Overview
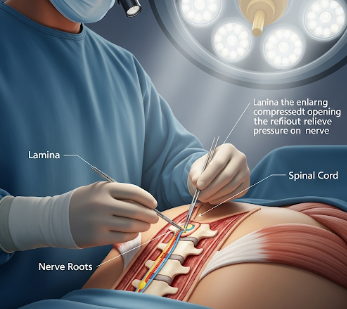
A Laminotomy is a surgical procedure designed to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots caused by conditions such as spinal stenosis, herniated discs, or bone spurs. Unlike a laminectomy, only a small portion of the lamina is removed, preserving more of the vertebra and maintaining spinal stability.
In Korea, patients can access highly experienced neurosurgeons and orthopedic spine specialists who use advanced minimally invasive techniques for a safe, precise, and effective procedure.
Highlights:
- ✅ Relieves nerve compression while preserving spinal stability
- ✅ Reduces back and leg pain, numbness, or weakness
- ✅ Available at leading spine centers in Korea
What is Laminotomy?
A Laminotomy involves the removal of a portion of the lamina, the bony arch forming the roof of the spinal canal, to create space for compressed nerves. This procedure helps relieve symptoms such as:
- Localized back pain
- Radiating pain in the arms or legs
- Numbness or tingling
- Weakness or difficulty walking
It is often performed at the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine, depending on where nerve compression occurs. Laminotomy is usually preferred when a less invasive option is suitable to maintain spinal stability.
What are the benefits?
- Pain relief: Alleviates chronic back or limb pain from nerve compression
- Maintains spinal stability: Only a small portion of lamina is removed
- Improved mobility: Reduces weakness and improves walking or hand function
- Enhanced quality of life: Enables resumption of daily activities
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Targeted decompression of compressed nerves
- ⚡ Lower risk of spinal instability compared to full laminectomy
- ⚡ Can be combined with other minimally invasive spine procedures if needed
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for a Laminotomy?
- Preoperative evaluation: Blood tests, MRI/CT imaging, and neurological assessments
- Medication adjustments: Stop blood thinners or medications as instructed
- Fasting instructions: No food or drink for several hours prior to surgery
- Consent and education: Discuss risks, benefits, and postoperative expectations
- Post-surgery support: Arrange caregiver assistance at home during recovery
2) What happens during a Laminotomy?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered
- Surgical approach: Open or minimally invasive, depending on the case
- Removal of lamina portion: Small section of lamina removed to relieve nerve pressure
- Optional decompression techniques: Removal of bone spurs or disc material if needed
- Closure: Incisions are closed and patient is moved to recovery
Duration: Usually 1–2 hours depending on number of levels treated
3) What happens after a Laminotomy?
- Recovery room monitoring: Vital signs and neurological function closely observed
- Pain management: Medications to control post-operative discomfort
- Early mobilization: Encouraged to prevent complications such as blood clots
- Physical therapy: Begins shortly after surgery to improve strength and flexibility
Highlights for post-operative care:
- ⚡ Monitor for signs of infection or neurological changes
- ⚡ Gradual return to daily activities as advised
- ⚡ Follow prescribed exercises to enhance spinal stability
- ⚡ Regular follow-up with the surgeon to track healing
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Infection or bleeding at surgical site
- Nerve injury leading to numbness, weakness, or pain
- Rare anesthesia complications
- Possibility of re-compression requiring future procedures
Benefits:
- Relief from chronic pain and neurological symptoms
- Maintains spinal stability while decompressing nerves
- Faster recovery compared to full laminectomy
- Improved mobility and quality of life
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Typically 1–3 days depending on procedure complexity
- Full recovery: Most patients regain normal function within 4–6 weeks
- Long-term outlook: Effective decompression reduces recurrence risk and allows return to daily activities
- Follow-up: Regular visits to monitor incision, neurological status, and physical therapy progress
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Adhere strictly to postoperative instructions
- ✅ Engage in recommended physical therapy
- ✅ Avoid lifting heavy objects or bending excessively in early recovery
- ✅ Monitor incision and overall health for complications
When To Call the Doctor
- Increasing pain, swelling, or redness at incision site
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness worsening after surgery
- Fever or signs of infection
- Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel function
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea offers advanced spinal care for Laminotomy:
- Top hospitals: Experienced spine surgeons with multidisciplinary teams
- Advanced diagnostics: MRI, CT, and nerve studies for precise planning
- Surgical options: Open or minimally invasive laminotomy
- Postoperative care: Specialized recovery units, pain management, and physiotherapy
- International patient support: Online consultations, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Online consultation and imaging review
- Preoperative evaluation and planning
- Laminotomy performed by spine specialists
- Postoperative monitoring and rehabilitation guidance
- Remote follow-up for ongoing care