Overview
The COVID-19 vaccine is a critical medical intervention designed to protect against the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19. Vaccination reduces the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death, while also helping communities achieve herd immunity.
In South Korea, COVID-19 vaccination programs have been widely implemented in hospitals, clinics, and public health centers, utilizing approved vaccines with stringent safety monitoring. The Korean healthcare system emphasizes timely administration, follow-up doses, and monitoring for adverse reactions to ensure population-wide protection.
What is the COVID-19 Vaccine?
The COVID-19 vaccine is a biological preparation that stimulates the immune system to recognize and fight SARS-CoV-2. There are several types of COVID-19 vaccines, including:
- mRNA vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna): Deliver genetic instructions to produce the spike protein, triggering an immune response.
- Viral vector vaccines (AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson): Use a harmless virus to deliver the spike protein gene.
- Protein subunit vaccines: Contain harmless pieces of the virus to stimulate immunity.
- Inactivated virus vaccines: Contain killed virus particles to provoke an immune response.
Purpose:
- Protect against COVID-19 infection and severe disease
- Reduce virus transmission in communities
- Prevent hospitalization and reduce healthcare burden
- Promote safe reopening of society and economies
Indications:
- Recommended for adults and children based on age-specific approvals
- Particularly important for elderly individuals, healthcare workers, and people with underlying conditions
What are the Benefits?
The COVID-19 vaccine provides multiple protective and societal benefits:
✔ Reduces risk of infection and severe COVID-19.
✔ Minimizes hospitalization and intensive care requirements.
✔ Protects vulnerable populations and reduces virus transmission.
✔ Supports global efforts to control the pandemic.
✔ Safe, effective, and scientifically proven through large-scale clinical trials.
✔ Boosters enhance immunity against emerging variants.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for the COVID-19 Vaccine?
- Medical evaluation: Discuss allergies, chronic conditions, or previous reactions to vaccines.
- Pre-vaccination health: Ensure no current fever or acute illness.
- Documentation: Bring identification and vaccination card if receiving a booster.
- Medication guidance: Continue regular medications unless instructed otherwise.
- Education: Learn about possible side effects and what to expect post-vaccination.
South Korean healthcare centers provide efficient pre-vaccination assessment to ensure safety and smooth administration.
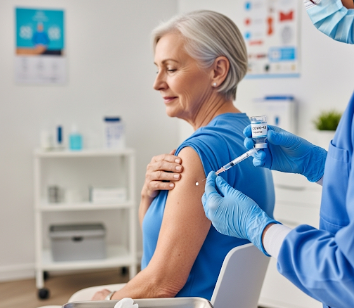
2) What happens during the COVID-19 Vaccine administration?
- Site preparation: Upper arm (deltoid muscle) is cleaned with antiseptic.
- Vaccine injection: Single or multiple doses administered depending on vaccine type and schedule.
- Observation: 15–30 minutes post-vaccination monitoring for any immediate adverse reactions.
- Documentation: Vaccination is recorded in the national registry for follow-up and boosters.
- Duration: The injection itself takes less than a minute, with total observation about 30 minutes.
South Korean clinics emphasize safe, rapid, and monitored vaccine administration, with trained healthcare staff present.
3) What happens after COVID-19 vaccination?
- Common side effects: Mild pain at injection site, fatigue, headache, low-grade fever.
- Self-care: Over-the-counter pain relievers, hydration, and rest if needed.
- When to seek medical attention: Severe allergic reactions, high fever, or prolonged symptoms.
- Follow-up doses: Some vaccines require 2-dose or booster schedules for full protection.
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Mild pain, redness, or swelling at injection site
- ➤ Fatigue, headache, or mild fever
- ➤ Rare allergic reactions (anaphylaxis)
- ➤ Very rare myocarditis or blood clot events (vaccine-specific)
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Highly effective in preventing severe COVID-19 illness
- ✔ Reduces hospitalization and ICU admissions
- ✔ Minimizes virus spread in communities
- ✔ Safe for most age groups and comorbidities
- ✔ Supports long-term pandemic control and public health
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate: Most side effects resolve within 1–3 days.
- Short-term: Immunity typically develops 2–4 weeks after each dose.
- Long-term: Full vaccination plus boosters provide sustained protection, especially against severe disease.
- Public health impact: Widespread vaccination contributes to community immunity, reduced mortality, and fewer pandemic restrictions.
South Korea’s vaccination program ensures comprehensive follow-up, booster schedules, and variant-specific updates for ongoing protection.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact a healthcare provider if:
- ➤ Severe allergic reaction (difficulty breathing, swelling, hives)
- ➤ High fever or persistent fatigue beyond a few days
- ➤ Chest pain, shortness of breath, or abnormal heart symptoms
- ➤ Signs of unusual blood clotting (leg swelling, severe headache)
- ➤ Any concerning or prolonged side effect post-vaccination
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea provides world-class COVID-19 vaccination services due to:
- Nationwide vaccination centers and hospital clinics
- Trained healthcare staff and strict safety protocols
- Comprehensive digital registration, scheduling, and follow-up system
- Approved vaccines with high efficacy and safety monitoring
- Public awareness programs and international patient guidance
Top centers for COVID-19 vaccination in Korea:
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul
- Regional public health centers across Korea