verview
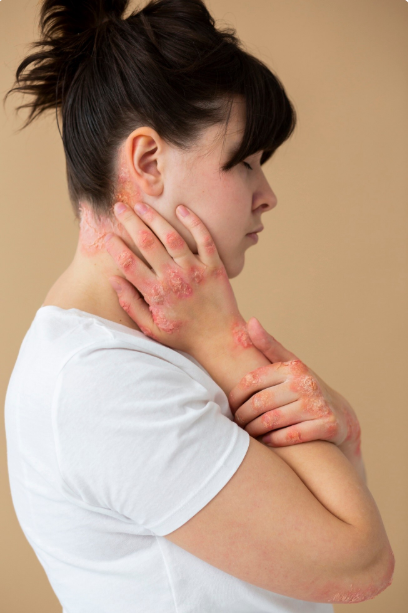
Chronic urticaria is a skin condition characterized by recurrent hives or wheals lasting six weeks or longer. It can cause significant discomfort due to itching and may be linked to autoimmune or allergic reactions. In Korea, specialized dermatology and allergy centers provide accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and management strategies for chronic urticaria.
What is Chronic Urticaria?
Chronic urticaria occurs when histamine and other chemicals are released by mast cells in the skin, causing hives, swelling, and itching. Unlike acute urticaria, which resolves within days, chronic urticaria persists for weeks or months and can significantly impact quality of life.
Symptoms
- Recurrent, raised, red or skin-colored hives
- Itching, sometimes severe, often worse at night
- Swelling of lips, eyelids, hands, or feet (angioedema)
- Burning or stinging sensation in affected areas
- Hives that appear and disappear unpredictably
- Symptoms may be triggered by stress, temperature changes, or certain foods
Causes
- Autoimmune reactions (most common in chronic cases)
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, or environmental triggers
- Infections or underlying chronic illnesses
- Physical triggers such as pressure, heat, cold, or sunlight
- Idiopathic: in many cases, no identifiable cause is found
Risk Factors
- Personal or family history of autoimmune disorders
- Female gender (more commonly affected)
- Chronic infections or inflammatory conditions
- Stress or psychological factors
- History of allergies or atopic conditions
Complications
- Sleep disturbances due to intense itching
- Anxiety, depression, or emotional stress
- Angioedema causing swelling of airway in severe cases
- Reduced quality of life and social discomfort
- Possible association with other autoimmune diseases
Prevention
- Identify and avoid known triggers (foods, medications, environmental factors)
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques or therapy
- Regular skin care and avoiding harsh chemicals
- Prompt treatment of infections or underlying illnesses
- Maintain overall health and immune balance
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms, preventing flare-ups, and addressing underlying causes:
- Medications:
- Non-sedating antihistamines (first-line therapy)
- Higher-dose antihistamines if standard doses are insufficient
- Short-term corticosteroids for severe flare-ups
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists in select cases
- Immunomodulatory medications (e.g., omalizumab) for refractory chronic urticaria
- Therapies and interventions:
- Avoidance strategies for triggers
- Skin care and moisturizers to reduce irritation
- Stress management and counseling for emotional support
- Specialized hospitals in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center Dermatology & Allergy, Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital
- Multidisciplinary teams including dermatologists, allergists, and immunologists
- Follow-up care:
- Regular monitoring of symptoms and treatment response
- Adjusting medications as needed to control flare-ups
- Education on trigger avoidance and lifestyle modifications