Overview
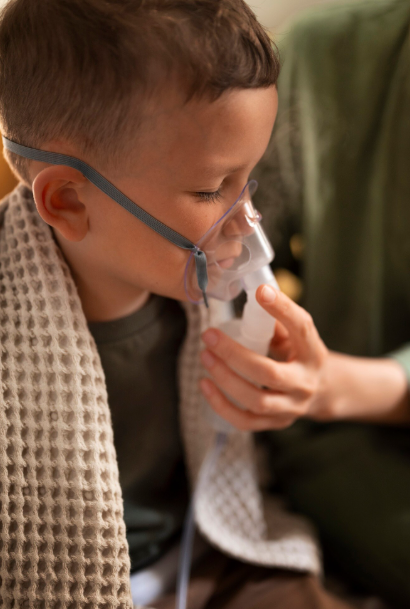
Childhood asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by airway inflammation, bronchial hyperreactivity, and reversible airflow obstruction. In Korea, it is one of the most common chronic diseases in children, with prevalence influenced by genetics, environmental factors, and urban living. Korean healthcare emphasizes early diagnosis, asthma management plans, and specialized pediatric care to minimize symptoms and prevent complications.
What is Childhood Asthma?
Asthma in children involves chronic inflammation of the airways, leading to recurring episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, and chest tightness. Triggers can include allergens, respiratory infections, exercise, and environmental irritants. While asthma cannot be cured, proper management allows most children to lead normal, active lives.
Symptoms
- Wheezing or whistling sounds during breathing
- Shortness of breath, especially at night or during physical activity
- Persistent cough, sometimes worse at night or early morning
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Fatigue due to disturbed sleep from nighttime symptoms
Causes
- Chronic inflammation of the airways triggered by immune system hypersensitivity
- Allergens such as dust mites, pollen, mold, pet dander
- Respiratory infections caused by viruses
- Environmental pollutants, smoke, or secondhand tobacco exposure
- Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in some children
Risk Factors
- Family history of asthma, eczema, or allergic rhinitis
- Exposure to tobacco smoke during pregnancy or childhood
- Urban living with higher air pollution levels
- Premature birth or low birth weight
- Recurrent viral respiratory infections during early childhood
- Obesity, which may exacerbate asthma symptoms
Complications
- Frequent asthma attacks leading to emergency visits or hospitalization
- Reduced lung function if not managed properly
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue affecting school performance
- Side effects from overuse of rescue medications
- Psychological stress or anxiety related to breathing difficulties
Prevention
- Avoid exposure to known allergens and environmental triggers
- Implement smoke-free environments at home and school
- Ensure routine vaccinations to prevent respiratory infections
- Encourage proper nutrition and physical activity
- Educate children and caregivers about early recognition of symptoms and asthma action plans
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea provides comprehensive pediatric asthma management, including:
- Medication management:
- Inhaled corticosteroids for long-term control
- Bronchodilators (short-acting and long-acting) for symptom relief
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists or other adjunctive therapies for specific cases
- Monitoring and follow-up:
- Regular lung function tests (spirometry)
- Personalized asthma action plans for children and caregivers
- Education on proper inhaler technique
- Hospital and specialist care:
- Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Severance Hospital
- Multidisciplinary teams including pediatric pulmonologists, allergists, and respiratory therapists
- Management of severe or refractory asthma cases, including biologic therapies
- Supportive care:
- School-based asthma programs
- Family education and counseling
- Environmental control strategies at home and school