Overview
Diabetes screening tests are diagnostic procedures used to detect diabetes or prediabetes early, allowing for timely intervention and management. Early detection helps prevent complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and vision problems.
In South Korea, diabetes screening is offered in advanced hospitals and clinics using state-of-the-art laboratory equipment and international-standard protocols, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
What are Diabetes Screening Tests?
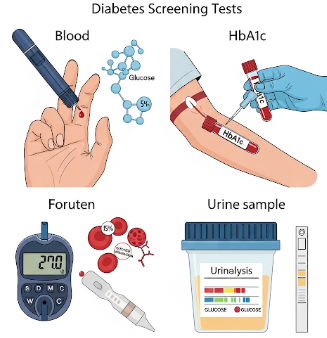
Diabetes screening involves blood tests that measure glucose levels or the body’s response to glucose. These tests help identify elevated blood sugar levels before symptoms appear.
Common Diabetes Screening Tests:
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG): Measures blood sugar after 8–12 hours of fasting
- HbA1c Test: Assesses average blood sugar levels over 2–3 months
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Measures blood sugar before and after consuming a glucose drink
- Random Blood Glucose Test: Measures blood sugar at any time of the day
Purpose:
- Detect diabetes and prediabetes early
- Assess risk factors such as obesity, family history, and lifestyle
- Monitor blood sugar levels for patients with risk factors
- Guide timely intervention and management strategies
What are the Benefits?
Diabetes screening tests provide several preventive and health management benefits:
✔ Early detection of diabetes or prediabetes.
✔ Reduces risk of long-term complications like heart disease and kidney failure.
✔ Allows timely lifestyle modifications and treatment.
✔ Supports effective monitoring and management of at-risk individuals.
✔ Improves overall health outcomes and quality of life.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Diabetes Screening Tests?
- Fasting tests: Avoid food and drinks (except water) for 8–12 hours before the test
- Medication review: Inform your doctor about medications that may affect blood sugar
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water before the test
- Medical history: Share personal and family history of diabetes, obesity, or metabolic disorders
Korean hospitals provide clear patient instructions and pre-test guidance to ensure accurate results.
2) What happens during Diabetes Screening Tests?
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG): Blood drawn from a vein after overnight fasting
- HbA1c Test: Blood sample collected to assess long-term glucose control
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
- Blood sample collected fasting
- Drink containing glucose consumed
- Blood samples collected at intervals to measure glucose response
- Random Blood Glucose Test: Single blood sample taken at any time
Duration:
- FBG and HbA1c: 5–10 minutes
- OGTT: 2–3 hours
Advanced Korean clinics use automated analyzers, precision lab equipment, and standardized protocols for highly accurate results.
3) What happens after Diabetes Screening Tests?
- Immediate: Normal daily activities can usually resume
- Results: Lab reports indicate normal, prediabetic, or diabetic ranges
- Follow-up: Additional testing or referral to an endocrinologist may be recommended
- Management: Lifestyle modification, medications, or further monitoring based on results
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Mild discomfort or bruising at blood draw site
- ➤ Rare fainting or dizziness during blood draw
- ➤ False-positive or false-negative results (rare, usually corrected with repeat testing)
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Detects diabetes early, even before symptoms appear
- ✔ Prevents long-term complications through timely intervention
- ✔ Provides accurate data for personalized management
- ✔ Supports lifestyle changes and medical treatment planning
- ✔ Improves long-term health outcomes
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: Minimal to no recovery time; normal activities can resume
- Short-term: Follow-up appointments may be needed for confirmatory tests
- Long-term: Regular diabetes screening is recommended for high-risk individuals
- Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, and regular monitoring help maintain healthy blood sugar levels
South Korean clinics provide structured follow-up programs, counseling, and patient education for optimal diabetes management.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your doctor if you notice:
- ➤ Elevated blood sugar readings on repeat tests
- ➤ Symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, or unexplained weight loss
- ➤ Persistent fatigue or blurred vision
- ➤ Signs of complications in known diabetic patients
- ➤ Uncertainty regarding test results or management
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea offers world-class diabetes screening services due to:
- Experienced endocrinologists and laboratory specialists
- Advanced laboratory equipment and standardized protocols
- Comprehensive pre-test instructions and patient guidance
- Integration with preventive health programs for at-risk patients
- International patient support including scheduling, reporting, and follow-up
- High accuracy and early detection rates
Top hospitals and clinics for Diabetes Screening Tests in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – Endocrinology & Laboratory Diagnostics
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – Advanced Diabetes Screening Clinic
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System) – Diabetes & Metabolism Center
- Seoul National University Hospital – Endocrinology and Laboratory Medicine