Overview
Smelly urine is a condition where urine has a strong, unusual, or foul odor. While occasional changes in urine smell can occur due to diet or dehydration, persistent or severe odor may indicate an underlying medical condition.
➤ Urine odor can vary from ammonia-like, sweet, or pungent depending on causes.
➤ Common triggers include diet, medications, infections, and metabolic disorders.
➤ In Korea, advanced urology and nephrology centers provide diagnostics and treatment to identify the root cause and manage symptoms effectively.
Key Facts
► Definition: Urine with an unusual, strong, or offensive smell.
► Prevalence: Common; often temporary but sometimes chronic.
► Associated symptoms: Discoloration, burning sensation, pain, frequency, or other urinary symptoms.
► Risk factors: Dehydration, UTIs, diabetes (diabetes mellitus), liver disease, diet rich in certain foods (asparagus, coffee).
► Treatment in Korea: Depends on the underlying cause, from hydration and dietary advice to antibiotics or advanced metabolic management.
What is Smelly Urine?
Smelly urine is a symptom indicating changes in urine composition caused by dietary components, metabolic byproducts, infections, or systemic conditions.
➔ The smell may be transient or persistent, depending on the underlying factor.
➔ Persistent or foul-smelling urine may indicate urinary tract infection, kidney disease, or metabolic disorders.
➔ Detection of associated symptoms such as pain, frequency, or color changes helps in diagnosis.
What Symptoms Are Related to Smelly Urine?
Smelly urine may occur alongside other symptoms, helping identify the cause:
→ Cloudy or discolored urine, suggesting infection or kidney disease.
→ Pain or burning during urination (dysuria), typical in urinary tract infections.
→ Frequent urination or urgency.
→ Fever or malaise, indicating infection.
→ Sweet or fruity smell, potentially linked to uncontrolled diabetes (ketonuria).
→ Foamy urine, possibly related to proteinuria or kidney issues.
→ Abdominal or flank pain, which may indicate kidney stones or infection.
Causes / Possible Causes of Smelly Urine
Dietary Causes
➤ Certain foods such as asparagus, coffee, garlic, or onions can temporarily alter urine odor.
➤ Dehydration concentrates urine, making it smell stronger.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
➔ Bacterial growth in the bladder or urethra produces ammonia-like or foul odors.
➔ Often accompanied by burning, frequency, and urgency.
Metabolic and Systemic Conditions
→ Diabetes mellitus can cause a sweet or fruity urine smell due to ketones.
→ Liver disease or jaundice may alter urine odor and color.
→ Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is a rare inherited metabolic disorder causing sweet-smelling urine in children.
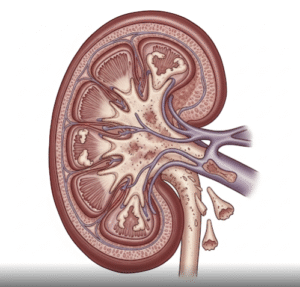
Kidney and Bladder Conditions
► Kidney stones or obstruction can produce strong or unusual odors.
► Proteinuria may cause foamy and foul-smelling urine.
Medications and Supplements
➤ Antibiotics, vitamins, and certain medications can change urine smell.
➤ Sulfa drugs, in particular, may produce a distinct odor.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Medical attention is needed if smelly urine is accompanied by:
➤ Pain, burning, or difficulty urinating.
➤ Fever, chills, or general malaise, suggesting infection.
➤ Persistent foul-smelling or unusually colored urine without obvious dietary cause.
➤ Unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or swelling, indicating kidney or systemic disease.
➤ Symptoms in children, as rare metabolic conditions can have serious implications.
Early consultation allows accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, preventing complications such as kidney damage or systemic infection.
Care and Treatment
Self-Care and Home Measures
► Drink adequate water to dilute urine and reduce odor.
► Adjust diet by limiting strong-smelling foods temporarily.
► Maintain good personal hygiene.
► Monitor urine for color, frequency, and odor changes to provide useful information to your doctor.
Medical Treatments
➔ Antibiotics for urinary tract infections.
➔ Blood sugar control in diabetic patients to reduce ketonuria and sweet-smelling urine.
➔ Treatment of kidney or bladder conditions, including stones, obstruction, or metabolic disorders.
➔ Adjustment of medications that may alter urine odor.
Advanced and Specialized Care
→ Metabolic testing for inherited disorders like MSUD in children.
→ Imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan) for kidney or bladder abnormalities.
→ Dietary counseling for chronic metabolic or kidney conditions.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers state-of-the-art urology, nephrology, and metabolic care, ensuring effective management of smelly urine:
Diagnosis in Korea
➤ Urinalysis, urine culture, and blood tests to detect infection, diabetes, or kidney dysfunction.
➤ Imaging: Ultrasound, CT, or MRI for structural abnormalities.
➤ Metabolic and genetic testing for inherited conditions.
Non-Surgical Care
► Hydration and dietary management tailored to patient needs.
► Medications for infections, diabetes, or kidney-related disorders.
► Regular monitoring of kidney function and urine composition.
Surgical & Advanced Interventions
➔ Treatment of kidney stones or bladder obstruction if needed.
➔ Endoscopic or minimally invasive procedures for structural abnormalities.
Rehabilitation and Lifestyle Support
→ Education on hydration, diet, and hygiene.
→ Monitoring of chronic conditions to prevent recurrence.
→ Integration of nephrology, urology, and nutrition care for holistic treatment.
Korean medical centers combine cutting-edge diagnostics, expert physicians, and patient-centered care, making them ideal for managing persistent smelly urine.