➤ Overview
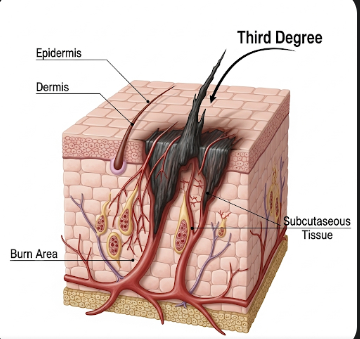
A third-degree burn, also known as a full-thickness burn, is a severe burn injury that destroys all layers of the skin, including the epidermis, dermis, and often underlying tissues such as fat, muscles, and sometimes bones. Unlike minor burns, third-degree burns may appear white, charred, leathery, or blackened and are often painless at the site due to nerve destruction.
In South Korea, treatment of third-degree burns is highly advanced and typically involves specialized burn centers, reconstructive surgery, and multidisciplinary care. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent infection, manage pain, and optimize functional and cosmetic outcomes.
➤ Key Facts
→ Third-degree burns destroy the full thickness of the skin and may extend to underlying tissues.
→ Common causes include fire, scalding liquids, electrical burns, chemicals, and prolonged contact with hot objects.
→ Burns are often painless initially due to nerve damage, but surrounding areas may be intensely painful.
→ Risk of infection, fluid loss, hypothermia, and shock is high.
→ In Korea, specialized burn units provide surgical intervention, skin grafting, and rehabilitation programs.
→ Complications can include scarring, contractures, and loss of function if untreated or improperly managed.
→ Early care focuses on stabilization, wound management, and preventing systemic complications.
➤ What is a Third-Degree Burn?
Third-degree burns are classified as full-thickness skin injuries:
→ Skin destruction – Epidermis and dermis completely destroyed.
→ Color changes – White, black, brown, or leathery appearance.
→ Painless at the burn site – Nerve endings are destroyed.
→ Surrounding partial-thickness burns – May still be red and painful.
→ Potential involvement of deeper tissues – Fat, muscles, tendons, and bones may be affected in severe cases.
→ Non-blanching skin – Skin does not turn white when pressed.
In South Korea, burn specialists classify burns by depth, size, and location to determine the most appropriate treatment.
➤ What Symptoms are Related to Third-Degree Burns?
Third-degree burns are often accompanied by other local and systemic symptoms:
→ Dry, leathery, or charred skin → Hallmark sign of full-thickness burn.
→ Black, white, or brown patches → Skin necrosis.
→ Swelling around the burn → Inflammatory response to tissue damage.
→ Blisters – Often present in adjacent second-degree burn areas.
→ Severe pain in surrounding areas → Peripheral tissue remains sensitive.
→ Shock symptoms – Low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, and pallor in extensive burns.
→ Infection risk – Fever, pus, or foul odor if not managed promptly.
→ Fluid loss – Risk of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
→ Functional impairment – Loss of mobility or dexterity in affected areas.
➤ What Causes / Possible Causes?
Third-degree burns are caused by high-intensity heat, chemical exposure, or electrical injuries:
→ Flames or fire – Residential fires, clothing catching fire, or explosions.
→ Scalding liquids – Hot water, oil, or steam causing prolonged contact burns.
→ Chemical burns – Strong acids, alkalis, or industrial chemicals.
→ Electrical burns – High-voltage shocks damaging skin and deeper tissues.
→ Friction burns – Caused by high-speed accidents or machinery.
→ Prolonged exposure to heat – Contact with hot objects or surfaces for extended periods.
➤ When Should I See My Doctor?
Third-degree burns are always a medical emergency. Immediate care is required if:
→ Burn covers a large area or involves critical regions (face, hands, feet, genitals, or joints).
→ Presence of charred, white, or leathery skin.
→ Patient experiences shock symptoms – Dizziness, rapid heartbeat, pale or clammy skin.
→ Electrical or chemical burns occur.
→ Burns affect breathing or airway – Smoke inhalation suspected.
→ Severe pain in surrounding areas.
→ Any sign of infection or tissue necrosis in untreated burns.
In Korea, emergency departments and specialized burn centers provide rapid stabilization and care for all severe burns.
➤ Care and Treatment
Treatment of third-degree burns focuses on stabilization, wound care, infection prevention, and functional recovery:
→ Immediate first aid – Remove clothing/jewelry, cool surrounding skin (not the burned area directly).
→ Fluid resuscitation – Intravenous fluids to prevent shock in extensive burns.
→ Pain management – Analgesics, sedatives, or anesthesia for wound care and surgery.
→ Wound cleaning and debridement – Removal of necrotic tissue to prevent infection.
→ Topical antimicrobial dressings – Reduce risk of bacterial infection.
→ Skin grafting – Autograft, allograft, or synthetic substitutes for full-thickness wounds.
→ Surgical intervention – Early excision, reconstruction, and functional restoration.
→ Rehabilitation – Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and scar management.
→ Psychological support – Counseling for trauma, anxiety, or body image concerns.
➤ Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides world-class burn care with advanced technologies and multidisciplinary teams:
Diagnosis in Korea
→ Depth assessment – Clinical examination, laser Doppler imaging, or high-resolution photography.
→ Laboratory tests – To monitor fluid balance, infection markers, and organ function.
→ Imaging studies – X-ray, CT, or MRI if underlying structures may be involved.
→ Airway evaluation – For inhalation burns or respiratory complications.
Medical Treatments in Korea
→ Emergency fluid resuscitation – Advanced protocols for severe burn shock.
→ Surgical interventions – Early excision, skin grafting, and reconstructive surgery.
→ Infection control – State-of-the-art antimicrobial dressings, systemic antibiotics, and sterile wound care.
→ Pain management – Multimodal analgesia including IV opioids and regional anesthesia.
Advanced Therapies in Korea
→ Artificial skin substitutes and bioengineered grafts – Promote faster healing.
→ Rehabilitation programs – Physical and occupational therapy to restore mobility.
→ Scar management – Silicone therapy, laser therapy, and compression garments.
→ Psychological care – Counseling and support for trauma and post-burn mental health issues.
Rehabilitation & Support in Korea
→ Long-term follow-up for functional recovery, scar prevention, and cosmetic outcomes.
→ Multidisciplinary approach involving burn surgeons, physiotherapists, psychologists, and nutritionists.
→ Family education on wound care, infection prevention, and rehabilitation exercises.