Overview
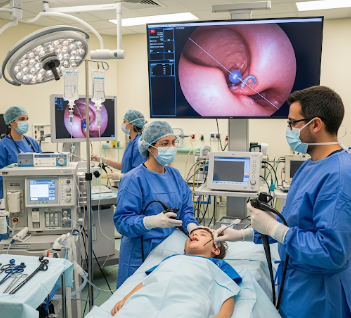
Upper GI endoscopy and dilatation (child) is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to examine and treat narrowing (strictures) in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum in children. Upper GI endoscopy allows the pediatric gastroenterologist to visualize the upper digestive tract, while dilatation widens the narrowed area to relieve swallowing difficulties, vomiting, or growth issues caused by obstruction.
South Korea is known for advanced pediatric endoscopy, providing minimally invasive procedures, safe sedation, and experienced pediatric specialists. Children benefit from gentle care, precise treatment, and rapid recovery in top Korean hospitals.
What is Upper GI Endoscopy and Dilatation (Child)?
Upper GI endoscopy in children involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) through the mouth to examine the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
Dilatation is performed when a stricture or narrowing is detected. Techniques include:
- ➤ Balloon dilatation – inflating a balloon at the stricture to widen it
- ➤ Bougie dilatation – gradually enlarging the narrowed area using tapered tubes
- ➤ Stent placement – occasionally used for severe or recurrent strictures
This procedure is safe, minimally invasive, and highly effective for treating pediatric gastrointestinal strictures.
What are the Benefits?
✔ Relieves swallowing difficulties (dysphagia)
✔ Improves nutrition and growth in children
✔ Minimally invasive and outpatient-friendly
✔ Reduces need for major surgery
✔ Quick recovery with low complication rates
✔ Specialized pediatric care in Korea with advanced imaging and precise dilatation
Procedure Details:
1) How should I prepare for Upper GI Endoscopy and Dilatation (Child)?
- ● Fasting: Child should not eat or drink for 6–8 hours prior
- ● Medication review: Certain medications may require adjustment (blood thinners, anti-inflammatories)
- ● Pre-procedure counseling: Parents receive guidance on sedation, procedure steps, and post-procedure care
- ● Child-friendly preparation: Korean hospitals use toys, videos, and distraction techniques to reduce anxiety
- ● Multilingual instructions provided for international patients
2) What happens during the procedure Upper GI Endoscopy and Dilatation (Child)?
- ➤ Sedation or anesthesia: Ensures child is comfortable and safe
- ➤ Endoscope insertion: Flexible tube gently inserted through the mouth
- ➤ Visualization: Gastroenterologist examines esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
- ➤ Dilatation:
- Balloon or bougie dilators widen the narrowed area
- Stents may be placed in severe cases
- ➤ Duration: Typically 20–45 minutes
- ➤ Korean advantage: Pediatric specialists use high-definition scopes and precise dilatation devices
3) What happens after an Upper GI Endoscopy and Dilatation (Child)?
- ● Recovery: Monitored until sedation wears off, usually 1–2 hours
- ● Diet: Start with clear liquids, then progress as tolerated
- ● Observation: Watch for pain, bleeding, or swallowing difficulty
- ● Follow-up: Gastroenterologist reviews results and schedules repeat dilatation if needed
- ● Korean hospitals: Offer structured follow-up, parental guidance, and multilingual care
Risks / Benefits
✔ Benefits:
- ✦ Relief from swallowing difficulties and vomiting
- ✦ Minimally invasive with fast recovery
- ✦ Can prevent major surgery
- ✦ Safe for children under pediatric supervision
⚠ Possible Risks (rare):
- ➔ Mild pain or discomfort
- ➔ Minor bleeding at the dilatation site
- ➔ Perforation of the esophagus (very rare)
- ➔ Reaction to sedation or anesthesia
- ➔ Infection, minimized with sterile technique
Recovery and Outlook
- ➤ Immediate recovery: Child usually resumes normal activity and diet within 24 hours
- ➤ Follow-up: Repeat endoscopy may be required if strictures recur
- ➤ Long-term outlook: High success rates with regular monitoring and early treatment
- ➤ Korean advantage: Experienced pediatric gastroenterologists, advanced equipment, and comprehensive follow-up ensure safety and effectiveness
When To Call the Doctor
Contact a doctor immediately if the child develops:
- ⚠ Severe chest pain or difficulty swallowing after procedure
- ⚠ Persistent vomiting or bleeding
- ⚠ Fever or signs of infection
- ⚠ Sudden weakness or lethargy
- ⚠ Recurrent obstruction symptoms
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a top destination for pediatric upper GI endoscopy and dilatation because of:
- 🌟 Specialized pediatric gastroenterologists
- 🌟 High-precision balloon and bougie dilators
- 🌟 Minimally invasive outpatient procedures
- 🌟 Multilingual care and international patient support
- 🌟 Integrated diagnostics and follow-up care
Top Korean Hospitals for Pediatric Upper GI Endoscopy and Dilatation:
- ✅ Seoul National University Children’s Hospital
- ✅ Asan Medical Center (Pediatric Gastroenterology)
- ✅ Samsung Medical Center (Child & Adolescent Care)
- ✅ Severance Children’s Hospital (Yonsei University)
- ✅ Bundang CHA Hospital (Advanced Pediatric GI Center)
✅ Quick Highlights Recap
- ➤ Endoscopy visualizes; dilatation widens narrowed areas in the upper GI tract
- ➤ Minimally invasive, safe, and effective for children
- ➤ Fast recovery — often same day discharge
- ➤ Rare risks, mostly manageable
- ➤ Korea provides advanced equipment, skilled pediatric gastroenterologists, and comprehensive follow-up care