➤ Overview
Sensitive teeth, also called dentin hypersensitivity, is a common dental condition where the teeth experience sharp, sudden pain in response to stimuli such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. This discomfort arises when the protective enamel wears down or the gums recede, exposing the underlying dentin or tooth root.
In South Korea, sensitive teeth are treated by dentists and dental specialists, who provide both preventive and restorative solutions. Modern Korean dental clinics offer advanced treatments that reduce pain, protect enamel, and improve oral health, ensuring long-term relief for patients.
➤ Key Facts
→ Sensitive teeth affect millions of people worldwide and are common in adults.
→ Pain is usually brief but sharp, triggered by temperature changes or certain foods.
→ Gum recession, enamel erosion, or cavities are common causes.
→ Good oral hygiene and preventive care can reduce the risk of hypersensitivity.
→ Treatments include desensitizing toothpaste, fluoride application, and dental procedures.
→ In Korea, dental clinics use advanced diagnostics and minimally invasive treatments.
→ Ignoring sensitive teeth may lead to worsening dental problems, including decay and gum disease.
➤ What is Sensitive Teeth?
Sensitive teeth occur when dentin, the inner layer of the tooth, becomes exposed. Dentin contains microscopic tubules that connect to the tooth nerve. When exposed, external stimuli such as hot, cold, sweet, or acidic substances stimulate the nerve endings, causing sharp pain or discomfort.
Sensitive teeth are not a disease themselves but a symptom of underlying dental issues, such as enamel erosion, gum recession, or tooth decay. Korean dental specialists emphasize early diagnosis and treatment to prevent progression and preserve oral health.
➤ What Symptoms are Related to Sensitive Teeth?
Sensitive teeth can present with several clear symptoms:
→ Sharp, sudden pain triggered by hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
→ Pain during brushing or flossing, particularly near the gum line.
→ Discomfort when breathing in cold air through the mouth.
→ Receding gums or visible tooth roots.
→ Mild swelling or redness of the gums near affected teeth.
→ Temporary pain lasting seconds to minutes but recurring frequently.
→ Increased sensitivity over time if underlying issues are not addressed.
➤ What Causes / Possible Causes?
Sensitive teeth can result from multiple dental and lifestyle factors:
→ Enamel erosion – Caused by acidic foods, beverages, or aggressive brushing.
→ Gum recession – Exposes tooth roots and increases sensitivity.
→ Tooth decay or cavities – Damaged enamel exposes dentin.
→ Cracked or fractured teeth – Allow stimuli to reach the nerves.
→ Dental procedures – Whitening treatments or orthodontic adjustments can temporarily increase sensitivity.
→ Grinding or clenching (bruxism) – Wears down enamel and exposes dentin.
→ Aging – Natural enamel thinning over time increases vulnerability.
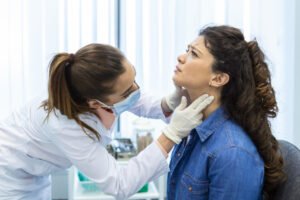
➤ When Should I See My Doctor?
Consult a dentist if sensitivity is persistent, severe, or worsening:
→ Pain lasts more than a few weeks despite at-home care.
→ Sensitivity occurs with swelling, bleeding, or pus, suggesting infection.
→ Teeth appear discolored, cracked, or damaged.
→ Difficulty eating or drinking due to pain or discomfort.
→ Existing dental work (fillings, crowns) becomes sensitive.
→ If home treatments like desensitizing toothpaste or fluoride rinses fail.
➤ Care and Treatment
Managing sensitive teeth involves both preventive care and targeted treatment:
→ Use desensitizing toothpaste – Blocks nerve pathways and reduces pain.
→ Fluoride application – Strengthens enamel and protects exposed dentin.
→ Soft-bristled toothbrush – Reduces enamel wear and gum irritation.
→ Avoid acidic foods and drinks – Minimizes enamel erosion.
→ Dental sealants or bonding – Covers exposed dentin in more severe cases.
→ Treatment for gum recession – Surgical or nonsurgical interventions to protect roots.
→ Night guards – Prevent damage from bruxism.
→ Regular dental check-ups – Early detection and prevention of underlying issues.
➤ Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced dental care for sensitive teeth, combining cutting-edge technology with expert clinical care:
Diagnosis in Korea
→ Comprehensive dental exams, including visual inspection and tactile testing.
→ X-rays or CT scans to identify decay, fractures, or structural problems.
→ Assessment of bite patterns and gum health.
Medical Treatments in Korea
→ Professional fluoride treatments to strengthen enamel.
→ Desensitizing agents applied in the dental office for immediate relief.
→ Dental restorations, such as composite bonding, to cover exposed dentin.
Advanced Therapies in Korea
→ Laser therapy to reduce dentin sensitivity and stimulate gum health.
→ Minimally invasive gum grafts to treat recession.
→ Custom night guards for patients with bruxism.
Rehabilitation & Support in Korea
→ Patient education on oral hygiene, diet, and preventive care.
→ Regular follow-ups to monitor sensitivity and prevent recurrence.
→ Integration of Western dentistry with Korean dental wellness programs for long-term oral health.