Overview
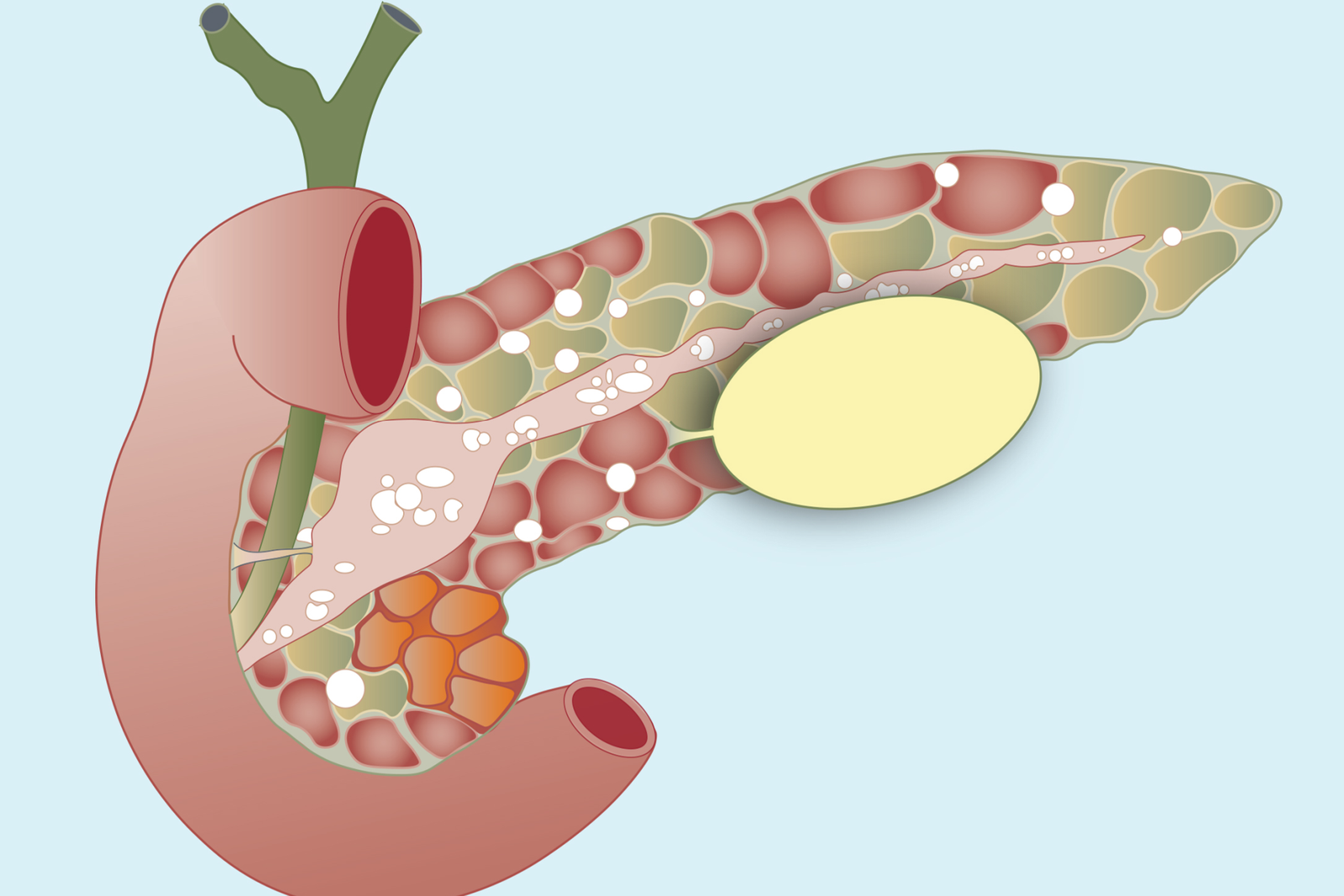
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term condition characterized by inflammation and irreversible damage to the pancreas, leading to impaired digestive enzyme production and hormonal dysfunction. In Korea, gastroenterology and pancreatic centers provide early diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, and lifestyle counseling to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
What is Chronic Pancreatitis?
Chronic pancreatitis occurs when repeated episodes of pancreatic inflammation cause permanent structural damage, fibrosis, and loss of function. It can lead to malabsorption, diabetes, and chronic abdominal pain. Early recognition and management are essential to prevent progressive pancreatic damage.
Symptoms
- Persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unintended weight loss
- Steatorrhea (fatty, foul-smelling stools)
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Diabetes or high blood sugar in advanced cases
Causes
- Chronic alcohol consumption (most common cause in adults)
- Genetic mutations (e.g., PRSS1, SPINK1, CFTR)
- Autoimmune pancreatitis
- Obstruction of pancreatic ducts (stones or strictures)
- Long-standing hypertriglyceridemia or high calcium levels
- Repeated acute pancreatitis episodes
Risk Factors
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Smoking
- Family history of pancreatitis
- History of gallstones or pancreatic duct obstruction
- High triglycerides or metabolic disorders
- Autoimmune or genetic predispositions
Complications
- Malabsorption leading to nutritional deficiencies
- Diabetes mellitus due to loss of insulin-producing cells
- Pancreatic pseudocysts or abscesses
- Chronic pain affecting quality of life
- Increased risk of pancreatic cancer in long-standing disease
- Digestive problems and weight loss
Prevention
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption
- Quit smoking
- Maintain a healthy diet and manage triglycerides
- Promptly treat gallstones or pancreatic duct obstructions
- Regular check-ups if there is a family history of pancreatitis
Treatment Options in Korea
Management focuses on symptom relief, preserving pancreatic function, and preventing complications:
- Medications:
- Pain management with analgesics or nerve-block procedures
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy to aid digestion
- Insulin or oral hypoglycemics if diabetes develops
- Medications to reduce stomach acid and protect pancreatic tissue
- Endoscopic or surgical interventions:
- Endoscopic removal of pancreatic duct stones or stents for strictures
- Surgical procedures (e.g., pancreatic resection or drainage) in refractory cases
- Lifestyle and dietary counseling:
- Low-fat diet and small, frequent meals
- Alcohol and smoking cessation programs
- Nutritional supplements to correct deficiencies
- Specialized hospitals in Korea:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital Gastroenterology Units
- Multidisciplinary teams including gastroenterologists, surgeons, dietitians, and pain management specialists
- Follow-up care:
- Regular monitoring of pancreatic function, blood sugar, and nutritional status
- Imaging studies for structural complications
- Long-term support for lifestyle modifications and symptom management