Overview
Cutaneous Lymphoma is a rare type of cancer that originates in the lymphocytes of the skin. Unlike other lymphomas that start in lymph nodes, this cancer primarily affects the skin, presenting with patches, plaques, or tumors. Early detection and treatment are critical to prevent systemic spread. South Korea offers advanced dermatology and oncology services for the diagnosis and management of cutaneous lymphoma.
What is Cutaneous Lymphoma?
Cutaneous Lymphoma arises from malignant T-cells or B-cells in the skin. It is broadly classified into:
- Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma (CTCL): Most common, includes Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome
- Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma (CBCL): Less common, usually indolent but may require aggressive therapy
The disease can remain localized in the skin or, in advanced stages, spread to lymph nodes, blood, or internal organs.
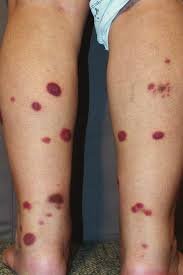
Symptoms
- Red or purple patches or plaques on the skin
- Thickened or scaly skin
- Tumors or nodules in advanced stages
- Itching (pruritus)
- Hair loss in affected areas
- Skin infections due to compromised barrier
Causes
- Exact cause is unknown
- Genetic mutations affecting T-cells or B-cells
- Immune system dysregulation
- Chronic skin inflammation in some cases
Risk Factors
- Age (more common in adults, typically 50–60 years)
- Male gender
- Weakened immune system
- History of chronic skin conditions
Complications
- Infection in affected skin
- Systemic spread to lymph nodes, liver, or spleen
- Severe itching and skin damage
- Psychological impact due to visible skin lesions
Prevention
- No known method to prevent cutaneous lymphoma
- Early dermatological consultation for persistent skin lesions
- Regular monitoring if immunocompromised
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for cutaneous lymphoma, combining dermatology, oncology, and supportive therapy:
- Diagnosis
- Skin biopsy for histopathology
- Immunophenotyping to distinguish T-cell or B-cell origin
- Blood tests and imaging (CT, PET-CT) to check for systemic involvement
- Medical Management
- Topical corticosteroids or retinoids for early-stage lesions
- Phototherapy (UVB or PUVA)
- Systemic therapies such as interferon, chemotherapy, or targeted agents for advanced disease
- Radiation Therapy
- Localized radiation for isolated skin lesions
- Total skin electron beam therapy (TSEBT) for widespread involvement
- Multidisciplinary Clinics
- Hospitals like Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, and Severance Hospital offer combined dermatology-oncology clinics
- Teams include dermatologists, hematologists, oncologists, and supportive care specialists
- Supportive Care
- Management of skin infections and pruritus
- Psychological counseling for coping with visible skin disease
- Nutritional support and lifestyle advice