Overview
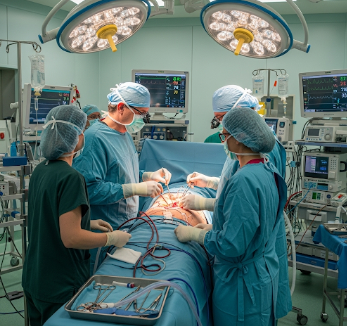
Open-heart surgery is a major procedure performed to repair or replace heart structures, such as heart valves, arteries, or chambers. It involves temporarily stopping the heart while a heart-lung bypass machine maintains circulation and oxygenation.
South Korea is renowned for advanced cardiac centers, where open-heart surgeries are performed with cutting-edge technology, minimally invasive approaches, and world-class post-operative care. Patients benefit from highly skilled surgeons, robotics-assisted techniques, and comprehensive rehabilitation programs.
What is Open-Heart Surgery?
Open-heart surgery refers to operations that require opening the chest (sternum) and operating directly on the heart. Common indications include:
✔ Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): Treats blocked arteries.
➔ Valve repair or replacement: Aortic, mitral, or tricuspid valve surgeries.
● Congenital heart defect repair: Corrects structural abnormalities from birth.
★ Heart transplant: Replaces a diseased heart with a donor organ.
What are the Benefits?
Open-heart surgery can significantly improve heart function, quality of life, and longevity:
✔ Restores normal blood flow in blocked arteries.
➔ Corrects faulty valves to prevent heart failure or arrhythmias.
● Repairs congenital defects, improving circulation and oxygen delivery.
★ Relieves severe symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue.
➤ Extends life expectancy in patients with advanced heart disease.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Open-Heart Surgery?
Preparation is critical for safety and success:
✔ Comprehensive cardiac evaluation: ECG, echocardiogram, coronary angiography, CT, or MRI.
➔ Blood tests: Assess kidney function, clotting, and overall health.
● Medication review: Adjust blood thinners or heart medications.
★ Lifestyle optimization: Quit smoking, maintain nutrition, and manage diabetes or hypertension.
➤ Patient counseling: Surgeons explain the procedure, risks, recovery, and lifestyle changes.
2) What happens during the procedure Open-Heart Surgery?
Open-heart surgery is performed under general anesthesia and can last 3–6 hours depending on complexity:
✔ Incision: Chest is opened via median sternotomy (or minimally invasive approaches in some centers).
➔ Heart-lung bypass: Machine takes over circulation while the heart is stopped.
● Repair or replacement: Surgeons perform CABG, valve repair/replacement, or defect correction.
★ Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of heart function, blood pressure, and oxygenation.
➤ Closure: Heart restarted, chest closed with wires, and drainage tubes placed.
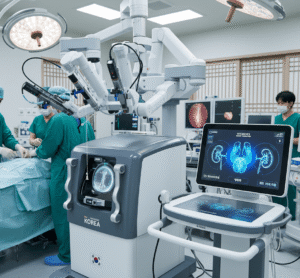
Korean cardiac centers often use robot-assisted or minimally invasive techniques to reduce trauma and improve cosmetic outcomes.
3) What happens after Open-Heart Surgery?
Postoperative care is crucial for recovery:
✔ Intensive Care Unit (ICU): 1–3 days for monitoring heart function and vital signs.
➔ Hospital stay: Typically 7–14 days depending on procedure and recovery.
● Pain management: Medications and monitoring for complications.
★ Cardiac rehabilitation: Gradual physical activity, diet control, and lifestyle counseling.
➤ Follow-up visits: Imaging and lab tests ensure proper healing and function.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection (sternum, lungs, or blood)
➔ Bleeding or need for transfusion
● Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat)
★ Stroke or heart attack (rare)
➤ Kidney or lung complications
Major Benefits:
✔ Restores blood flow and heart function
➔ Prevents progression of heart failure
● Relieves severe symptoms like chest pain and fatigue
★ Improves survival in patients with advanced cardiac disease
➤ Enables patients to return to daily life with better quality of life
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: ICU 1–3 days; hospital stay 7–14 days.
➔ Physical activity: Gradual increase with cardiac rehab over 6–12 weeks.
● Lifestyle management: Diet, exercise, and medication adherence essential.
★ Long-term prognosis: Most patients experience improved heart function and symptom relief.
➤ Follow-up: Regular cardiac check-ups, imaging, and blood tests for optimal outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Seek immediate help if patients experience:
✔ Chest pain or pressure
➔ Shortness of breath or dizziness
● Fever or signs of infection at the incision site
★ Irregular heartbeat or fainting
➤ Swelling in legs or sudden weight gain (possible fluid retention)
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is recognized for world-class cardiac surgery with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center, Severance Hospital, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced surgical techniques: Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted open-heart surgery.
● Multidisciplinary teams: Cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, anesthesiologists, and rehabilitation specialists.
★ High success rates and low complication rates.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel assistance, and post-surgical care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Open-heart surgery repairs or replaces heart structures
➔ Performed under general anesthesia with heart-lung bypass
● Minimally invasive and robotic techniques available in Korea
★ Risks include infection, bleeding, arrhythmia, or organ complications
➤ Korean hospitals provide world-class outcomes with advanced rehabilitation