Overview
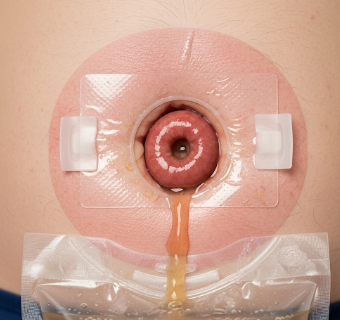
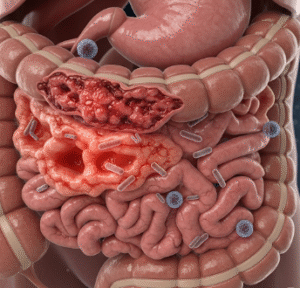
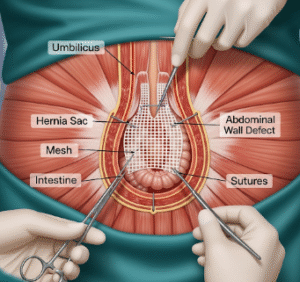
An ostomy is a surgical procedure that creates an opening (stoma) in the abdominal wall to allow waste (urine or feces) to exit the body when normal excretion through the bladder or bowel is not possible. Ostomies are often performed for cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, trauma, or congenital conditions.
South Korea offers advanced ostomy care in specialized hospitals with experienced surgeons, comprehensive pre- and post-operative education, and state-of-the-art stoma appliances to ensure comfort, safety, and quality of life for patients.
What is Ostomy?
Ostomy involves creating a surgically constructed opening on the abdomen to divert bodily waste. The main types include:
✔ Colostomy: Diverts stool from the colon to a stoma.
➔ Ileostomy: Diverts stool from the small intestine.
● Urostomy: Diverts urine from the urinary tract when the bladder is removed or nonfunctional.
★ Continent ostomy: Uses internal reservoirs with catheterizable stoma for controlled emptying.
Ostomies may be temporary (allowing healing) or permanent (long-term solution).
What are the Benefits?
Ostomy can significantly improve health and quality of life when normal excretion is compromised:
✔ Relieves bowel or bladder obstruction
➔ Prevents infection and complications from diseased or damaged organs
● Allows healing after surgery or injury
★ Improves quality of life by providing safe and manageable waste elimination
➤ Enables patients to maintain daily activities despite underlying conditions
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Ostomy?
Preparation ensures safety and optimal outcomes:
✔ Pre-operative assessment: Blood tests, imaging, and evaluation of abdominal anatomy.
➔ Dietary adjustments: Bowel prep may be required for intestinal ostomies.
● Medication review: Blood thinners or anticoagulants may need adjustment.
★ Stoma site marking: Done by specialized nurses to ensure optimal placement for comfort and appliance adherence.
➤ Patient education: Counseling on ostomy management, appliances, and lifestyle modifications.
2) What happens during the procedure Ostomy?
Ostomy surgery is performed under general anesthesia and typically lasts 1–3 hours depending on the type:
✔ Incision: Surgeon opens the abdominal wall.
➔ Creating the stoma: Intestinal or urinary segment is brought to the surface.
● Securing the stoma: The opening is sutured to the skin and shaped for proper function.
★ Appliance fitting: Temporary or permanent ostomy bag applied immediately post-surgery.
➤ Duration: Simple ostomy can take ~1 hour; complex or reconstructive procedures may take longer.
Korean hospitals often use minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques to reduce recovery time and post-operative pain.
3) What happens after Ostomy?
Recovery involves stoma care and monitoring:
✔ Hospital stay: Usually 3–7 days, depending on type and patient condition.
➔ Pain management: Medications provided as needed.
● Stoma education: Nurses teach cleaning, bag changing, and monitoring for complications.
★ Diet and hydration: Adjusted based on type of ostomy.
➤ Follow-up: Regular visits to monitor stoma health and appliance function.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at surgical site
➔ Stoma blockage or leakage
● Skin irritation around stoma
★ Hernia formation near stoma
➤ Emotional or psychological impact requiring counseling
Major Benefits:
✔ Allows normal waste elimination when bladder or bowel function is compromised
➔ Prevents life-threatening complications from obstruction or disease
● Improves comfort, hygiene, and quality of life
★ Temporary or permanent solutions tailored to patient needs
➤ Minimally invasive techniques in Korea reduce complications and recovery time
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: 2–4 weeks for incision healing; adjustment to stoma care may take longer.
➔ Lifestyle adaptation: Patients learn to manage appliances, diet, and activity.
● Follow-up care: Regular stoma checkups and monitoring for complications.
★ Long-term outlook: Most patients lead full, active lives with proper ostomy care.
➤ Support networks: Korean hospitals provide access to support groups, counseling, and nursing care.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if you notice:
✔ Redness, swelling, or pain at the stoma site
➔ Unusual bleeding or leakage
● Persistent diarrhea or constipation affecting stoma function
★ Foul odor or signs of infection
➤ Changes in stoma color (pale, dark, or purple) indicating compromised blood supply
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers advanced ostomy care and surgery with:
✔ Top hospitals: Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center.
➔ Experienced multidisciplinary teams: Surgeons, stoma care nurses, nutritionists, and rehabilitation specialists.
● Minimally invasive techniques for faster recovery and less pain.
★ Comprehensive patient education and support programs for stoma management.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel arrangements, and follow-up care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Ostomy creates a surgical stoma for urine or stool diversion
➔ Types include colostomy, ileostomy, urostomy, and continent ostomy
● Minimally invasive techniques in Korea improve recovery
★ Risks include infection, leakage, hernia, and skin irritation
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced surgical care, stoma education, and support