Overview
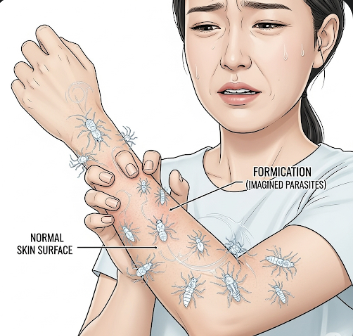
Formication is a sensation of insects crawling on or under the skin, even when no insects are present. It is a type of paresthesia, often associated with neurological, psychiatric, or systemic conditions. Formication can be distressing, itchy, or painful, significantly impacting daily life and sleep. In Korea, neurology, dermatology, and psychiatry clinics provide comprehensive evaluation, identifying underlying causes and delivering targeted treatments to relieve symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Highlights:
➤ Sensation of crawling or tingling on the skin without real insects
➤ Can be associated with neurological, psychiatric, or systemic conditions
➤ Early diagnosis is crucial to manage symptoms and address underlying causes
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Uncommon but can occur in individuals with neuropathy, substance use, or certain mental health conditions
➤ Age affected: More common in older adults due to peripheral neuropathy, but can occur at any age
➤ Gender: Affects both males and females
➤ Impact: Causes discomfort, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and social distress
➤ Prognosis: Treatable if underlying cause is addressed; persistent cases may require long-term management
What is Formication?
Formication is a cutaneous sensation resembling crawling, tingling, or pricking on the skin, often described as:
- Feeling of ants, bugs, or insects moving on the skin
- Localized or generalized; can affect hands, arms, legs, or torso
- May be intermittent or continuous
It is considered a type of paresthesia, which also includes tingling, numbness, or pins-and-needles sensations. While the sensation is real, no external stimulus is present.
Highlights:
➤ Formication is a symptom, not a disease itself
➤ Can indicate underlying neurological, psychiatric, or systemic issues
➤ Assessment involves history, physical exam, and laboratory testing
What Symptoms Are Related to Formication?
➤ Crawling sensation on the skin – Often described as ants, insects, or worms
➤ Itching or pruritus – May lead to scratching and skin lesions
➤ Tingling, prickling, or burning sensations
➤ Sleep disturbance – Sensation can worsen at night
➤ Anxiety or restlessness – Often accompanies persistent formication
➤ Skin damage from scratching – Secondary infections may develop
➤ Associated neurological signs: Numbness, weakness, or coordination problems in some cases
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms can affect quality of life and daily functioning
➣ Presence of additional neurological signs may indicate serious underlying disorders
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Peripheral neuropathy: Diabetes, vitamin B12 deficiency, or nerve compression
➤ Substance use: Alcohol, cocaine, methamphetamine, or withdrawal from certain drugs
➤ Medications: Some stimulants, antidepressants, or chemotherapy agents
➤ Psychiatric disorders: Delusional parasitosis, anxiety, or psychosis
➤ Hormonal changes: Menopause or thyroid dysfunction
➤ Systemic conditions: Chronic kidney disease, liver disease, or infections
➤ Skin conditions: Dermatitis or eczema may exacerbate sensations
Highlights:
➣ Formication is multifactorial, often involving neurological, psychiatric, or systemic components
➣ Identifying the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent or worsening crawling sensations
➤ Skin lesions, bleeding, or signs of infection from scratching
➤ Associated neurological symptoms: Numbness, weakness, or coordination issues
➤ Substance use or withdrawal-related sensations
➤ Sleep disturbances or anxiety affecting daily life
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation at a Korean neurology, dermatology, or psychiatry clinic ensures accurate diagnosis
➣ Timely evaluation prevents complications and improves symptom control
Care and Treatment
➤ Address underlying cause:
- Blood sugar control for diabetic neuropathy
- Vitamin supplementation for deficiencies
- Medication adjustment if drug-induced
➤ Symptomatic relief: - Topical agents such as calamine lotion or menthol creams
- Oral antihistamines for itch
➤ Neurological management: Medications like gabapentin or pregabalin for neuropathic sensations
➤ Psychiatric support: Cognitive behavioral therapy or antipsychotic therapy for delusional parasitosis
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Avoid alcohol or stimulants; maintain skin hygiene
➤ Monitoring: Regular follow-up for chronic or recurrent cases
Highlights:
➣ Effective management combines symptom relief and treatment of underlying cause
➣ Multidisciplinary care is often required for complex or persistent cases
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Neurology clinics: Evaluation of neuropathy, nerve conduction studies, and pharmacologic therapy
➤ Dermatology clinics: Management of secondary skin lesions and pruritus
➤ Psychiatry clinics: Assessment and treatment of anxiety, psychosis, or delusional parasitosis
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Nerve imaging or electrophysiology: To detect neuropathic causes
➤ Medication adjustment or initiation: For underlying neurological or psychiatric disorders
➤ Hospitalization: Rare, only if severe psychiatric or systemic conditions are present
➤ Follow-up care: Continuous monitoring of symptoms, skin health, and underlying conditions
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Education on skin care, symptom monitoring, and lifestyle modifications
➤ Multidisciplinary support involving neurologists, dermatologists, and psychiatrists
➤ Regular evaluation to prevent secondary infections and manage chronic symptoms
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide comprehensive assessment, multidisciplinary treatment, and long-term management
➣ Early intervention improves quality of life and reduces distressing symptoms