Overview
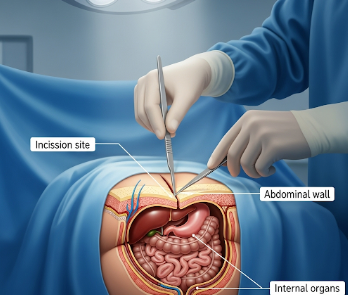
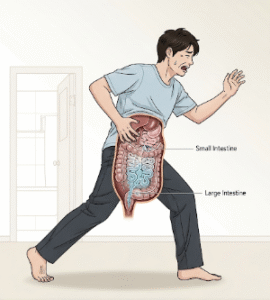
Laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a large incision in the abdominal wall to access the abdominal cavity. It is used for diagnostic purposes or to perform surgery on abdominal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, or reproductive organs.
In Korea, laparotomy is performed by highly skilled general, gastrointestinal, or gynecologic surgeons, depending on the underlying condition. Although it is more invasive than laparoscopic surgery, it allows direct access for complex surgical interventions.
Highlights:
- ✅ Direct access to abdominal organs for diagnosis or surgery
- ✅ Can address complex abdominal conditions
- ✅ Performed by experienced surgeons in advanced medical centers
What is Laparotomy?
Laparotomy involves making a single, large incision in the abdominal wall to provide surgeons with full access to the abdominal cavity. This approach is often chosen when minimally invasive methods are not suitable due to the complexity or urgency of the condition.
Indications include:
- Abdominal trauma or emergency surgery
- Tumor removal (e.g., liver, ovarian, or gastrointestinal tumors)
- Treatment of severe infections or abscesses
- Complex gynecological or gastrointestinal procedures
- Unexplained abdominal pain requiring direct examination
Important: While laparotomy is more invasive than laparoscopy, it allows complete visualization and access for safe management of critical abdominal conditions.
What are the benefits?
- Full access: Allows surgeons to see and treat multiple abdominal organs
- Versatile procedure: Can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes
- Immediate intervention: Critical for emergencies such as trauma or bleeding
- Effective management: Ensures complex conditions can be treated safely
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Suitable for emergencies or complex surgeries
- ⚡ Provides a controlled surgical environment
- ⚡ Enables comprehensive treatment of abdominal pathologies
- ⚡ High success rate when performed by experienced surgeons
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Laparotomy?
- Preoperative evaluation: Blood tests, imaging (CT, MRI, ultrasound), and physical examination
- Medication review: Stop blood thinners or other medications as instructed
- Fasting: Usually 6–8 hours before surgery
- Consent and education: Discuss procedure, risks, expected outcomes, and recovery
- Lifestyle preparation: Arrange for postoperative care and limit physical activity after discharge
2) What happens during Laparotomy?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia administered
- Incision: A large abdominal incision is made to access the abdominal cavity
- Surgical intervention: The target organ or area is treated (removal, repair, or biopsy)
- Hemostasis and inspection: Bleeding is controlled, and surrounding tissues checked
- Closure: Incision closed in layers with sutures or staples; drains may be placed if needed
Duration: Varies depending on complexity; typically 1–4 hours
3) What happens after Laparotomy?
- Recovery monitoring: Vital signs, wound condition, and overall stability observed in hospital
- Pain management: Analgesics administered for moderate-to-severe pain
- Activity: Gradual mobilization; avoid strenuous activity for several weeks
- Follow-up care: Wound care, monitoring for infection, and evaluation of surgical outcomes
Highlights for post-procedure care:
- ⚡ Moderate pain and tenderness expected at the incision site
- ⚡ Hospital stay may last several days depending on surgery type
- ⚡ Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity for at least 4–6 weeks
- ⚡ Attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing and recovery
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Infection or wound complications
- Bleeding or hematoma
- Injury to surrounding organs (bowel, bladder, blood vessels)
- Postoperative adhesions or hernias
- Anesthesia-related complications
Benefits:
- Direct access for complex or emergency abdominal surgery
- Comprehensive management of abdominal pathologies
- Enables both diagnostic and therapeutic interventions
- High success rates when performed by experienced surgeons
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Typically 3–10 days depending on procedure complexity
- Full recovery: 4–8 weeks for most patients; gradual return to normal activities
- Long-term outlook: Excellent if underlying condition is managed successfully
- Follow-up: Regular postoperative visits to monitor wound healing, organ function, and overall recovery
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Keep the incision clean and dry
- ✅ Gradually increase activity as advised by your surgeon
- ✅ Watch for signs of infection or abnormal symptoms
- ✅ Attend all follow-up visits to ensure full recovery
When To Call the Doctor
- Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- Severe abdominal pain not relieved by medication
- Excessive bleeding or wound discharge
- Nausea, vomiting, or inability to eat or drink
- Swelling or redness around the incision site
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides advanced laparotomy care:
- Top hospitals: Specialized general surgery centers with expert surgeons
- Advanced diagnostics: CT, MRI, ultrasound, and laboratory tests for preoperative planning
- Surgical expertise: Experienced surgeons manage complex or emergency abdominal conditions
- Postoperative care: Pain management, wound monitoring, and rehabilitation guidance
- International patient support: Online consultations, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Online consultation and preoperative assessment
- Pre-surgery preparation including imaging and lab tests
- Laparotomy performed by expert surgeons
- Postoperative monitoring, pain management, and gradual mobilization
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing, recovery, and overall outcomes