Overview
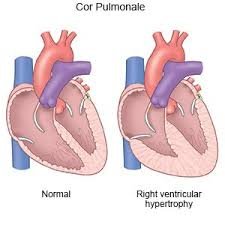
Cor Pulmonale is a condition in which the right ventricle of the heart enlarges and weakens due to high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). It typically arises as a complication of chronic lung diseases that impair oxygen exchange, causing the right side of the heart to work harder. If untreated, it can lead to right-sided heart failure and serious health complications.
What is Cor Pulmonale?
Cor Pulmonale occurs when increased resistance in the pulmonary circulation forces the right ventricle to pump against higher pressure, leading to hypertrophy (thickening) and eventual heart failure. Common causes include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, and chronic blood clots in the lungs.
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Fatigue and weakness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen (edema)
- Chest discomfort or pressure
- Palpitations
- Cyanosis (bluish lips or skin)
- Dizziness or fainting in severe cases
Causes
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Interstitial lung disease or pulmonary fibrosis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Sleep apnea
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Congenital heart diseases affecting pulmonary circulation
Risk Factors
- Chronic lung conditions
- Smoking or exposure to lung irritants
- Obesity and sleep apnea
- Family history of pulmonary hypertension
- High altitude exposure without proper acclimatization
Complications
- Right-sided heart failure
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
- Liver congestion and dysfunction
- Fluid retention leading to edema and ascites
- Reduced exercise tolerance
- Increased risk of sudden cardiac death in advanced cases
Prevention
- Avoid smoking and lung irritants
- Manage chronic lung diseases effectively
- Maintain a healthy weight and treat sleep apnea
- Get vaccinations to prevent respiratory infections
- Regular monitoring for individuals at risk of pulmonary hypertension
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced cardiopulmonary care with specialized facilities for Cor Pulmonale management.
- Diagnosis
- Echocardiography: Evaluates right heart function and pulmonary pressures
- Chest X-ray: Detects lung disease and heart enlargement
- CT or MRI: Detailed imaging of lungs and heart
- Pulmonary function tests: Assess lung capacity
- Right heart catheterization: Confirms pulmonary hypertension
- Medical Management
- Oxygen therapy for chronic low oxygen levels
- Diuretics to reduce fluid buildup
- Pulmonary vasodilators (e.g., sildenafil)
- Anticoagulants for pulmonary embolism
- Medications to treat underlying lung disease (bronchodilators, anti-inflammatories)
- Surgical and Interventional Procedures
- Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy for chronic pulmonary embolism
- Lung transplantation in severe cases
- Right heart assist devices in advanced heart failure
- Lifestyle and Supportive Care
- Low-sodium diet to manage fluid retention
- Pulmonary rehabilitation and physical exercise programs
- Regular follow-up and monitoring of heart and lung function