Overview
Cholesterol embolism, also known as atheroembolism, is a condition in which cholesterol crystals or atheromatous debris break off from large arteries and lodge in smaller blood vessels, causing organ damage. While rare, it can lead to serious complications in affected patients. In Korea, modern hospitals provide early diagnosis, supportive care, and specialized management to prevent progression and reduce complications.
What is Cholesterol Embolism?
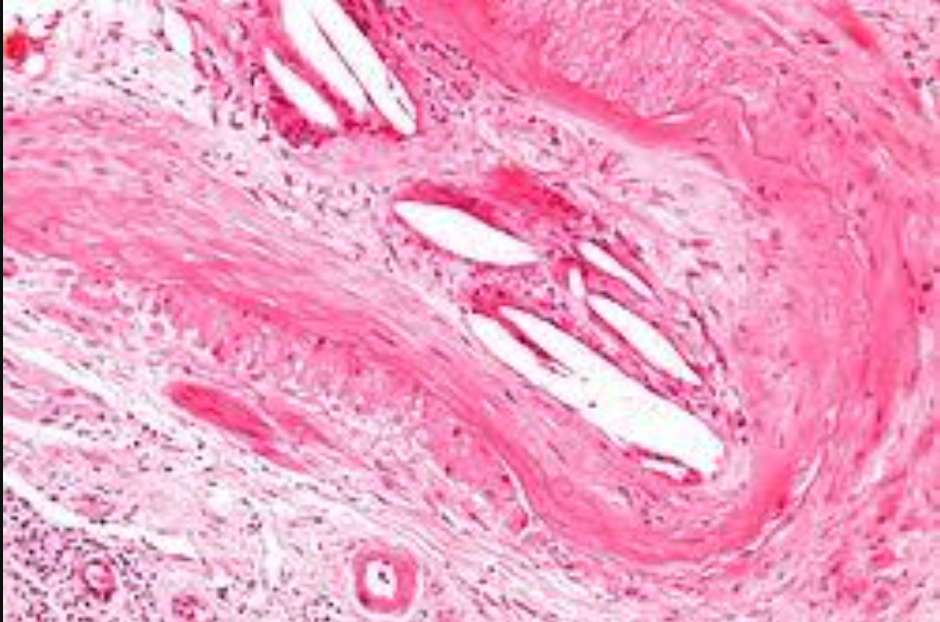
Cholesterol embolism occurs when fragments of cholesterol plaques from major arteries, such as the aorta, detach and block smaller downstream arteries. This can result in tissue ischemia, inflammation, and organ dysfunction. It often follows vascular procedures like angiography or surgery but may also occur spontaneously in patients with severe atherosclerosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the organs affected and may include:
- Skin manifestations: purple or blue discoloration, livedo reticularis, or painful nodules
- Renal dysfunction: reduced urine output or elevated creatinine levels
- Gastrointestinal issues: abdominal pain, nausea, or diarrhea
- Neurological symptoms: confusion, weakness, or stroke-like episodes
- Fever or general malaise
Causes
- Dislodgment of cholesterol crystals from atherosclerotic plaques
- Invasive vascular procedures such as angiography, stent placement, or surgery
- Anticoagulation therapy (may increase risk of plaque disruption)
- Advanced atherosclerosis due to age, diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia
Risk Factors
- Older age, especially over 60 years
- Severe atherosclerosis or peripheral vascular disease
- History of vascular interventions or surgery
- Diabetes, hypertension, or high cholesterol
- Smoking or sedentary lifestyle
- Kidney disease or impaired vascular health
Complications
- Acute or chronic kidney failure
- Skin ulceration or necrosis
- Gastrointestinal ischemia or infarction
- Neurological deficits if cerebral vessels are affected
- Multi-organ failure in severe cases
Prevention
- Careful assessment before vascular procedures
- Management of underlying atherosclerosis through lifestyle and medications
- Controlling blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels
- Avoid unnecessary anticoagulation unless medically indicated
- Smoking cessation and regular exercise
Treatment Options in Korea
There is no specific cure for cholesterol embolism; treatment is mainly supportive and focuses on preventing complications:
- General care:
- Monitoring kidney and liver function, blood pressure, and affected organs
- Pain management and skin care for ischemic lesions
- Avoidance of further vascular interventions unless necessary
- Medications:
- Statins to stabilize atherosclerotic plaques
- Blood pressure control and management of comorbidities
- Limited role of corticosteroids in severe inflammatory reactions
- Specialized hospitals in Korea:
- Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Samsung Medical Center, Severance Hospital
- Multidisciplinary teams including cardiology, nephrology, and vascular surgery
- Advanced imaging and interventional support for diagnosis and management
- Follow-up care:
- Regular monitoring for kidney function, vascular health, and skin lesions
- Lifestyle modifications and medications to prevent further embolic events