
- 🌟 High-definition endoscopes and advanced monitoring systems
- 🌟 Child-friendly hospital environments with experienced nursing care
- 🌟 Rapid reporting and multilingual support for international patients
- 🌟 Affordable and safe procedures compared to Western countries
Top Korean Hospitals for Pediatric Upper GI Endoscopy:
- ✅ Seoul National University Children’s Hospital
- ✅ Asan Medical Center (Pediatric Gastroenterology)
- ✅ Samsung Medical Center (Child & Adolescent Care)
- ✅ Severance Children’s Hospital (Yonsei University)
✅ Quick Highlights Recap
- ➤ Upper GI endoscopy examines esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
- ➤ Safe, minimally invasive, and quick procedure
- ➤ Sedation ensures comfort for children
- ➤ Fast recovery — typically same day discharge
- ➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced technology and child-focused care