Overview
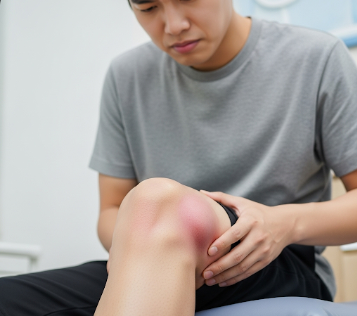
Joint effusion, commonly referred to as a swollen joint, occurs when excess fluid accumulates within a joint space, causing pain, stiffness, and limited movement. This condition can affect any joint but is most commonly seen in the knees, elbows, shoulders, and ankles.
In Korea, orthopedic and rheumatology clinics provide advanced evaluation and treatment for joint effusion. With proper diagnosis, underlying causes such as injury, infection, arthritis, or inflammatory conditions can be effectively managed, preventing long-term joint damage.
Key Facts
- ➔ Joint effusion can occur at any age, but prevalence increases with aging and joint-related conditions.
- ➔ Swelling may be accompanied by pain, warmth, redness, or decreased mobility.
- ➔ Common causes include trauma, arthritis, infection, and inflammatory diseases.
- ➔ Early diagnosis is important to prevent joint damage or chronic pain.
- ➔ Treatments vary from conservative management to minimally invasive procedures and surgical intervention depending on severity.
What is Joint Effusion (Swollen Joint)?
Joint effusion is the accumulation of excess synovial fluid within a joint capsule, leading to swelling and discomfort. Synovial fluid normally lubricates and nourishes the joint, but abnormal accumulation can cause pressure, pain, and restricted motion.
- ➔ Acute effusion: Rapid onset, often caused by trauma or infection.
- ➔ Chronic effusion: Gradual fluid buildup due to arthritis or inflammatory conditions.
- ➔ Reactive effusion: Secondary to injury or irritation of the joint lining.
- ➔ Septic effusion: Caused by bacterial infection, often requiring urgent medical attention.
Identifying the type of effusion is essential for proper management and to prevent complications.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Symptoms of joint effusion vary depending on the cause and severity:
- ➔ Visible swelling and enlargement of the affected joint
- ➔ Pain, tenderness, or discomfort around the joint
- ➔ Warmth and redness over the joint
- ➔ Stiffness or limited range of motion
- ➔ Difficulty bearing weight or using the joint normally
- ➔ Occasionally fever or systemic symptoms if infection is present
Recognizing these symptoms early can help differentiate benign effusions from serious conditions like septic arthritis or inflammatory arthritis.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Joint effusion may arise from multiple causes:
- ➔ Trauma or injury: Ligament sprains, fractures, or meniscus tears in the knee.
- ➔ Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout can cause fluid accumulation.
- ➔ Infections: Septic arthritis due to bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens.
- ➔ Inflammatory conditions: Autoimmune disorders such as lupus or psoriatic arthritis.
- ➔ Overuse or repetitive motion: Stress on the joint leading to synovial irritation.
- ➔ Tumors or cysts: Rare causes such as synovial cysts or benign/malignant growths.
Proper evaluation is crucial to distinguish between these causes and provide targeted treatment.
When Should I See My Doctor
Seek medical attention if joint swelling is:
- ➔ Rapid in onset or accompanied by severe pain
- ➔ Associated with redness, warmth, or fever
- ➔ Limiting joint movement or function
- ➔ Occurring after an injury with instability or deformity
- ➔ Persistent or recurrent, suggesting an underlying chronic condition
- ➔ Suspected to be infected (septic arthritis), which requires urgent intervention
Early assessment ensures prompt treatment and reduces the risk of joint damage or chronic disability.
Care and Treatment
Treatment of joint effusion depends on underlying cause, severity, and patient condition:
- ➔ Rest and activity modification: Avoiding weight-bearing or strenuous activity on the affected joint.
- ➔ Ice and compression: Reduces swelling and alleviates pain.
- ➔ Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication: NSAIDs or acetaminophen to control discomfort and inflammation.
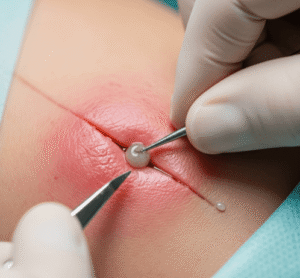
- ➔ Aspiration (arthrocentesis): Removing excess joint fluid for relief and diagnostic purposes.
- ➔ Physical therapy: Gentle exercises to restore mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles.
- ➔ Treatment of underlying condition: Managing arthritis, infection, or autoimmune disease as indicated.
- ➔ Surgery: Rarely required but may be indicated for severe joint damage, persistent effusion, or structural problems.
Prompt and targeted treatment ensures symptom relief and prevents complications such as chronic stiffness or joint degeneration.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean orthopedic and rheumatology centers provide comprehensive care for joint effusion:
- ➔ Clinical evaluation: Physical examination, joint aspiration, and history taking to identify underlying causes.
- ➔ Imaging studies: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to detect joint damage, fluid accumulation, or structural abnormalities.
- ➔ Minimally invasive procedures: Joint aspiration, steroid injections, or viscosupplementation for pain and inflammation.
- ➔ Medical therapy: NSAIDs, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), or antibiotics for infection.
- ➔ Physical rehabilitation: Targeted exercises and physiotherapy to restore joint function.
- ➔ Multidisciplinary care: Collaboration between orthopedics, rheumatology, and physical therapy for optimal outcomes.
Leading hospitals such as Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide advanced diagnostics and treatment, ensuring rapid relief and long-term joint health.
In Summary: Joint effusion is a common yet potentially serious condition characterized by swollen joints, pain, and limited movement. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and targeted treatment in Korea can relieve symptoms, restore joint function, and prevent long-term damage.
- ➔ Key Takeaway: Persistent or painful joint swelling should be evaluated promptly to identify underlying causes and prevent complications.
- ➔ Action Point: Seek consultation with an orthopedic or rheumatology specialist for comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment.