➤ Overview
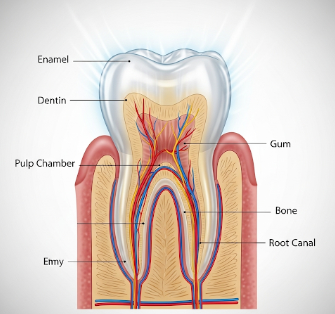
Translucent teeth refer to teeth that appear partially see-through or glass-like, often at the edges. While some degree of translucency is normal, excessive translucency may indicate enamel thinning, enamel erosion, or other dental conditions. This can affect aesthetic appearance, tooth strength, and overall oral health.
In South Korea, dentists routinely evaluate translucent teeth using clinical examination, digital imaging, and enamel thickness assessment. Early recognition allows preventive care, cosmetic enhancement, and treatment of underlying causes, ensuring both functional and visual dental health.
➤ Key Facts
→ Healthy teeth may show mild translucency at the edges, especially in younger individuals.
→ Excessive translucency often reflects enamel erosion or structural weakening.
→ Causes include dietary acids, teeth grinding, acid reflux, or genetic enamel defects.
→ In Korea, cosmetic dentistry and preventive programs address both function and aesthetics.
→ Persistent translucency may lead to tooth sensitivity, chipping, or accelerated wear.
→ Early evaluation helps prevent further enamel damage and maintain oral health.
→ Treatment ranges from preventive care to cosmetic restorations depending on severity.
➤ What is Translucent Teeth?
Translucent teeth are characterized by increased light transmission through enamel, making them appear partially transparent:
→ Normal translucency – Slight see-through edges in healthy teeth.
→ Excessive translucency – May indicate enamel thinning or wear.
→ Location-specific – Often most noticeable at incisal edges of front teeth.
→ Aesthetic concern – Can affect confidence and appearance of the smile.
→ Structural impact – Weakened enamel can increase risk of chipping or decay.
→ Indicator of underlying causes – Diet, oral habits, medical conditions, or genetic factors.
Dentists in Korea evaluate translucency using shade guides, transillumination, and high-resolution imaging for accurate diagnosis.
➤ What Symptoms are Related to Translucent Teeth?
Translucent teeth may be associated with other oral health issues:
→ Tooth sensitivity → Pain with hot, cold, or sweet stimuli.
→ Enamel wear or erosion → Thinning enamel increases translucency.
→ Discoloration → Translucent teeth may appear yellow due to underlying dentin exposure.
→ Chipping or cracks → Structural weakening can lead to breakage.
→ Rough or uneven edges → May result from enamel loss.
→ Bad breath (halitosis) → If enamel loss exposes dentin or bacterial accumulation.
→ Occlusal wear → Grinding or clenching exacerbates translucency.
→ Associated conditions – Acid reflux or frequent vomiting can accelerate enamel erosion.
➤ What Causes / Possible Causes?
Translucent teeth arise from various intrinsic and extrinsic factors:
→ Enamel erosion – Acidic foods, drinks, or gastric reflux.
→ Genetic conditions – Amelogenesis imperfecta affecting enamel development.
→ Bruxism (teeth grinding) – Mechanical wear increases translucency.
→ Aging – Natural thinning of enamel over time.
→ Excessive fluoride – Fluorosis can alter enamel structure.
→ Poor oral hygiene – Contributes to enamel weakening and discoloration.
→ Dietary factors – Acidic fruits, soda, and energy drinks erode enamel.
→ Medical conditions – Acid reflux, eating disorders, or gastrointestinal disorders.
→ Trauma – Damage to enamel from injury or dental procedures.
➤ When Should I See My Doctor?
Dental evaluation is recommended if translucency is:
→ Noticeable or worsening at tooth edges.
→ Associated with sensitivity, pain, or chipping.
→ Linked to discoloration or enamel defects.
→ Caused by diet, acid reflux, or medical conditions affecting enamel.
→ Aesthetic concern – Affecting self-confidence or appearance.
→ In Korea, dentists provide comprehensive enamel assessment, preventive advice, and cosmetic planning.
➤ Care and Treatment
Management depends on severity and underlying cause:
→ Preventive measures – Reduce acidic food/drink intake, use fluoride toothpaste.
→ Occlusal guards – Protect teeth from grinding and further enamel wear.
→ Professional cleaning and remineralization – Strengthen enamel with fluoride or calcium treatments.
→ Cosmetic restorations – Bonding, veneers, or crowns for aesthetic improvement.
→ Diet and lifestyle modification – Manage acid reflux and reduce enamel erosion.
→ Regular dental monitoring – Track enamel health and prevent progression.
→ Oral hygiene optimization – Proper brushing, flossing, and fluoride rinses.
→ Treatment of systemic causes – Address reflux, eating disorders, or genetic conditions.
➤ Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced dental care for translucent teeth, combining preventive, restorative, and cosmetic solutions:
Diagnosis in Korea
→ Clinical examination – Visual inspection and transillumination techniques.
→ Digital imaging – High-resolution photos and intraoral scans to assess enamel thickness.
→ Occlusal analysis – Identify grinding or clenching contributing to enamel wear.
→ Medical evaluation – Assess for acid reflux, dietary habits, or systemic factors.
Medical Treatments in Korea
→ Fluoride and remineralization therapy – Strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity.
→ Dietary and lifestyle guidance – Prevent further erosion.
→ Protective appliances – Night guards for bruxism management.
→ Bonding or cosmetic restoration – Repair translucent or weakened teeth for aesthetics.
Advanced Therapies in Korea
→ Veneers and crowns – Correct appearance and protect enamel.
→ Multidisciplinary dental care – Collaboration between general dentists, cosmetic specialists, and orthodontists if needed.
→ Patient education programs – Focus on enamel preservation, dietary counseling, and oral hygiene.
Rehabilitation & Support in Korea
→ Regular follow-ups to monitor enamel and tooth structure.
→ Guidance on maintaining oral health and preventing progression.
→ Cosmetic support to ensure satisfactory aesthetic outcomes.