Overview
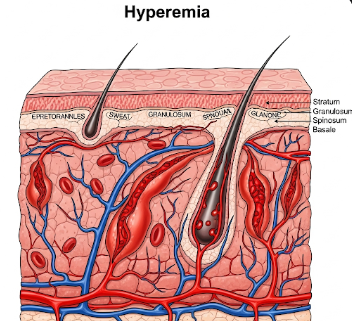
Hyperemia is a condition characterized by an excess of blood in a part of the body, resulting in redness, warmth, and sometimes swelling. It occurs when blood vessels dilate to increase blood flow to a specific tissue or organ, often as a response to injury, inflammation, or increased metabolic activity.
Hyperemia can be physiological (normal and beneficial, such as during exercise) or pathological (related to disease or injury). In South Korea, hospitals and clinics offer diagnostic tools, treatment, and management plans for hyperemia caused by various conditions.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ Hyperemia is an increased blood flow to a specific body part, leading to redness and warmth.
🟢 ➤ Can be physiological (normal) or pathological (due to disease).
🟢 ➤ Symptoms often include redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in affected areas.
🟢 ➤ Common causes: inflammation, infection, trauma, or increased metabolic demand.
🟢 ➤ Early diagnosis helps identify underlying causes and prevent complications.
🟢 ➤ South Korean medical centers provide imaging, blood tests, and treatment for hyperemia-related conditions.
What is Hyperemia?
Hyperemia occurs when arterioles in a tissue dilate, allowing increased blood flow into the capillaries.
Key points:
➤ Physiological hyperemia – occurs naturally, e.g., in muscles during exercise or in the skin after warming.
➤ Pathological hyperemia – occurs in response to inflammation, infection, trauma, or certain diseases.
➤ Hyperemia is different from congestion, which is caused by impaired venous outflow rather than increased arterial inflow.
➤ Can be localized (specific organ or tissue) or generalized (affecting larger body areas).
Symptoms Related to Hyperemia
Symptoms vary depending on location and cause:
🟢 ➤ Redness or erythema in the affected area.
🟢 ➤ Warmth or a sensation of heat.
🟢 ➤ Swelling or edema in the tissue.
🟢 ➤ Tenderness or mild pain when touched.
🟢 ➤ Functional changes – such as increased blood flow in muscles during exercise or in inflamed organs.
🟢 ➤ Visible veins may become more pronounced in some cases.
Causes / Possible Causes
Hyperemia can arise from various physiological and pathological processes:
Physiological Causes
➤ Exercise: muscles demand more oxygen and nutrients, causing arterioles to dilate.
➤ Emotional responses: blushing occurs due to increased blood flow to facial skin.
➤ Temperature regulation: skin hyperemia helps dissipate heat.
Pathological Causes
➤ Inflammation – injury or infection triggers localized hyperemia to deliver immune cells and nutrients.
➤ Infection – bacterial or viral infections can cause redness and swelling.
➤ Trauma – tissue damage induces hyperemia as part of the healing process.
➤ Liver disease or systemic conditions – in some cases, systemic hyperemia occurs due to disease-related vascular changes.
Drug-Induced or Iatrogenic Hyperemia
➤ Certain medications (e.g., vasodilators, niacin) may cause temporary hyperemia.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Consult a healthcare provider if:
🟢 ➤ Redness, swelling, or warmth persists without a clear cause.
🟢 ➤ Hyperemia is accompanied by pain, fever, or other systemic symptoms.
🟢 ➤ There is sudden onset in vital organs, such as the brain, eyes, or liver.
🟢 ➤ You have underlying chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or liver disease.
Early evaluation helps identify underlying causes, prevent complications, and guide appropriate treatment.
Care and Treatment
Management of hyperemia depends on the cause and severity:
For Physiological Hyperemia
➤ Usually self-limiting and resolves once the triggering activity or condition ends.
➤ No specific treatment is required, but monitoring is advised if symptoms are frequent or severe.
For Pathological Hyperemia
➤ Treat underlying cause – infections, inflammation, or injury may require medications or interventions.
➤ Anti-inflammatory drugs – such as NSAIDs to reduce redness, warmth, and swelling.
➤ Topical treatments – creams or gels may relieve discomfort in localized hyperemia.
Lifestyle Measures
➤ Rest affected areas if trauma-induced.
➤ Maintain hydration and healthy circulation.
➤ Avoid triggers such as prolonged heat exposure or certain medications unless prescribed.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ Korean hospitals provide diagnostic imaging (ultrasound, CT, MRI) and blood tests to determine the cause of hyperemia.
➤ Treatment plans may involve multidisciplinary teams, including internal medicine, vascular specialists, and dermatologists, depending on the affected area.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ Hyperemia is an increased blood flow to a body part, causing redness, warmth, and sometimes swelling.
🟢 ➤ Can be physiological (exercise, blushing) or pathological (infection, inflammation, trauma).
🟢 ➤ Symptoms: redness, warmth, swelling, tenderness, and visible veins.
🟢 ➤ Causes: exercise, emotional response, infection, trauma, inflammation, liver disease, or medications.
🟢 ➤ Treatment focuses on addressing underlying causes, anti-inflammatory measures, and supportive care.
🟢 ➤ South Korea offers advanced imaging, diagnostic evaluation, and multidisciplinary treatment for hyperemia.