Overview
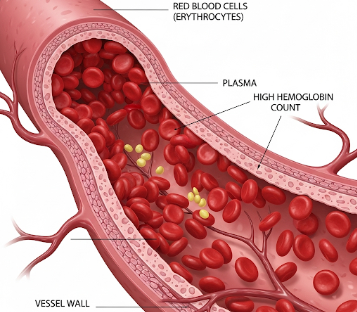
A high hemoglobin count, medically known as polycythemia or erythrocytosis, is a condition in which the hemoglobin level in the blood exceeds normal limits. Hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
While high hemoglobin can sometimes enhance oxygen delivery, abnormally elevated levels may increase blood viscosity, raising the risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart complications.
In South Korea, modern hematology centers and medical facilities provide accurate testing, diagnosis, and personalized treatment to manage high hemoglobin and reduce associated health risks.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ High hemoglobin count refers to levels above the normal range for men, women, or children.
🟢 ➤ Can be temporary (physiological) or chronic due to underlying conditions.
🟢 ➤ Causes include dehydration, lung diseases, heart disease, bone marrow disorders, and living at high altitudes.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms may be mild or absent but can include fatigue, headaches, dizziness, or vision problems.
🟢 ➤ Early diagnosis and monitoring prevent complications such as blood clots or stroke.
🟢 ➤ Korean healthcare centers provide laboratory testing, imaging, and individualized care plans.
What is High Hemoglobin Count?
High hemoglobin count, or polycythemia, occurs when the number of red blood cells or hemoglobin concentration rises above normal.
Key points:
➤ Hemoglobin is the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.
➤ High hemoglobin increases blood thickness (viscosity), which can strain the cardiovascular system.
➤ It may be primary (caused by bone marrow disorders like polycythemia vera) or secondary (due to oxygen deficiency from lung disease, heart disease, or living at high altitude).
➤ Routine blood tests, complete blood count (CBC), and specialized testing help identify the cause and guide treatment.
Symptoms Related to High Hemoglobin Count
Symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity but may include:
🟢 ➤ Headaches and dizziness due to reduced blood flow.
🟢 ➤ Fatigue or weakness from impaired circulation.
🟢 ➤ Shortness of breath, especially during exertion.
🟢 ➤ Blurred vision or visual disturbances.
🟢 ➤ Reddening of the face or hands (plethora).
🟢 ➤ Tingling or numbness in extremities.
🟢 ➤ Increased risk of blood clots, stroke, or heart attack in severe cases.
Causes / Possible Causes
High hemoglobin may arise from physiological adaptation or pathological conditions:
Primary Causes
➤ Polycythemia vera – a bone marrow disorder that produces excess red blood cells.
Secondary Causes
➤ Chronic hypoxia from lung disease, sleep apnea, or congenital heart disease.
➤ High altitude living – reduced oxygen levels stimulate red blood cell production.
➤ Smoking – carbon monoxide exposure increases hemoglobin as a compensatory mechanism.
Dehydration
➤ Reduced plasma volume can concentrate hemoglobin and make levels appear elevated.
Other Causes
➤ Certain tumors or kidney disorders may produce erythropoietin, stimulating red blood cell production.
➤ Use of anabolic steroids or erythropoietin-stimulating agents can also elevate hemoglobin.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Medical consultation is essential if high hemoglobin is suspected or detected in blood tests:
🟢 ➤ Persistent headaches, dizziness, or visual changes.
🟢 ➤ Shortness of breath, fatigue, or unusual redness in face and hands.
🟢 ➤ History of cardiovascular or lung disease.
🟢 ➤ Family history of blood disorders or polycythemia.
🟢 ➤ Blood tests showing abnormally high hemoglobin or hematocrit levels.
Early evaluation allows diagnosis of underlying causes, risk assessment for complications, and timely treatment.
Care and Treatment
Management of high hemoglobin focuses on reducing blood thickness, treating underlying causes, and preventing complications:
Lifestyle and Hydration
➤ Maintain adequate hydration to reduce blood viscosity.
➤ Avoid smoking and exposure to high altitudes if possible.
Medications
➤ Drugs such as hydroxyurea may be prescribed for polycythemia vera to reduce red blood cell production.
➤ Low-dose aspirin may be recommended to reduce clotting risk.
Phlebotomy (Therapeutic Blood Removal)
➤ Periodic blood removal can lower hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, particularly in primary polycythemia.
Treatment of Secondary Causes
➤ Manage chronic lung or heart diseases to improve oxygen delivery.
➤ Adjust medications or hormone therapy if they contribute to elevated hemoglobin.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ Korean hospitals offer specialized hematology and cardiopulmonary services, including laboratory monitoring, imaging, and individualized treatment plans.
➤ Multidisciplinary care ensures safety and optimal outcomes.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ High hemoglobin count is an abnormally elevated hemoglobin level in the blood.
🟢 ➤ Causes: polycythemia vera, chronic hypoxia, high altitude, dehydration, smoking, or certain tumors.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms: headaches, dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, visual disturbances, redness in face/hands.
🟢 ➤ Early diagnosis and monitoring prevent complications like blood clots, stroke, or heart attack.
🟢 ➤ Treatment includes hydration, medications, phlebotomy, and management of underlying causes.
🟢 ➤ South Korea provides advanced hematology care, monitoring, and individualized treatment plans.