Overview
External cardioversion is a medical procedure used to restore a normal heart rhythm in patients with certain types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias), such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, or supraventricular tachycardia. Unlike internal procedures, external cardioversion uses controlled electrical shocks delivered through the chest wall to reset the heart’s electrical activity.
In South Korea, external cardioversion is performed in advanced cardiology centers and hospitals, with state-of-the-art defibrillators, cardiac monitoring, and expert cardiologists. The procedure is safe, highly effective, and widely used to manage arrhythmias that do not respond to medication.
What is External Cardioversion?
External cardioversion is a non-invasive procedure that delivers a precise electrical shock to the heart through the chest, synchronized with the heart’s rhythm. This resets abnormal electrical signals, allowing the heart to regain a normal rhythm.
It is typically recommended for:
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib) → irregular and often rapid heart rhythm
- Atrial flutter → rapid but regular atrial contractions
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) → abnormally fast heartbeat originating above the ventricles
- Patients not responding to medications or requiring urgent rhythm correction
The procedure is quick, effective, and can be performed on an outpatient basis in many cases.
What are the benefits?
External cardioversion offers multiple advantages:
- Restores normal heart rhythm → reduces symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, or shortness of breath
- ➤ Non-invasive procedure → performed through the chest wall without surgery
- ➤ Rapid symptom relief → heart rhythm correction occurs immediately in most cases
- ➤ Can prevent complications → reduces risk of stroke or heart failure associated with prolonged arrhythmia
- ➤ High success rates in Korea → performed by expert cardiologists with advanced monitoring
- ➤ Minimal recovery time → many patients resume normal activities shortly after the procedure
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for External Cardioversion?
Proper preparation is essential for safety and effectiveness:
- Medical evaluation → ECG, echocardiogram, blood tests, and review of medications
- Medication adjustment → anticoagulants may be prescribed to reduce stroke risk; some medications may need temporary cessation
- Fasting → typically no food or drink for 4–6 hours before the procedure
- Consent and explanation → discussion of procedure, benefits, risks, and sedation plan
- Pre-procedure monitoring → vital signs and baseline cardiac rhythm
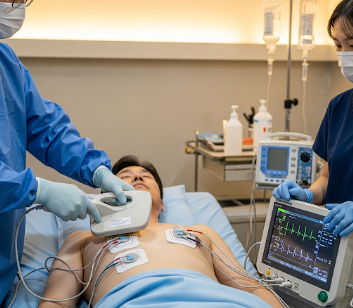
2) What happens during the procedure External Cardioversion?
The procedure usually takes 20–30 minutes:
- Sedation → light sedation or anesthesia is administered to minimize discomfort
- Electrode placement → pads are placed on the chest (and sometimes back) for shock delivery
- Synchronization → shock is synchronized with the R wave of the ECG to reduce the risk of ventricular arrhythmias
- Electrical shock delivery → one or more controlled shocks may be administered
- Monitoring → heart rhythm is continuously monitored, and additional shocks may be applied if needed
- Immediate evaluation → ECG confirms restoration of normal rhythm
In Korea, cardiologists use advanced defibrillators and continuous monitoring to ensure maximum safety and efficacy.
3) What happens after an External Cardioversion?
- Immediate monitoring → patients are observed for heart rhythm stability, blood pressure, and oxygen levels
- Recovery from sedation → patients typically regain full consciousness within 30–60 minutes
- Short-term care → monitor for dizziness, palpitations, or minor chest discomfort
- Medication adjustment → anticoagulants and antiarrhythmics may be continued or adjusted
- Follow-up → regular ECGs and cardiology visits to maintain normal rhythm
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- Temporary skin irritation or minor burns at electrode sites
- Mild chest discomfort or soreness
- Arrhythmia recurrence → sometimes multiple cardioversion attempts are needed
- Rare complications → stroke, heart attack, or adverse reaction to sedation
Key Benefits:
- Rapid correction of abnormal heart rhythm
- ➤ Non-invasive and highly effective
- ➤ Reduces risk of arrhythmia-related complications
- ➤ High success rates when performed in Korean cardiology centers
- ➤ Minimal downtime and quick recovery
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate recovery → most patients can sit up and walk shortly after sedation wears off
- Short-term monitoring → observe for arrhythmia recurrence or post-procedure dizziness
- Long-term management → antiarrhythmic medications and lifestyle modifications may be recommended
- Success rate → 70–90% for atrial flutter; slightly lower for long-standing AFib
- In Korea, patients benefit from expert follow-up, comprehensive cardiac care, and advanced monitoring, ensuring safe long-term outcomes
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Recurrent palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- ➤ Chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting
- ➤ Severe dizziness or prolonged weakness
- ➤ Signs of stroke → sudden numbness, difficulty speaking, or facial droop
- ➤ Any unusual symptoms post-procedure
Timely evaluation ensures safe recovery and effective rhythm management.
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class external cardioversion services:
- Expert cardiologists → skilled in arrhythmia management and synchronized cardioversion
- Advanced defibrillators and monitoring → high precision for safe rhythm restoration
- Comprehensive care → pre-procedure evaluation, cardioversion, and post-procedure follow-up
- Minimally invasive approach → outpatient or short hospital stay
- International patient support → multilingual staff, appointment scheduling, and personalized cardiac care
Patients choosing Korea for external cardioversion can expect safe, effective, and rapid correction of arrhythmias, making it a top destination for cardiac procedures in Asia.