Overview
Calciphylaxis is a rare but serious condition in which calcium accumulates in small blood vessels of the skin and fat, leading to tissue damage, blood clots, and painful skin ulcers. It most often occurs in people with advanced chronic kidney disease or those undergoing dialysis. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care are critical, and South Korea offers advanced nephrology, dermatology, and wound care services for effective treatment.
What is Calciphylaxis?
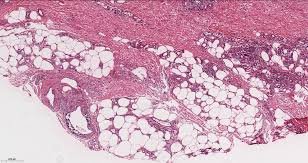
Calciphylaxis is characterized by the calcification of small and medium-sized blood vessels, causing vascular blockages, tissue ischemia, and necrosis. It is frequently associated with end-stage renal disease, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and imbalances in calcium and phosphate levels. The condition is life-threatening due to risks of severe infections and systemic complications.
Symptoms
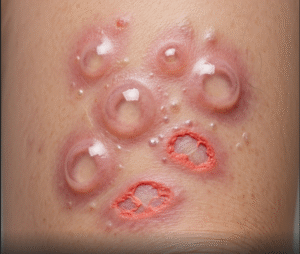
- Painful purple or dark patches on the skin
- Hard nodules or firm areas of the skin
- Non-healing ulcers that may become infected
- Necrotic (blackened) tissue in severe cases
- Itching, burning sensations, and severe localized pain
Causes
Calciphylaxis can result from:
- Chronic kidney disease and long-term dialysis
- Imbalances of calcium and phosphate in the blood
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Certain medications (e.g., warfarin, corticosteroids)
- Obesity, diabetes, or malnutrition
Risk Factors
- End-stage renal disease or prolonged dialysis
- High calcium-phosphate product in the blood
- Female gender (slightly higher prevalence)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Obesity
- Medications affecting calcium metabolism
Complications
- Severe skin infections and sepsis
- Chronic, non-healing ulcers
- Tissue necrosis potentially requiring amputation
- Increased mortality due to systemic infections
- Significant pain and reduced quality of life
Prevention
- Proper management of kidney disease and dialysis
- Maintaining balanced calcium and phosphate levels
- Regular monitoring of parathyroid hormone levels
- Early recognition and treatment of skin changes
- Avoiding medications that worsen calcium deposition
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for calciphylaxis through nephrology, dermatology, wound care, and pain management:
- Diagnosis
- Skin biopsy to detect calcium deposits
- Blood tests for calcium, phosphate, and parathyroid hormone
- Imaging (X-ray, CT) to identify vascular calcification
- Medical Management
- Sodium thiosulfate therapy to dissolve calcium deposits
- Analgesics for pain management
- Medications to control phosphate and calcium levels
- Wound Care
- Specialized dressings and infection prevention
- Debridement of necrotic tissue when necessary
- Topical antimicrobial therapy
- Surgical Intervention
- Surgical removal of severely necrotic tissue if required
- Rarely, amputation in extreme cases to prevent systemic infection
- Supportive Care
- Optimized dialysis and nutritional support
- Infection monitoring and management
- Palliative care for pain and quality of life improvement