Overview
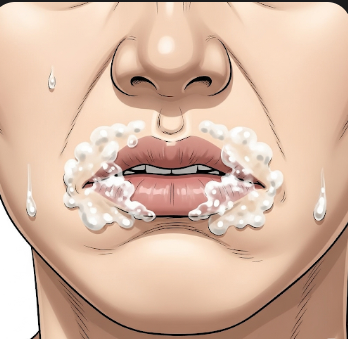
Foaming at the mouth, medically referred to as ptyalism with frothy oral secretions, is a symptom characterized by the presence of frothy or bubbly saliva around the lips. It can be alarming and may indicate a range of underlying medical conditions, from mild issues like oral irritation to serious emergencies such as seizures, poisoning, or neurological disorders. In Korea, neurology, emergency medicine, and toxicology clinics are equipped to evaluate and manage patients presenting with this symptom, providing rapid diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Highlights:
➤ Presence of frothy or bubbly saliva around the mouth
➤ Can indicate minor irritation or a medical emergency
➤ Requires prompt evaluation if sudden or associated with other symptoms
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Uncommon as an isolated symptom; often associated with seizures or poisoning
➤ Age affected: Can occur at any age, depending on cause
➤ Gender: Affects both males and females
➤ Impact: May signal neurological distress, poisoning, or severe systemic illness
➤ Prognosis: Dependent on underlying cause and timely intervention
What is Foaming at the Mouth?
Foaming at the mouth occurs when excessive saliva mixes with air, creating a frothy appearance. Key features include:
- Frothy, bubbly saliva at the oral cavity
- May accompany seizures, convulsions, or severe agitation
- Can be associated with respiratory distress or loss of consciousness
Types of Causes:
- Neurological: Epileptic seizures, rabies, or other CNS infections
- Toxicological: Ingestion of poisons, medications, or chemicals
- Local oral causes: Severe irritation, dental infections, or trauma
- Systemic: Heart failure, metabolic disorders, or severe nausea
Highlights:
➤ Foaming at the mouth is usually a symptom, not a disease
➤ Urgency depends on associated neurological or systemic signs
➤ Identification of cause is critical for treatment
What Symptoms Are Related to Foaming at the Mouth?
➤ Seizures or convulsions – Sudden uncontrolled movements
➤ Excessive salivation – Hypersalivation with froth
➤ Altered consciousness: Drowsiness, confusion, or coma
➤ Muscle rigidity or spasms – Common in neurological causes
➤ Respiratory difficulty – May occur if airway is obstructed
➤ Fever or systemic symptoms: Suggest infection or poisoning
➤ Behavioral changes: Agitation, anxiety, or aggression in certain cases
Highlights:
➣ Often occurs with severe neurological or toxicological events
➣ Presence with respiratory or consciousness changes requires immediate medical attention
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Epileptic seizures: Generalized tonic-clonic seizures can produce frothy oral secretions
➤ Rabies or other viral encephalitis: Characterized by hypersalivation and agitation
➤ Poisoning or toxicity: Organophosphate, insecticide, or chemical ingestion
➤ Severe oral irritation: Burns, infections, or trauma to the mouth
➤ Neurological disorders: Stroke, brain injury, or tumors affecting salivary control
➤ Systemic causes: Heart failure or pulmonary edema may rarely produce frothy sputum
Highlights:
➣ Causes range from emergent life-threatening conditions to local irritations
➣ Early identification is critical to prevent complications
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Sudden onset with seizures or convulsions – Emergency care required
➤ Difficulty breathing, choking, or airway obstruction
➤ Altered consciousness or confusion – Indicates neurological compromise
➤ Exposure to toxins or ingestion of harmful substances
➤ Persistent frothing without obvious cause
Highlights:
➣ Immediate consultation at a Korean emergency or neurology clinic is warranted
➣ Rapid intervention can prevent serious morbidity or mortality
Care and Treatment
➤ Emergency care: Ensure airway patency, monitor breathing and circulation
➤ Medications:
- Anticonvulsants: For seizure control
- Antitoxins or antidotes: If poisoning is suspected
- Sedatives or muscle relaxants: For severe agitation
➤ Supportive care: Oxygen therapy, IV fluids, and monitoring of vital signs
➤ Local care: Oral cleaning, wound management, or dental evaluation if needed
➤ Hospitalization: Often required for severe neurological or toxicological causes
Highlights:
➣ Treatment focuses on stabilizing the patient and addressing the underlying cause
➣ Early intervention significantly improves outcomes
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Neurology clinics: Seizure management, EEG monitoring, and CNS evaluation
➤ Emergency departments: Rapid resuscitation and supportive care
➤ Toxicology centers: Poison identification, antidote administration, and observation
➤ Dental and oral care clinics: For trauma or infections causing local frothing
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Airway management: Intubation if airway obstruction occurs
➤ Mechanical ventilation: For respiratory compromise
➤ Hospital admission: For monitoring and ongoing care
➤ Follow-up care: Neurological assessment, medication adjustment, and rehabilitation
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Education on seizure precautions, toxin avoidance, and early recognition of warning signs
➤ Monitoring for recurrence of seizures or frothing episodes
➤ Multidisciplinary support for neurological, toxicological, and oral health recovery
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide comprehensive emergency care, specialized treatment, and long-term follow-up
➣ Rapid medical attention ensures stabilization, prevention of complications, and recovery