Overview
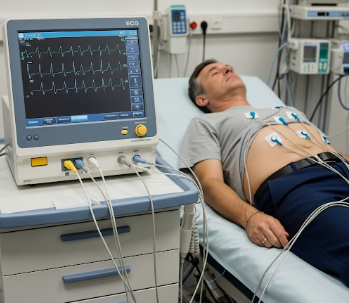
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, non-invasive test used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. It is one of the most common diagnostic tools in cardiology, helping detect heart rhythm disorders, heart attacks, and other cardiac conditions.
In South Korea, ECG tests are widely available at hospitals, clinics, and specialized cardiac centers. With advanced medical equipment and skilled cardiologists, Korea ensures accurate readings and timely interpretations for both locals and international patients.
What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
An ECG records the electrical impulses that trigger heartbeats. Sensors called electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs to measure heart rate, rhythm, and electrical conduction.
It is typically used to:
- Detect arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat)
- Identify heart attacks or ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart)
- Monitor heart conditions in high-risk patients
- Evaluate the effectiveness of heart medications
- Assist in preoperative assessments before surgery
The procedure is quick, painless, and does not involve radiation, making it safe for patients of all ages.
What are the benefits?
An ECG provides multiple advantages:
- Non-invasive and painless → no needles or surgery required
- ➤ Quick results → typically available within minutes
- ➤ Early detection of heart problems → prevents serious complications
- ➤ Guides treatment plans for conditions like arrhythmias or coronary artery disease
- ➤ Monitors ongoing heart health for chronic patients
- ➤ Widely available in Korea with advanced machines ensuring precise readings
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
Preparation is minimal, making it convenient for patients:
- Clothing → wear loose clothing or a two-piece outfit for easy electrode placement.
- Avoid lotions or oils → they can interfere with electrode contact.
- Inform your doctor → mention any medications or conditions that may affect heart rate.
- Relaxation → stay calm, as stress can alter heart rhythm during the test.
- No fasting required → patients can eat or drink normally.
2) What happens during the procedure Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
The test is simple and typically takes 5–10 minutes:
- Electrode placement → small sticky pads are attached to the chest, arms, and legs.
- Connection to ECG machine → electrodes transmit electrical signals to a monitor.
- Recording → the machine prints a graph showing the heart’s electrical activity.
- Breathing instructions → patients are asked to remain still and breathe normally during the recording.
- Completion → electrodes are removed, and the printout is given to the doctor for analysis.
In Korea, ECGs are performed using modern digital machines, often linked to electronic medical records for quick expert review.
3) What happens after an Electrocardiogram (ECG)?
- Immediate results → the cardiologist interprets the reading and explains findings.
- Follow-up tests → if abnormalities are detected, additional tests like echocardiogram, stress test, or Holter monitoring may be recommended.
- No restrictions → patients can resume normal activities immediately.
- Documentation → ECG records are stored for future reference or routine monitoring.
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Very minimal; some patients may experience mild skin irritation from electrodes.
- Rarely, anxiety from test results can cause temporary stress.
Benefits:
- Early detection of heart disease → reduces risk of severe cardiac events
- ➤ Non-invasive, safe, and painless for all ages
- ➤ Quick and reliable diagnosis for arrhythmias, heart attacks, and conduction problems
- ➤ Easily repeatable for ongoing monitoring without harm
Recovery and Outlook
- No recovery time needed → ECG is non-invasive, and patients can immediately return to daily activities.
- Regular monitoring → for patients with chronic heart disease, routine ECGs help track heart health.
- Long-term benefits → early detection enables timely interventions, improving overall heart outcomes.
In Korea, ECG results are often integrated with advanced cardiac monitoring systems, providing accurate and actionable insights for doctors and patients alike.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if ECG results indicate:
- Abnormal heart rhythms or skipped beats
- ➤ Chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath
- ➤ Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- ➤ Other symptoms suggesting a heart problem
Prompt evaluation is essential for preventing serious cardiac complications.
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is renowned for state-of-the-art cardiac care, offering:
- Advanced ECG machines with high precision and digital reporting
- Expert cardiologists trained in diagnosing complex arrhythmias
- Comprehensive heart check-up packages, combining ECG with echocardiography, blood tests, and stress tests
- Quick, same-day results for patients seeking efficient care
- Personalized follow-up plans for chronic or high-risk patients
Patients choosing Korea for ECG can expect accurate diagnostics, minimal waiting times, and expert care, making it one of the best countries globally for cardiac evaluation.