Overview
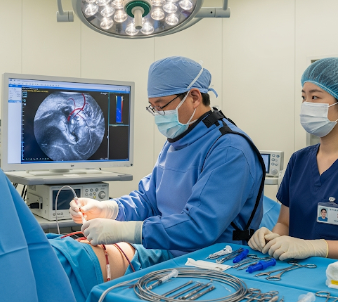
Cardiac catheterisation is a medical procedure that allows doctors to diagnose and treat certain heart conditions by inserting a thin, flexible tube (catheter) into the heart or its blood vessels. This minimally invasive procedure helps evaluate blood flow, heart function, and the presence of blockages.
In South Korea, cardiac catheterisation is performed in state-of-the-art cardiac centers with advanced imaging technology, robotic-assisted tools, and highly skilled cardiologists. It is a critical diagnostic and therapeutic procedure for conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart valve problems, and congenital heart defects.
What is Cardiac Catheterisation?
Cardiac catheterisation involves inserting a catheter through a blood vessel in the arm, wrist, or groin and guiding it into the heart.
Types of cardiac catheterisation include:
- Diagnostic catheterisation: Measures heart pressure, blood flow, and oxygen levels.
- Interventional catheterisation: Includes angioplasty or stent placement to open blocked arteries.
- Electrophysiological studies: Evaluates electrical activity in the heart to treat arrhythmias.
The procedure provides direct visualization of the heart and coronary arteries, allowing precise diagnosis and treatment.
What are the Benefits?
Cardiac catheterisation provides several life-saving and diagnostic advantages:
✔ Accurate assessment of coronary artery disease and heart function.
✔ Minimally invasive treatment of blockages with angioplasty and stenting.
✔ Early detection of heart valve or structural heart problems.
✔ Guides treatment planning for medications or surgery.
✔ Short recovery time compared to open-heart surgery.
✔ In South Korea, advanced imaging and robotic assistance enhance safety and outcomes.
Procedure Details
1) How should I prepare for Cardiac Catheterisation?
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests, ECG, chest X-ray, and imaging studies.
- Medication review: Inform your doctor about blood thinners or other heart medications.
- Fasting: Usually 6–8 hours before the procedure.
- Hydration: Drink water unless instructed otherwise.
- Arrange transportation: Sedation is often used, so driving afterward is not advised.
Korean hospitals provide digital pre-procedure instructions and personalized consultation for international patients.
2) What happens during the procedure Cardiac Catheterisation?
- The patient is given local anesthesia and sometimes mild sedation.
- A catheter is inserted through an artery in the wrist, arm, or groin.
- Using fluoroscopy (live X-ray imaging), the catheter is guided to the heart.
- Contrast dye may be injected to visualize arteries and chambers.
- Diagnostic measurements are taken, or interventions like balloon angioplasty or stent placement may be performed.
- The procedure typically lasts 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on complexity.
Korean cardiac centers often use high-resolution imaging and robotic guidance for precision and reduced complication rates.
3) What happens after a Cardiac Catheterisation?
- Patients are monitored in a recovery area for several hours.
- Pressure dressing or compression device is applied at the catheter site to prevent bleeding.
- Mild bruising or soreness at the insertion site is common.
- Most patients resume light activities within a day and normal activities within a week.
- Follow-up consultations ensure proper healing and review results.
South Korean hospitals provide post-procedure care packages, including nursing support, medication guidance, and follow-up imaging.
Risks / Benefits
Potential Risks:
- ➤ Bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site
- ➤ Infection (rare with sterile technique)
- ➤ Arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat
- ➤ Allergic reaction to contrast dye
- ➤ Very rarely, heart attack or stroke
Major Benefits:
- ✔ Accurate diagnosis and assessment of heart conditions
- ✔ Minimally invasive treatment options for blocked arteries
- ✔ Early detection of heart disease and preventive care
- ✔ Shorter recovery compared to open-heart procedures
- ✔ Advanced Korean cardiac centers ensure high safety and success rates
Recovery and Outlook
- Immediate recovery: Patients may need to lie flat for several hours to prevent bleeding.
- 1–2 days: Most can resume normal daily activities.
- 1–2 weeks: Avoid strenuous exercise or lifting heavy objects.
- Long-term outlook: Enables better management of heart disease and reduces the risk of heart attack or other complications.
In South Korea, patients benefit from expert cardiologists, advanced imaging, and comprehensive follow-up care, resulting in excellent long-term outcomes.
When To Call the Doctor
Contact your cardiologist immediately if you experience:
- ➤ Severe bleeding or swelling at the catheter site
- ➤ Chest pain or pressure
- ➤ Shortness of breath or dizziness
- ➤ Fever or signs of infection
- ➤ Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
Best Korea Option / Process
South Korea is recognized as a world leader in cardiac care, offering:
- High-tech cardiac catheterization labs with robotic-assisted systems
- Multidisciplinary teams including interventional cardiologists, anesthesiologists, and nurses
- Rapid, accurate diagnostics and treatment for coronary artery disease and structural heart issues
- Comprehensive care for international patients, including translation, accommodation, and follow-up services
- Affordable treatment packages without compromising quality
Top hospitals for cardiac catheterisation in Korea include:
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul
- Samsung Medical Center
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System)