Overview
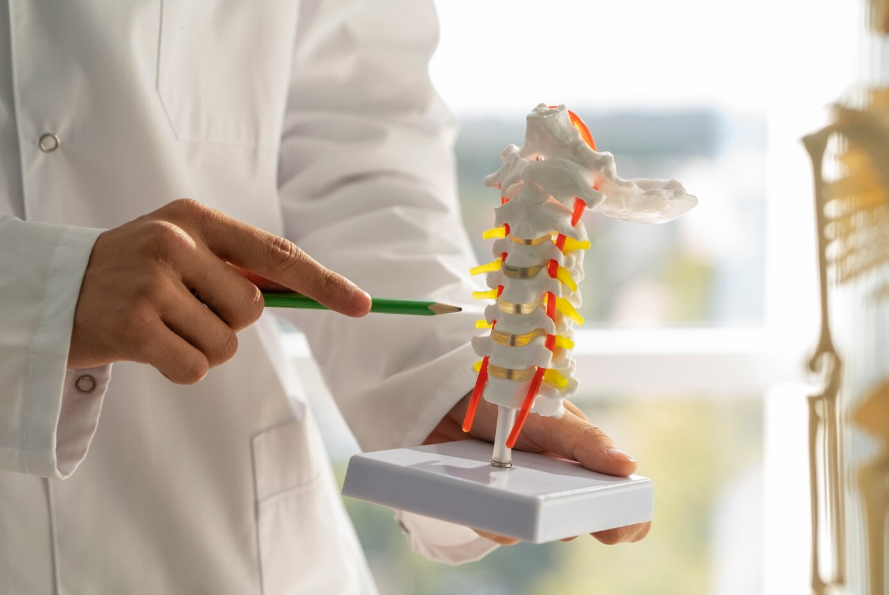
Cervical radiculopathy is a condition caused by compression or irritation of a nerve root in the cervical spine, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness radiating from the neck into the shoulder, arm, or hand. In Korea, advanced diagnostic imaging and orthopedic/neurosurgical care enable accurate diagnosis and effective treatment to relieve symptoms and restore function.
Symptoms
- Neck pain radiating to the shoulder, arm, or hand
- Numbness or tingling in the arm, hand, or fingers
- Weakness in specific muscles controlled by the affected nerve
- Pain worsened by neck movements, coughing, or sneezing
- Loss of coordination or fine motor skills in the hand in severe cases
Causes
- Herniated cervical discs pressing on nerve roots
- Cervical spondylosis (degenerative changes)
- Bone spurs narrowing the nerve passage
- Spinal stenosis
- Trauma or injury to the neck
- Repetitive strain or poor posture
Risk Factors
- Age-related degeneration (commonly over 40)
- Occupations requiring repetitive neck movements or heavy lifting
- Sedentary lifestyle or poor posture
- History of cervical spine injury
- Smoking, which accelerates disc degeneration
- Genetic predisposition to spinal problems
Diagnosis
In Korea, cervical radiculopathy is diagnosed using:
- Physical examination to assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory changes
- X-rays to detect degenerative changes or alignment issues
- MRI to visualize herniated discs, nerve compression, and soft tissue
- CT scan for detailed bone assessment if needed
- Electromyography (EMG) to evaluate nerve function
- Patient history of symptom onset, duration, and aggravating factors
Prevention
- Maintaining good posture and ergonomic workstation setup
- Avoiding prolonged static neck positions
- Regular neck and shoulder exercises
- Proper lifting techniques to reduce neck strain
- Weight management and healthy lifestyle to reduce spinal stress
- Early evaluation of neck pain to prevent nerve damage
Treatment Options in Korea
- Non-Surgical Management
- Pain relief with NSAIDs or acetaminophen
- Physical therapy to improve posture, flexibility, and strength
- Cervical collars or traction in selected cases
- Activity modification and ergonomic adjustments
- Interventional Treatments
- Epidural steroid injections or selective nerve root blocks for severe pain
- Minimally invasive procedures for nerve decompression
- Surgical Treatment
- Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF)
- Cervical disc replacement for suitable candidates
- Posterior cervical foraminotomy to relieve nerve pressure
- Performed at specialized Korean orthopedic and neurosurgical centers
- Rehabilitation
- Post-treatment physical therapy to restore mobility and strength
- Gradual return to daily activities and work
- Regular follow-up to monitor nerve recovery