Overview
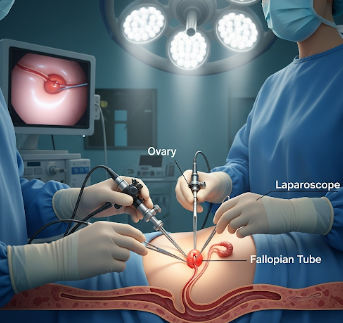
Laparoscopic Oophorectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove one or both ovaries. This procedure is typically performed to treat ovarian cysts, tumors, endometriosis, or as a preventive measure in women at high risk for ovarian cancer.
In Korea, laparoscopic oophorectomy is performed by highly skilled gynecologic surgeons using advanced laparoscopic techniques, which reduce pain, minimize scarring, and shorten recovery time.
Highlights:
- ✅ Removal of one or both ovaries for medical or preventive reasons
- ✅ Minimally invasive with shorter recovery than open surgery
- ✅ Reduces risk of ovarian-related complications or malignancy
What is Laparoscopic Oophorectomy?
Laparoscopic Oophorectomy involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The ovary (or ovaries) is then carefully removed, often with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues.
Indications include:
- Ovarian cysts or benign tumors
- Ovarian cancer or suspected malignancy
- Endometriosis affecting the ovaries
- Prophylactic surgery in high-risk patients (e.g., BRCA mutation carriers)
Important: Laparoscopic oophorectomy is generally preferred over open surgery due to smaller incisions, faster recovery, and lower complication rates.
What are the benefits?
- Minimally invasive: Smaller incisions, reduced pain, and faster recovery
- Reduced risk of complications: Less blood loss and lower infection rates
- Preservation of surrounding tissues: Less trauma to nearby reproductive structures
- Preventive or therapeutic outcomes: Treats ovarian disease or reduces cancer risk
Key benefits highlighted:
- ⚡ Shorter hospital stay compared to open surgery
- ⚡ Lower postoperative pain and faster return to daily activities
- ⚡ Minimal scarring for improved cosmetic results
- ⚡ Safe and effective for both benign and malignant conditions
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Laparoscopic Oophorectomy?
- Preoperative evaluation: Ultrasound, MRI, blood tests, and pelvic examination
- Medication review: Stop blood thinners or other medications as instructed
- Fasting: Typically 6–8 hours before surgery
- Consent and education: Discuss procedure, risks, fertility implications, and recovery
- Lifestyle preparation: Maintain optimal nutrition and avoid smoking for better healing
2) What happens during Laparoscopic Oophorectomy?
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia administered
- Incision and port placement: 2–4 small incisions made in the abdomen
- Ovary removal: Laparoscope and instruments used to detach and remove the ovary(ies)
- Inspection and hemostasis: Surrounding tissues inspected and bleeding controlled
- Closure: Incisions closed with sutures or adhesive strips; laparoscopic ports removed
Duration: Typically 1–2 hours depending on complexity and whether one or both ovaries are removed
3) What happens after Laparoscopic Oophorectomy?
- Recovery monitoring: Vital signs and abdominal site observed in the hospital
- Pain management: Oral analgesics for mild discomfort
- Activity: Gradual return to normal activities; avoid heavy lifting for several weeks
- Follow-up care: Monitor incision healing, hormone changes, and overall recovery
Highlights for post-procedure care:
- ⚡ Mild abdominal pain, bloating, or shoulder tip pain may occur
- ⚡ Avoid strenuous exercise or heavy lifting for 2–4 weeks
- ⚡ Monitor for signs of infection, bleeding, or unusual discharge
- ⚡ Attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and address any hormonal concerns
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Infection or bleeding
- Injury to surrounding structures (bladder, bowel, blood vessels)
- Hormonal changes if both ovaries are removed
- Rare anesthesia-related complications
Benefits:
- Minimally invasive with faster recovery
- Effective treatment or prevention of ovarian disease
- Reduced risk of ovarian cancer in high-risk patients
- Low complication rates when performed by experienced surgeons
Recovery and Outlook
- Hospital stay: Usually outpatient or 1 day depending on complexity
- Full recovery: 2–4 weeks for most patients; mild discomfort may persist
- Long-term outlook: Excellent for treating ovarian pathology or reducing cancer risk
- Follow-up: Regular postoperative visits to monitor incision, recovery, and hormonal status
Tips for optimal recovery:
- ✅ Follow all postoperative instructions carefully
- ✅ Maintain hydration, balanced nutrition, and gentle activity
- ✅ Report any abnormal bleeding, fever, or severe pain immediately
- ✅ Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing and hormone levels
When To Call the Doctor
- Fever, chills, or signs of infection
- Excessive bleeding or unusual discharge
- Severe abdominal pain not relieved by medications
- Dizziness, fainting, or other concerning symptoms
Best Korea Option / Process
Korea provides advanced laparoscopic oophorectomy care:
- Top hospitals: Specialized gynecologic surgery centers with expert surgeons
- Advanced diagnostics: Ultrasound, MRI, and blood tests for preoperative planning
- Minimally invasive techniques: Laparoscopic approach for smaller incisions, faster recovery, and reduced pain
- Postoperative care: Pain management, activity guidance, and follow-up monitoring
- International patient support: Online consultations, appointment scheduling, and telemedicine follow-up
Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Online consultation and preoperative evaluation
- Pre-surgery preparation and fasting instructions
- Laparoscopic oophorectomy performed by experienced gynecologic surgeons
- Postoperative monitoring, pain management, and activity guidance
- Follow-up visits to ensure healing, monitor hormone levels, and assess recovery