Overview
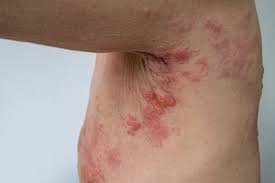
Groin irritation and infection are common conditions that affect the skin and soft tissues around the inner thighs, genital area, and buttocks. These problems can be caused by fungal infections, bacterial infections, chafing, or skin conditions. While not usually life-threatening, groin infections can cause significant discomfort, itching, and swelling. In Korea, advanced dermatology and infectious disease care provide effective diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms
- Itching, burning, or stinging sensation in the groin
- Redness, rashes, or scaling of the skin
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Foul odor or oozing discharge (if bacterial infection)
- Swelling of nearby lymph nodes in severe cases
- Cracked or peeling skin due to fungal infection (e.g., jock itch)
Causes
- Fungal infections (Tinea cruris, commonly known as jock itch)
- Bacterial infections (Staphylococcus or Streptococcus)
- Viral infections (Herpes simplex virus)
- Excessive sweating and moisture buildup
- Poor personal hygiene
- Wearing tight or synthetic clothing
- Skin friction (chafing) during sports or physical activity
Risk Factors
- Warm and humid climate conditions
- Obesity (more skin folds increase friction and sweating)
- Diabetes or weakened immune system
- Athletes or individuals engaged in regular sports
- Sharing towels, clothes, or personal items
- Prolonged use of tight undergarments
Diagnosis
Doctors in Korea use several methods to diagnose groin irritation and infection:
- Physical examination of the rash and surrounding skin
- Skin scraping or culture test to confirm fungal or bacterial infection
- Blood tests for underlying conditions like diabetes
- Viral swabs if herpes or viral causes are suspected
- Dermatoscopy in dermatology clinics to closely examine skin lesions
Prevention
- Maintain good hygiene by washing and drying the groin area thoroughly
- Use antifungal powders or sprays if prone to fungal infections
- Wear loose, breathable cotton underwear
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors
- Change sweaty clothes immediately after exercise
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce skin friction
- Boost immunity with a balanced diet and exercise
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers comprehensive treatment for groin irritation and infection through dermatology and infectious disease clinics:
- Medications
- Topical antifungal creams (clotrimazole, terbinafine) for fungal infections
- Oral antifungal drugs for recurrent or severe cases
- Antibiotic creams or oral antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antiviral medications (acyclovir, valacyclovir) for herpes infections
- Dermatology Care
- Specialized dermatology clinics provide laser therapy or phototherapy for chronic skin issues
- Skin barrier-repair creams prescribed for irritation and dryness
- Lifestyle and Hygiene Counseling
- Korean hospitals emphasize hygiene education to prevent recurrence
- Nutritional counseling for weight management and immunity support
- Advanced Testing
- University hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital and Asan Medical Center offer advanced microbiology testing for resistant infections
Prognosis
With proper treatment, most groin infections resolve within 1–3 weeks. Fungal infections may recur if hygiene and preventive measures are not maintained. Chronic or recurrent infections require long-term management and lifestyle changes. In Korea, the prognosis is excellent due to advanced diagnostic tools, personalized treatment plans, and follow-up care.