Overview
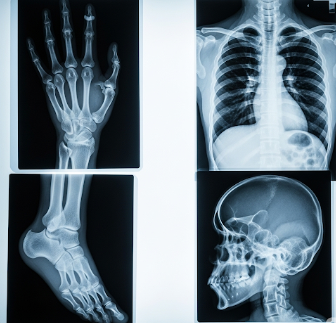
X-rays are a diagnostic imaging technique that uses electromagnetic radiation to create images of the inside of the body. They are one of the most commonly used medical imaging methods, helping doctors diagnose fractures, infections, tumors, and a variety of other conditions.
South Korea is recognized for advanced radiology services, high-resolution imaging, and rapid diagnostic support, making it a top destination for both local and international patients. Patients benefit from accurate diagnosis, fast results, and access to modern imaging technology.
X-rays are typically recommended for patients who:
- ➤ Experience bone fractures, joint pain, or trauma
- ➤ Need diagnosis for lung, chest, or abdominal conditions
- ➤ Require preoperative or follow-up imaging
- ➤ Seek quick, non-invasive diagnostic evaluation
What is an X-ray?
An X-ray is a form of electromagnetic radiation that passes through the body to create an image of the internal structures. Dense tissues like bones absorb more X-rays, appearing white on the image, while soft tissues appear darker.
Key points:
- Painless and non-invasive
- Provides real-time or static images for medical evaluation
- Can be enhanced with contrast materials for better visualization of organs
- Korean hospitals utilize digital X-rays, high-resolution detectors, and advanced software for precise diagnosis
What are the Benefits?
✔ Quick, accurate imaging for diagnosis
✔ Non-invasive and painless procedure
✔ Minimal radiation exposure with modern equipment
✔ Useful for a wide range of medical conditions
✔ Korean clinics provide digital imaging with fast results and expert radiologists
Additional benefits include:
- ➤ Immediate detection of fractures, bone abnormalities, and infections
- ➤ Enables monitoring of chronic conditions like arthritis or lung disease
- ➤ Can guide surgical planning or post-operative follow-up
- ➤ Low-cost and widely available in most healthcare settings in Korea
Procedure Details:
1) How should I prepare for an X-ray?
- ● Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing; remove metal objects such as jewelry or belts
- ● Medical history: Inform the radiologist if pregnant or recently underwent other imaging studies
- ● Special instructions: For contrast X-rays, follow fasting or hydration guidelines as advised
- ● Korean hospitals: Offer patient guidance, preparation instructions, and real-time imaging support
2) What happens during the procedure X-ray?
- ➤ Positioning: Patient positioned on X-ray table or standing, depending on the body part
- ➤ Procedure steps:
- Technician aligns X-ray machine over the targeted area
- Patient may be asked to hold still or hold breath for a few seconds
- X-ray beams pass through the body and are captured by digital detectors or film
- Multiple views may be taken for comprehensive assessment
- ➤ Duration: Typically 5–15 minutes
- ➤ Korean advantage: Use of digital detectors and advanced imaging software ensures high-quality images with minimal exposure
3) What happens after an X-ray?
- ● Immediate care: No recovery needed; patients can resume normal activities
- ● Results: Images are reviewed by a radiologist, with results sent to your doctor
- ● Follow-up: May include additional imaging or treatment recommendations based on findings
- ● Korean hospitals: Provide fast image processing, detailed radiology reports, and expert consultations
Risks / Benefits
✔ Benefits:
- ✦ Quick and accurate diagnostic tool
- ✦ Non-invasive and painless
- ✦ Minimal radiation exposure with modern technology
- ✦ Widely applicable for bones, chest, abdomen, and more
⚠ Possible Risks (rare):
- ➔ Minimal radiation exposure, generally considered safe
- ➔ Rare allergic reaction if contrast material is used
- ➔ Repeated imaging may slightly increase cumulative radiation dose
- ➔ Not suitable for detailed soft tissue imaging compared to MRI or CT
Recovery and Outlook
- ➤ Immediate recovery: No downtime; patients can continue daily activities
- ➤ Activity: No restrictions; normal routine can be resumed immediately
- ➤ Long-term outcome: Provides valuable diagnostic information for treatment planning and monitoring
- ➤ Korean advantage: Hospitals provide digital image storage, remote access, and expert radiology interpretation
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
- ⚠ Unexplained symptoms despite normal X-ray results
- ⚠ Persistent pain, swelling, or other clinical concerns
- ⚠ Reactions to contrast material (if used), such as rash or difficulty breathing
- ⚠ Need for further imaging or clarification of results
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is a leader in diagnostic imaging, including X-rays, due to:
- 🌟 Highly skilled radiologists with specialized expertise
- 🌟 Digital X-ray systems with minimal radiation exposure
- 🌟 Quick turnaround for image review and reporting
- 🌟 Integration with advanced imaging modalities for comprehensive evaluation
- 🌟 Multilingual support for international patients seeking safe and accurate diagnostics
Top Korean Hospitals for X-rays:
- ✅ Seoul National University Hospital (Radiology Dept.)
- ✅ Asan Medical Center
- ✅ Samsung Medical Center
- ✅ Severance Hospital (Yonsei University)
- ✅ Bundang CHA Hospital
✅ Quick Highlights Recap
- ➤ Non-invasive imaging using electromagnetic radiation to visualize internal structures
- ➤ Quick, painless, and minimal recovery time
- ➤ Widely used for bone, chest, abdominal, and other medical diagnoses
- ➤ Rare complications; minimal radiation exposure
- ➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced digital imaging, expert radiologists, and fast results