Overview
Primary anti-reflux surgery, commonly known as fundoplication, is a surgical procedure designed to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It is recommended for patients whose acid reflux is not controlled with medication, or who experience complications such as esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, or severe regurgitation.
South Korea is renowned for expert gastrointestinal surgeons, advanced laparoscopic techniques, and comprehensive post-operative care, making fundoplication safe, effective, and minimally invasive.
What is Primary Anti-Reflux Surgery (Fundoplication)?
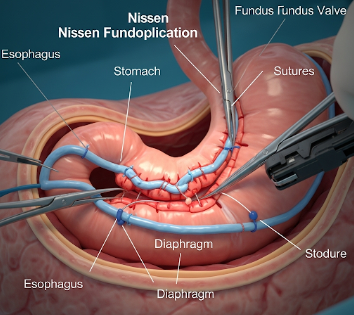
Fundoplication involves wrapping the upper part of the stomach (fundus) around the lower esophagus to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent acid reflux. Key points include:
✔ Restores normal anti-reflux barrier.
➔ Reduces heartburn, regurgitation, and esophageal irritation.
● Minimally invasive options: Laparoscopic fundoplication is standard for faster recovery.
★ Durable solution: Provides long-term control of GERD symptoms.
This surgery is suitable for patients with severe GERD, hiatal hernia, or complications from chronic reflux.
What are the Benefits?
Fundoplication offers multiple advantages:
✔ Relief from chronic heartburn and acid regurgitation.
➔ Reduces the risk of esophageal complications like ulcers or Barrett’s esophagus.
● Minimally invasive surgery with shorter hospital stay.
★ Improves quality of life by allowing normal eating and reducing reliance on medication.
➤ Long-term effectiveness with low recurrence rates when performed correctly.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Primary Anti-Reflux Surgery?
Preparation ensures safety and optimal outcomes:
✔ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging, and esophageal studies such as endoscopy or pH monitoring.
➔ Medication review: Stop certain anticoagulants or anti-inflammatory drugs as instructed.
● Fasting: Typically 6–8 hours before surgery.
★ Lifestyle adjustments: Smoking cessation and weight management may improve results.
➤ Patient counseling: Discuss procedure, anesthesia, risks, and post-operative care.
2) What happens during the procedure Fundoplication?
Fundoplication is usually performed laparoscopically under general anesthesia:
✔ Small incisions: Several tiny cuts in the abdomen to insert laparoscopic instruments.
➔ Hiatal repair: Weakness in the diaphragm opening is repaired if a hiatal hernia is present.
● Fundus wrap: The upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter.
★ Sutures or mesh fixation: Ensures the wrap stays in place.
➤ Procedure duration: Typically 1–2 hours depending on complexity.
Korean surgeons are experienced in laparoscopic and robot-assisted techniques for precise, minimally invasive fundoplication.
3) What happens after Primary Anti-Reflux Surgery?
Post-operative care focuses on healing, diet, and monitoring for complications:
✔ Hospital stay: Usually 1–3 days.
➔ Pain management: Mild abdominal discomfort treated with analgesics.
● Diet progression: Clear liquids initially, gradually advancing to soft foods over weeks.
★ Activity restrictions: Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise for several weeks.
➤ Follow-up: Regular monitoring of symptom resolution, esophageal healing, and wrap integrity.
Risks / Benefits
Possible Risks:
✔ Temporary difficulty swallowing
➔ Gas bloating or flatulence
● Infection or bleeding at incision sites
★ Rare wrap migration or loosening
➤ Injury to surrounding structures (esophagus, stomach, or diaphragm)
Major Benefits:
✔ Effective control of acid reflux and GERD symptoms
➔ Reduces risk of esophageal damage and ulcers
● Minimally invasive with shorter recovery than open surgery
★ Long-term symptom relief and improved quality of life
➤ Can eliminate or reduce dependence on anti-reflux medications
Recovery and Outlook
✔ Immediate recovery: Most patients resume walking and light activity within 1–2 days.
➔ Pain and swelling: Mild discomfort managed with analgesics.
● Dietary progression: Clear liquids initially, progressing to soft foods and eventually a normal diet.
★ Full recovery: Usually 3–6 weeks, depending on patient condition.
➤ Long-term outcome: Most patients achieve durable symptom control and enhanced quality of life.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice:
✔ Severe or worsening abdominal pain
➔ Fever, chills, or signs of infection
● Persistent difficulty swallowing or vomiting
★ Severe bloating or inability to pass gas
➤ Recurrent reflux symptoms despite surgery
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides expert fundoplication services with:
✔ Leading hospitals: Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital.
➔ Advanced laparoscopic and robot-assisted techniques for precise anti-reflux surgery.
● Experienced gastrointestinal surgeons: Skilled in both primary and revisional fundoplication.
★ Comprehensive care: Preoperative evaluation, surgery, post-op monitoring, and dietary guidance.
➤ Medical tourism support: Translation, appointment coordination, and continuity of care for international patients.
✅ Highlights:
✔ Fundoplication corrects GERD and prevents acid reflux
➔ Minimally invasive with laparoscopic or robotic techniques
● Improves quality of life and reduces medication dependence
★ Risks include temporary swallowing difficulties, bloating, or rare surgical complications
➤ Korean hospitals provide advanced technology, skilled surgeons, and comprehensive post-op care