Overview
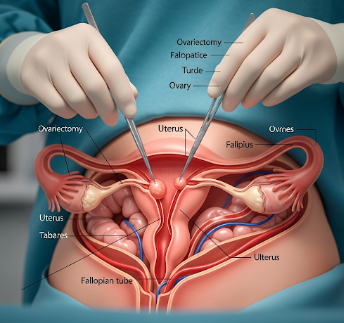
Ovariectomy, also known as oophorectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove one or both ovaries. This procedure is commonly performed to treat ovarian cysts, tumors, endometriosis, or reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
South Korea is recognized for advanced gynecological surgery, offering minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, robotic-assisted surgery, and expert post-operative care, ensuring safety and optimal recovery for women.
What is Ovariectomy?
Ovariectomy involves surgically removing the ovary or ovaries while preserving surrounding reproductive structures if possible. Types include:
✔ Unilateral ovariectomy: Removal of one ovary.
➔ Bilateral ovariectomy: Removal of both ovaries, often performed for high cancer risk.
● Laparoscopic ovariectomy: Minimally invasive, small incisions, faster recovery.
★ Open (laparotomy) ovariectomy: For large masses, complex cases, or emergency situations.
The procedure may be elective or emergency, depending on the patient’s condition.
What are the Benefits?
Ovariectomy offers several important benefits:
✔ Removes diseased or cancerous ovarian tissue.
➔ Prevents recurrence of ovarian cysts or tumors.
● Reduces risk of ovarian cancer in high-risk patients.
★ Alleviates pain and hormonal issues caused by ovarian disease.
➤ Improves overall reproductive health and quality of life.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Ovariectomy?
Preparation ensures safety and optimal outcomes:
✔ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound, CT, or MRI), and physical examination.
➔ Medication review: Blood thinners or hormone therapies may need adjustment.
● Fasting: Typically 6–8 hours prior to anesthesia.
★ Patient counseling: Discuss surgical technique, risks, recovery, and hormonal implications.
➤ Lifestyle adjustments: Smoking cessation and optimization of general health.
2) What happens during the procedure Ovariectomy?
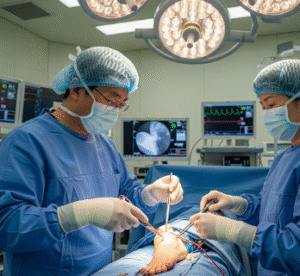
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 1–2 hours:
✔ Incision: Laparoscopic (small incisions) or open (larger abdominal incision).
➔ Ovary identification: Diseased ovary located and carefully dissected.
● Ovary removal: Ovary is excised; tissue may be sent for pathological examination.
★ Hemostasis: Bleeding is controlled and surrounding structures preserved.
➤ Closure: Incisions sutured and sterile dressing applied.
Korean surgeons often use laparoscopic or robotic techniques for precision and reduced recovery time.
3) What happens after Ovariectomy?
Post-operative care focuses on healing, pain management, and hormonal monitoring:
✔ Hospital stay: Typically 1–2 days for laparoscopic; longer for open surgery.
➔ Pain management: Medications for post-op discomfort.
● Activity restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity for 2–4 weeks.
★ Wound care: Keep incision clean; monitor for infection or swelling.
➤ Follow-up: Hormone level monitoring and routine check-ups to ensure recovery.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Infection at incision site
➔ Bleeding or hematoma
● Injury to surrounding structures (bladder, bowel, or blood vessels)
★ Hormonal changes leading to early menopause (if both ovaries removed)
➤ Rare complications: blood clots or anesthesia-related issues
Major Benefits:
✔ Removes diseased or high-risk ovarian tissue
➔ Alleviates pain and hormonal imbalances
● Reduces risk of ovarian cancer in high-risk patients
★ Preserves surrounding reproductive structures when possible
➤ Minimally invasive techniques reduce recovery time and surgical complications
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Initial recovery: 1–2 weeks for laparoscopic; 4–6 weeks for open surgery.
➔ Activity: Gradual return to normal activities; avoid heavy lifting initially.
● Hormonal management: Discuss post-operative hormone replacement therapy if needed.
★ Long-term outcome: Relief from ovarian disease symptoms, reduced cancer risk, and improved quality of life.
➤ Follow-up: Regular gynecological exams and imaging if indicated.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
✔ Redness, swelling, or discharge at incision site
➔ Fever or signs of infection
● Severe abdominal pain or bloating
★ Irregular bleeding or hormonal changes
➤ Persistent nausea, vomiting, or urinary/bowel issues
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides world-class ovariectomy care with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced techniques: Laparoscopic, robotic, and open surgical approaches.
● Expert gynecological surgeons: Skilled in complex ovarian surgeries.
★ Comprehensive post-op care: Pain management, hormonal support, and follow-up.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, travel coordination, and post-operative follow-up for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Ovariectomy removes diseased or high-risk ovaries
➔ Reduces pain, prevents recurrence, and lowers ovarian cancer risk
● Minimally invasive techniques improve recovery and reduce complications
★ Risks include infection, bleeding, hormonal changes, or injury to surrounding organs
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced surgical expertise, safety, and post-operative support