Overview
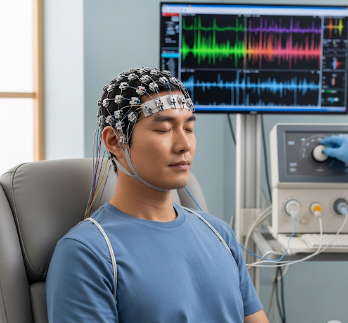
An Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that records the electrical activity of the brain. It is widely used to detect neurological disorders, monitor brain function, and assist in treatment planning for conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, brain injuries, and certain psychiatric disorders.
In South Korea, EEG is offered in top hospitals and specialized neurology centers, using state-of-the-art digital equipment. Korean medical facilities provide accurate interpretations and patient-friendly procedures, making EEG a safe and reliable diagnostic tool for both local and international patients.
What is an Electroencephalogram (EEG)?
An EEG measures the electrical signals produced by brain neurons. During the test, electrodes are attached to the scalp to record brain waves, which are displayed as a graph or digital recording.
EEG is commonly used to:
- Detect epileptic seizures and abnormal brain activity
- Diagnose sleep disorders like narcolepsy or insomnia
- Monitor brain function after head injuries or surgeries
- Evaluate cognitive disorders or degenerative neurological conditions
- Guide treatment planning for psychiatric and neurological diseases
This test is safe, painless, and non-invasive, making it suitable for adults, children, and even infants.
What are the benefits?
EEG offers numerous advantages for patients and clinicians:
- Non-invasive and painless → no needles or surgery required
- ➤ Quick assessment of brain function → usually completed within 30–60 minutes
- ➤ Early detection of neurological disorders → helps prevent severe complications
- ➤ Guides treatment decisions → particularly for epilepsy or seizure management
- ➤ Monitors disease progression in patients with chronic neurological conditions
- ➤ Widely available in Korea with digital EEG systems providing precise and reliable results
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Electroencephalogram (EEG)?
Preparation is simple and focuses on ensuring accurate recordings:
- Clean hair → wash hair the night before; avoid oils or hair products.
- Medication review → inform your doctor of medications, especially sedatives or anticonvulsants.
- Sleep instructions → some EEGs may require partial sleep deprivation.
- Diet and caffeine → avoid excessive caffeine, as it can affect brain activity.
- Relaxation → stay calm, as anxiety may influence results.
2) What happens during the procedure Electroencephalogram (EEG)?
EEG is non-invasive and usually takes 30–60 minutes:
- Electrode placement → small electrodes or a cap with sensors is attached to the scalp.
- Connection to EEG machine → electrodes detect brain electrical activity.
- Recording → brain waves are recorded as patients rest quietly; occasionally, patients may be asked to open/close eyes or perform specific tasks.
- Stimulation tests → light flashes (photostimulation) or deep breathing (hyperventilation) may be used to trigger brain responses.
- Completion → electrodes are removed, and data is sent to a neurologist for analysis.
In Korea, EEG is often performed with digital and high-resolution machines, ensuring precise detection of even subtle abnormalities.
3) What happens after an Electroencephalogram (EEG)?
- Immediate feedback → preliminary results may be shared quickly, while full interpretation may take a few days.
- No restrictions → patients can resume normal activities immediately.
- Follow-up → additional testing or treatment plans may be recommended based on results.
- Record storage → EEG recordings are stored digitally for future comparison and monitoring.
Risks / Benefits
Risks:
- Very minimal; some patients may experience mild scalp irritation from electrode adhesive.
- Rarely, epileptic patients may experience a seizure during the test.
Benefits:
- Early detection of brain abnormalities → critical for timely interventions
- ➤ Non-invasive, safe, and painless
- ➤ Supports accurate diagnosis for epilepsy, sleep disorders, and cognitive issues
- ➤ Monitors treatment effectiveness over time
- ➤ Easily repeatable for long-term follow-up
Recovery and Outlook
- No recovery required → EEG is non-invasive, allowing patients to return to normal activities immediately.
- Monitoring → patients with chronic neurological conditions benefit from periodic EEGs to track changes in brain activity.
- Long-term prognosis → early detection and ongoing monitoring improve management and quality of life.
In Korea, patients benefit from highly trained neurologists and advanced EEG technology, ensuring accurate diagnosis and optimal outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- Abnormal EEG results indicate unusual brain activity
- ➤ Seizures occur during or after the test
- ➤ Persistent headaches or neurological symptoms worsen
- ➤ Sleep disturbances or cognitive issues continue despite treatment
Prompt consultation ensures early intervention and better management of neurological conditions.
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides world-class neurological diagnostic care:
- Advanced digital EEG machines → high precision and rapid interpretation
- Expert neurologists with specialization in epilepsy, sleep, and cognitive disorders
- Comprehensive testing packages → EEG combined with MRI or other neurodiagnostic tools
- Quick results and follow-up care → integrated with hospital electronic systems
- Patient-friendly environment → international support for non-Korean patients
Patients choosing Korea for EEG can expect accurate diagnostics, efficient service, and expert follow-up, making it an excellent option for brain health evaluation.