Overview
Chloasma, also known as melasma, is a common skin condition characterized by dark, irregular patches on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. It is more common in women and is often associated with hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics. In Korea, where skincare and dermatology are highly advanced, effective treatments and preventive strategies are widely available.
What is Chloasma?
Chloasma (melasma) is a type of hyperpigmentation that occurs when the skin produces excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. It is sometimes referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” because it frequently develops during pregnancy due to hormonal fluctuations. Although harmless, it can cause cosmetic concerns and affect self-confidence.
Symptoms
- Brown, tan, or grayish patches on the skin
- Symmetrical pigmentation on both sides of the face
- Commonly affects:
- Cheeks
- Forehead
- Nose bridge
- Upper lip
- Chin
- Usually does not cause itching, pain, or physical discomfort
Causes
- Overproduction of melanin in skin cells
- Triggered by:
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, birth control pills, hormone therapy)
- Sun exposure (UV radiation stimulates melanin production)
- Genetic predisposition
- Skin irritation from cosmetics or skincare products
- Thyroid dysfunction (in some cases)
Risk Factors
- Women of reproductive age (especially pregnant women)
- People with darker skin tones (Asian, Hispanic, Middle Eastern populations)
- Family history of melasma
- Use of hormonal medications (oral contraceptives, HRT)
- Frequent or prolonged sun exposure
Complications
- Psychological distress due to cosmetic appearance
- Recurrence even after treatment if sun protection is not maintained
- Resistance to treatment in some individuals
- Darkening of patches with continued UV exposure
Prevention
- Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher)
- Wearing hats and avoiding direct sunlight
- Using gentle skincare products to avoid irritation
- Avoiding unnecessary hormonal medications if possible
- Regular dermatological check-ups if prone to pigmentation issues
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea is a global leader in dermatology and cosmetic skin treatments, offering advanced and effective solutions for chloasma.
1. Medical Treatments
- Topical creams: Hydroquinone, tretinoin, corticosteroids, or combination creams prescribed by dermatologists
- Oral medications: Tranexamic acid (sometimes used in Korea for resistant cases)
2. Dermatological Procedures
- Chemical peels: Mild acids to remove pigmented skin layers
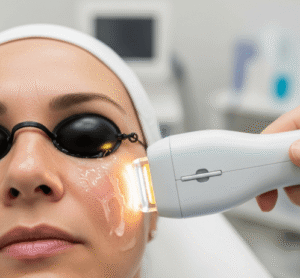
- Laser therapy: Q-switched Nd:YAG laser and fractional lasers, popular in Korean dermatology clinics
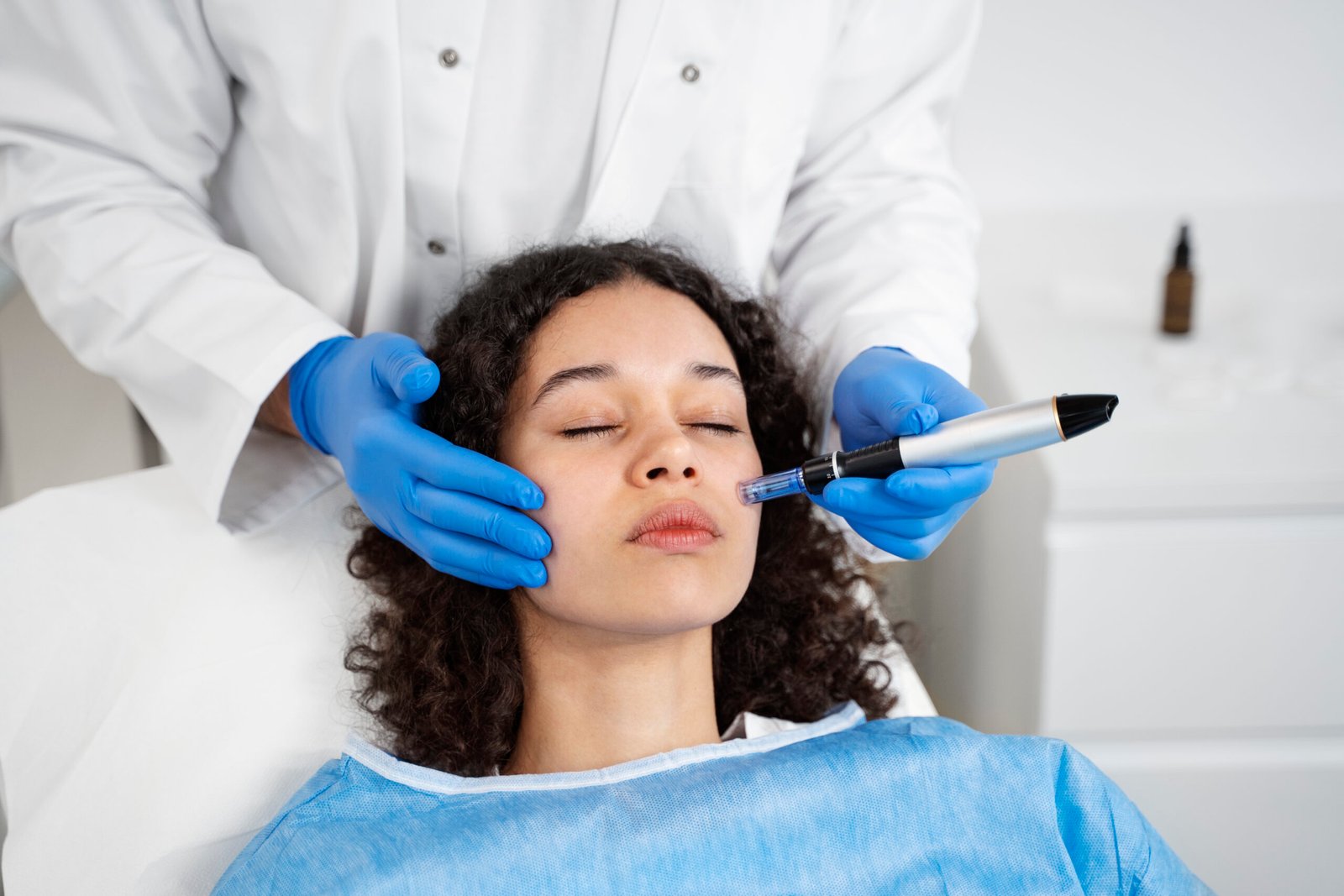
- Microneedling with PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma): Helps improve skin tone and stimulate regeneration
3. Cosmetic Skincare
- Korean dermatology clinics often combine medical-grade brightening serums, vitamin C, niacinamide, and arbutin to reduce pigmentation
- Customized skincare routines are recommended to prevent irritation and recurrence