Overview
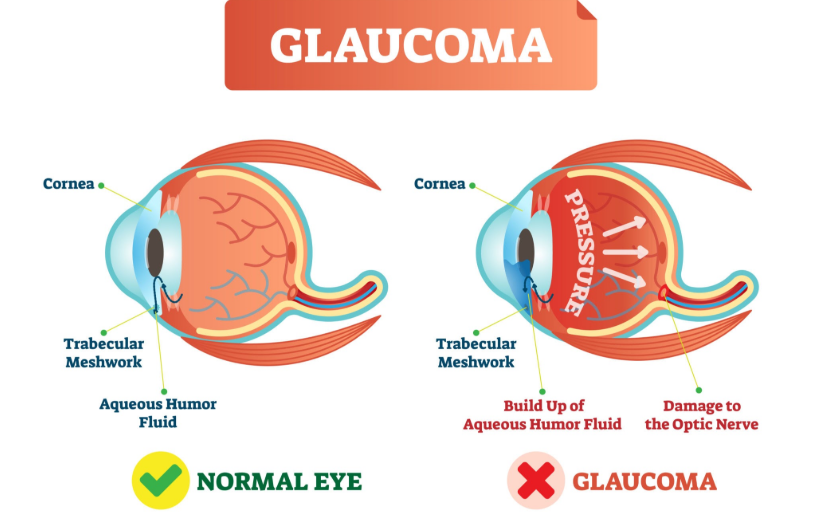
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases characterized by damage to the optic nerve, often associated with elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). It is a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. In South Korea, glaucoma poses a significant public health challenge, with increasing prevalence and a growing burden on healthcare resources.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
Recent studies indicate that the prevalence of glaucoma in South Korea is approximately 3.5% among individuals aged 40 years and older. The prevalence increases with age, with higher rates observed in males compared to females. Notably, the incidence of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG) is higher in East Asian populations, including Koreans, compared to Western populations.
Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development and progression of glaucoma:
- Elevated Intraocular Pressure (IOP): The most significant risk factor.
- Age: Risk increases with age, particularly after 40 years.
- Family History: A family history of glaucoma increases risk.
- Ethnicity: Higher prevalence in East Asian populations.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and myopia are associated with increased risk.
Diagnosis
Early detection is crucial for preventing vision loss. Diagnostic methods include:
- Tonometry: Measures IOP.
- Ophthalmoscopy: Examines the optic nerve for signs of damage.
- Perimetry: Assesses the visual field to detect loss of peripheral vision.
- Gonioscopy: Evaluates the angle of the anterior chamber to determine the type of glaucoma.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options for glaucoma:
- Medications:
- Topical Eye Drops: Prostaglandin analogs, beta-blockers, alpha agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
- Oral Medications: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for patients with inadequate response to topical therapy.
- Laser Therapies:
- Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT): A first-line treatment for open-angle glaucoma.
- Laser Peripheral Iridotomy (LPI): Commonly used for angle-closure glaucoma.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Trabeculectomy: Creates a new drainage pathway for aqueous humor.
- Tube Shunt Surgery: Involves implanting a tube to drain fluid.
- Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS): Includes procedures like iStent implantation.
- Innovative Technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Screening: AI-based systems, such as Mediwhale, are being utilized for early detection and monitoring of glaucoma through non-invasive retinal scans.