Overview
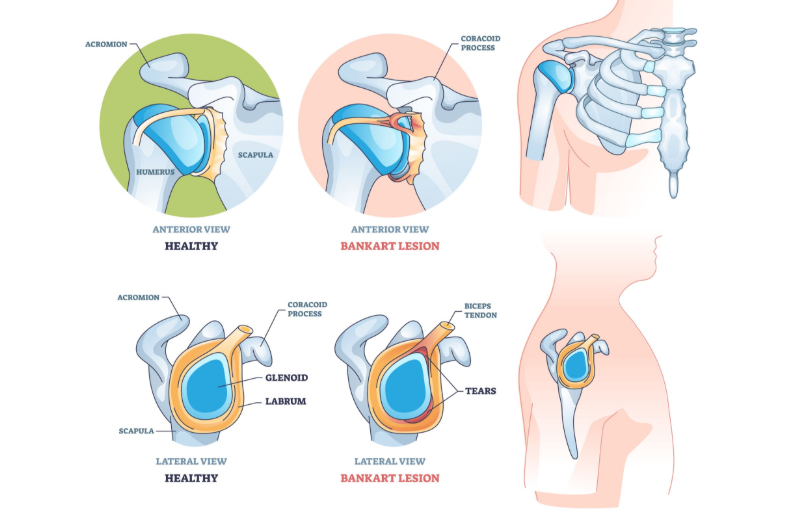
A glenoid labrum tear involves damage to the cartilage ring (labrum) that surrounds the shoulder socket (glenoid), leading to shoulder instability, pain, and functional limitations. In South Korea, advancements in medical research and healthcare infrastructure have significantly improved the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of individuals affected by glenoid labrum tears.
What is a Glenoid Labrum Tear?
The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the shoulder socket and provides attachment points for ligaments and tendons. Tears can occur due to trauma, repetitive overhead motions, or degenerative changes. Common types include:
- SLAP Lesion (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior): Involves the top part of the labrum where the biceps tendon attaches.
- Bankart Lesion: Occurs in the lower part of the labrum, often associated with shoulder dislocations.
- Posterior Labral Tear: Involves the back part of the labrum, less common but can result from specific injuries.
Symptoms
Individuals with a glenoid labrum tear may experience:
- Shoulder pain, especially with overhead activities
- A feeling of instability or “catching” in the shoulder
- Decreased range of motion
- Weakness in the shoulder
- Popping or grinding sensations
Causes and Risk Factors
Common causes include:
- Traumatic events like falls or accidents
- Repetitive overhead activities (e.g., baseball, swimming, weightlifting)
- Shoulder dislocations or subluxations
- Degenerative changes due to aging
Risk factors encompass:
- Participation in high-impact or overhead sports
- Previous shoulder injuries
- Anatomical variations
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical Examination: Assessing shoulder stability and range of motion.
- Imaging Studies:
- MRI: Detailed images of soft tissues.
- MR Arthrography: Contrast-enhanced MRI for better visualization of labral tears.
- CT Arthrography: For patients who cannot undergo MRI.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers state-of-the-art medical care for glenoid labrum tears, with leading hospitals providing comprehensive treatment options:
- Non-Surgical Management:
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stabilizing shoulder muscles.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections for pain relief.
- Surgical Intervention:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive procedure to repair or remove the torn labrum.
- Rehabilitation: Post-surgery physical therapy to restore function and strength.
Rehabilitation in Korea
Rehabilitation programs in South Korea are tailored to individual needs, focusing on:
- Restoring range of motion
- Strengthening shoulder muscles
- Enhancing proprioception and coordination
- Gradual return to sports and daily activities
Innovative approaches, such as robotic-assisted rehabilitation, are being explored to improve outcomes for patients with shoulder injuries.