Overview
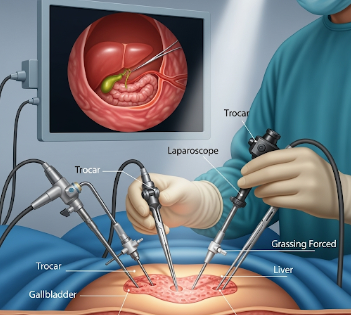
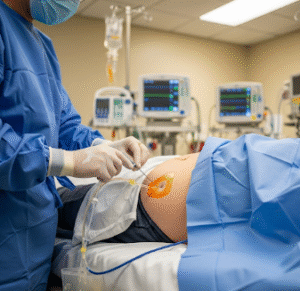
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to examine and operate on organs inside the abdomen or pelvis. It allows surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions using a laparoscope—a thin tube with a camera and light—reducing recovery time, scarring, and risk of infection.
In Korea, laparoscopy is widely available for gynecological, urological, gastrointestinal, and general surgical procedures, with access to highly skilled surgeons and advanced surgical equipment.
Highlights:
- ✅ Minimally invasive with small incisions
- ✅ Shorter hospital stay and faster recovery
- ✅ Can be used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes
What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy involves the insertion of a laparoscope and specialized instruments into the abdominal or pelvic cavity. The camera provides a magnified view for the surgeon, allowing for precise diagnosis and treatment.
It can be used for:
- Diagnostic purposes: Detect causes of pain, infertility, or abnormal growths
- Surgical procedures: Removal of gallbladder, appendix, ovarian cysts, fibroids, or hernia repair
- Biopsy: Taking tissue samples without large incisions
Important: Laparoscopy is preferred over traditional open surgery when feasible, due to reduced pain, quicker recovery, and minimal scarring.
What are the benefits?
- Reduced recovery time: Most patients return to normal activities within days
- Minimal scarring: Small incisions result in better cosmetic outcomes
- Lower risk of infection: Less exposure of internal tissues
- Accurate diagnosis and treatment: Direct visualization of internal organs
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Less post-operative pain compared to open surgery
- ⚡ Shorter hospital stay and faster return to daily life
- ⚡ Can combine diagnosis and treatment in one procedure
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Laparoscopy?
- Preoperative evaluation: Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI) as needed
- Fasting instructions: No food or drink for 6–8 hours prior to surgery
- Medication adjustments: Stop blood thinners or medications as advised
- Consent and education: Understand procedure, risks, benefits, and recovery expectations
- Arrange post-surgery care: Plan for someone to assist after hospital discharge
2) What happens during a Laparoscopy?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered
- Insertion of trocars: Small incisions (0.5–1.5 cm) are made to insert the laparoscope and instruments
- Gas insufflation: Abdomen is inflated with CO₂ to provide working space
- Surgical procedure: Depending on the condition, removal, repair, or biopsy is performed
- Closure: Instruments are removed, and small incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive
Duration: Usually 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on complexity
3) What happens after a Laparoscopy?
- Recovery room monitoring: Vital signs and post-anesthesia observation
- Pain management: Mild discomfort is common at incision sites or shoulder tip due to gas
- Activity: Most patients can walk the same day and gradually resume normal activities
- Follow-up care: Incision check, suture removal if necessary, and monitoring for complications
Highlights for post-operative care:
- ⚡ Watch for fever, bleeding, or signs of infection
- ⚡ Resume light activities as advised, avoid heavy lifting for 1–2 weeks
- ⚡ Maintain hydration and balanced diet to aid recovery
- ⚡ Follow-up appointments for monitoring and additional care
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Bleeding or infection at incision sites
- Injury to internal organs (rare)
- Reaction to anesthesia
- Postoperative pain or shoulder tip discomfort
Benefits:
- Minimally invasive with faster recovery
- Reduced hospital stay and lower overall complications
- Effective for both diagnosis and treatment
- Improved cosmetic outcomes with smaller scars
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Often outpatient or 1 day for minor procedures
- Full recovery: Typically 1–2 weeks depending on procedure type
- Long-term outlook: Most patients experience complete recovery and minimal scarring
- Follow-up: Required to monitor incision sites and ensure proper healing
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Follow postoperative instructions carefully
- ✅ Resume activities gradually
- ✅ Monitor incision for redness, swelling, or discharge
- ✅ Attend all scheduled follow-up visits
When To Call the Doctor
- Fever, persistent abdominal pain, or vomiting
- Redness, swelling, or discharge at incision sites
- Unusual bleeding or inability to urinate
- Severe pain not relieved by prescribed medications
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea offers advanced laparoscopic care across multiple specialties:
- Top hospitals: Skilled surgeons with modern laparoscopic equipment
- Advanced diagnostics: Ultrasound, CT, MRI for accurate planning
- Surgical options: Diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy
- Postoperative care: Short hospital stay, pain management, and early mobilization
- International patient support: Online consultations, hospital appointments, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Online consultation and review of tests
- Preoperative evaluation and preparation
- Laparoscopy performed using minimally invasive techniques
- Postoperative monitoring and early mobilization
- Follow-up via telemedicine or in-person visits